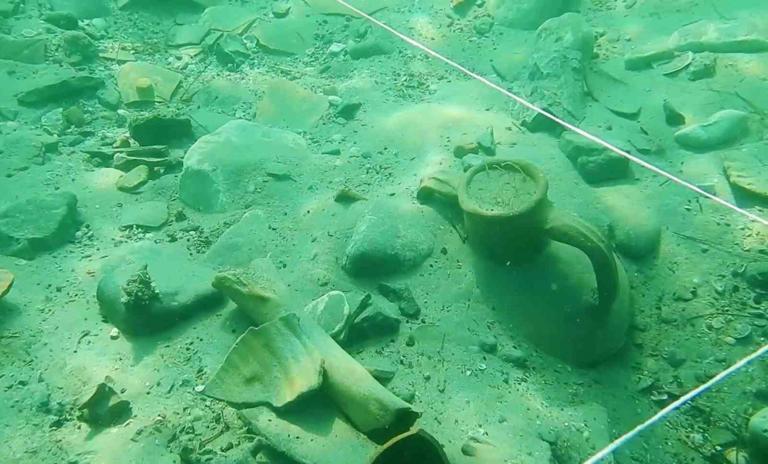
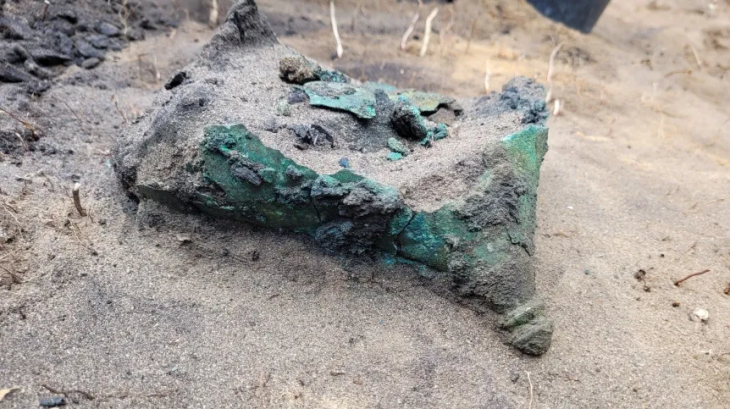
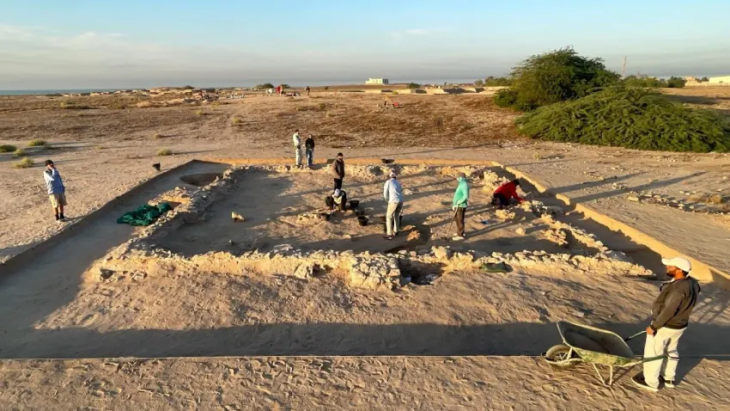
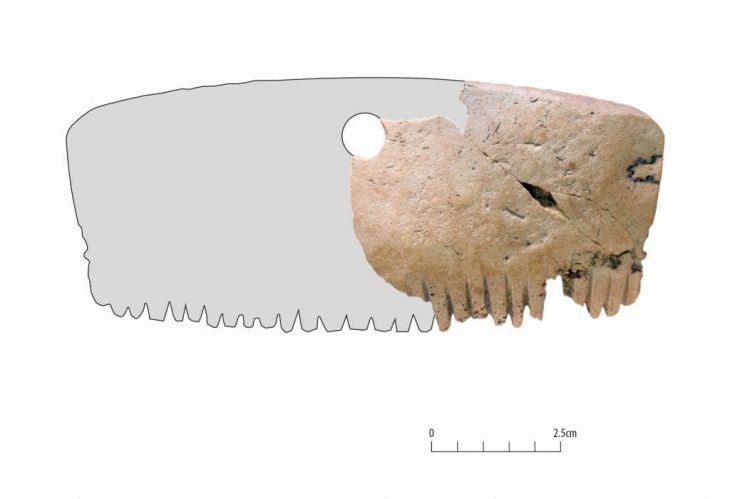
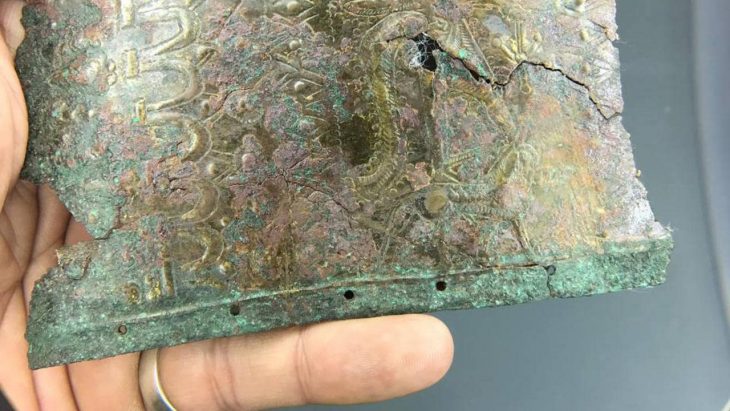
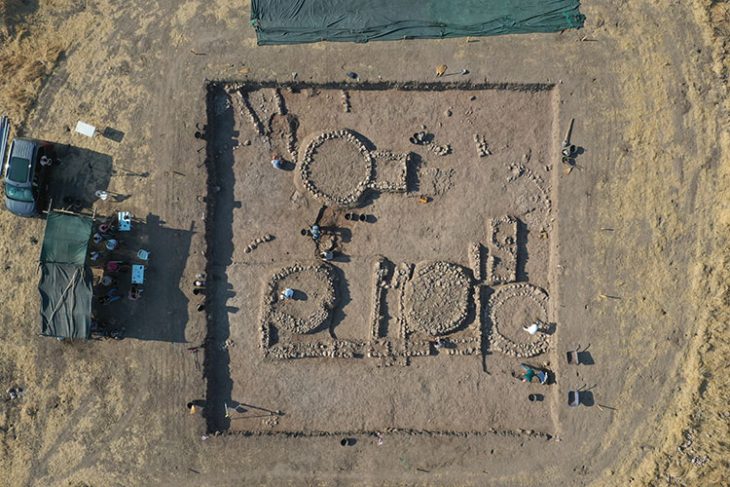Dozens of historical artifacts dating from the 4th century BC to the 12th century AD were unearthed in the first scientific underwater excavation in the Kerpe region in Kocaeli’s Kandıra district.
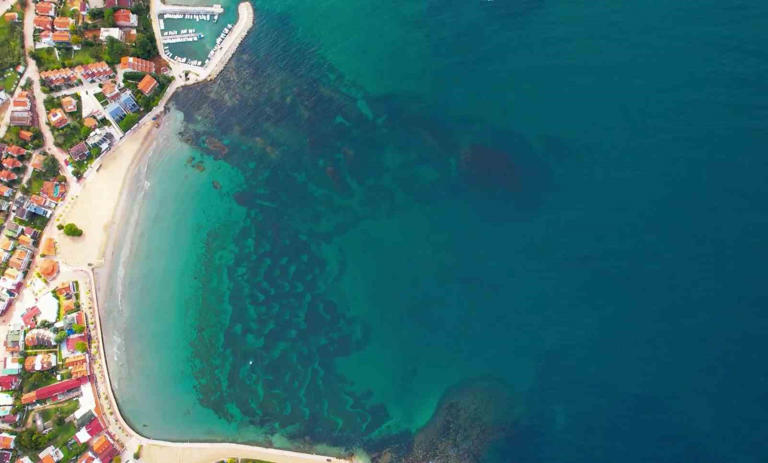
Ancient Kerpe Bay is situated in Kandıra, a district of Kocaeli, which has the longest coastline along the Black Sea (52 km) in Turkey . Kerpe is located in the bay protected from northerly winds and Black Sea surges.
Kerpe was known as “Kalpe”, which means “pot, jug, jug, jug” in the Hellenic language. It is an old and important place, dating back to the fifth century B.C. Kerpe Bay, a naturally protected port on the Black Sea coast, was used as an emporium (upp-market) and coastal town in the seventh century by colonists from Miletus or Megara to use and protect Black Sea trade routes. After the collapse of the Bithynia kingdom, the Kerpe settlement continued in Eastern Roman and Western Roman periods as well due to its strategic position. In addition, it developed into a stop for the Genoese ships and served also as the route for wood and wood coal transport to Istanbul during the Ottoman period.

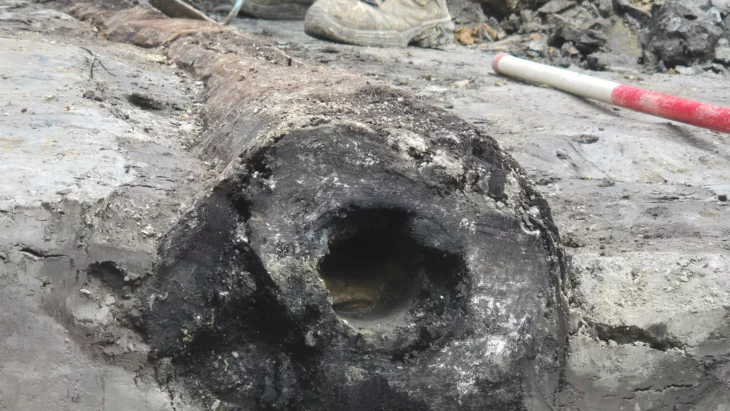
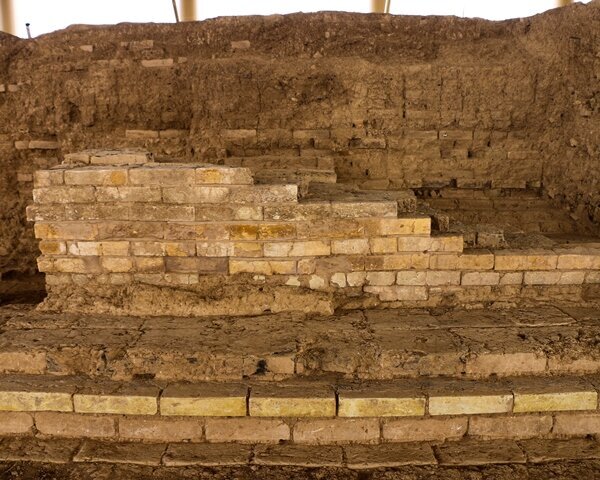
The remains of the pier belonging to the Ancient Kalpe Harbor were mostly submerged underwater, leading to underwater excavation works initiated in 2020.
The excavations are conducted by the Kocaeli Museum Directorate under the supervision of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
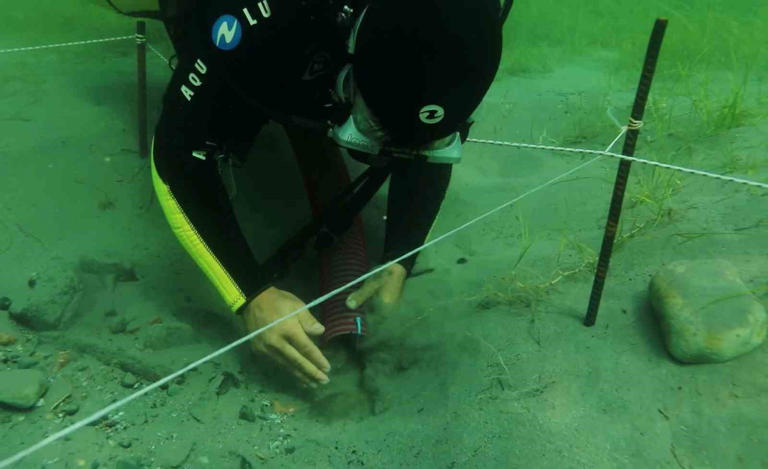

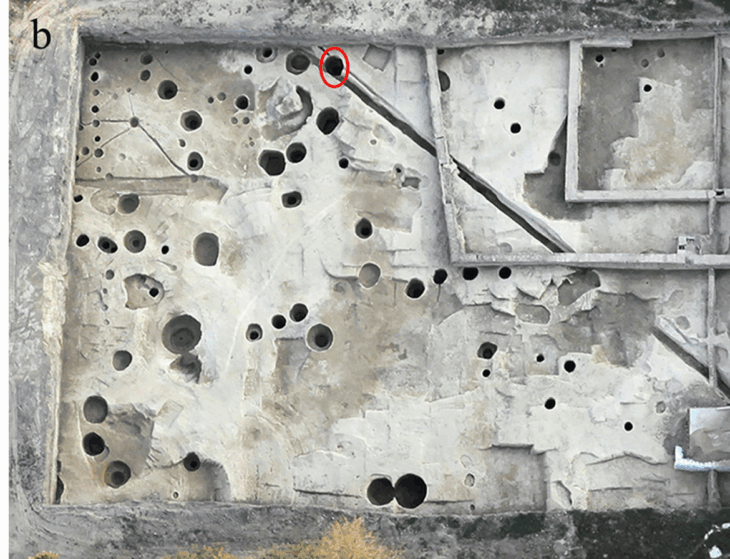
The excavation team worked 80 meters away from the shore at a depth of 4 meters to reach the remains scattered over an area of approximately 2,000 square meters.
During the excavations, they unearthed two parts of the ancient pier and numerous remnants of amphorae (two-handled pottery typical of the ancient period) from underwater.
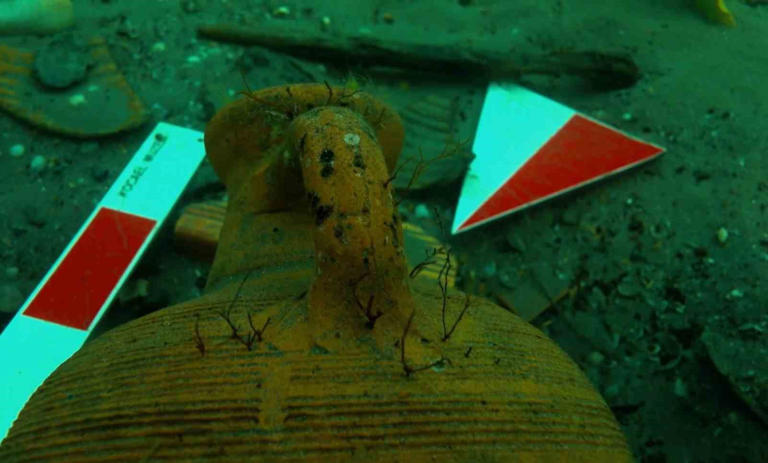

These artifacts are being showcased in the Kocaeli Archaeology Museum under the exhibition titled “The Silent Harbor of the Black Sea: Kalpe.”
Serkan Gedük, Director of Kocaeli Museum, stated:
“We believe that it is extremely valuable in terms of emphasizing the commercial relations between the east and the west from the Antiquity to the Ottoman period in the Black Sea. Therefore, we are trying to exhibit the cultural assets unearthed during the underwater excavations chronologically and with some animations in our museum. During the excavation works, we have identified many underwater cultural heritages, ranging from commercial amphorae remains dating from the 4th century BC to the 12th century AD, to red-glazed ceramics, lamps, pipe fragments, various cultural assets belonging to the Ottoman period and shipwreck remains that we have detected in the region.”