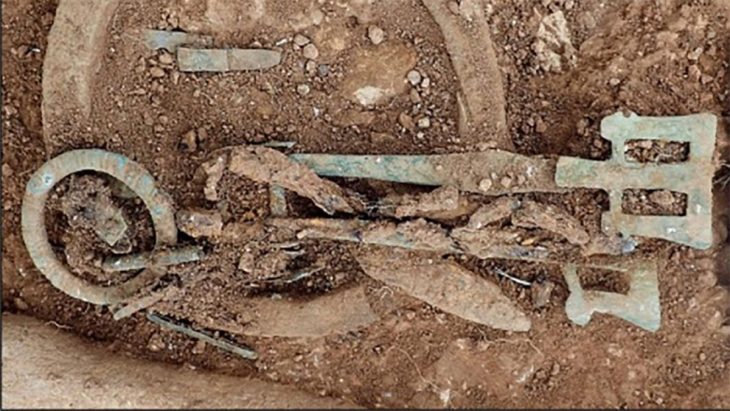
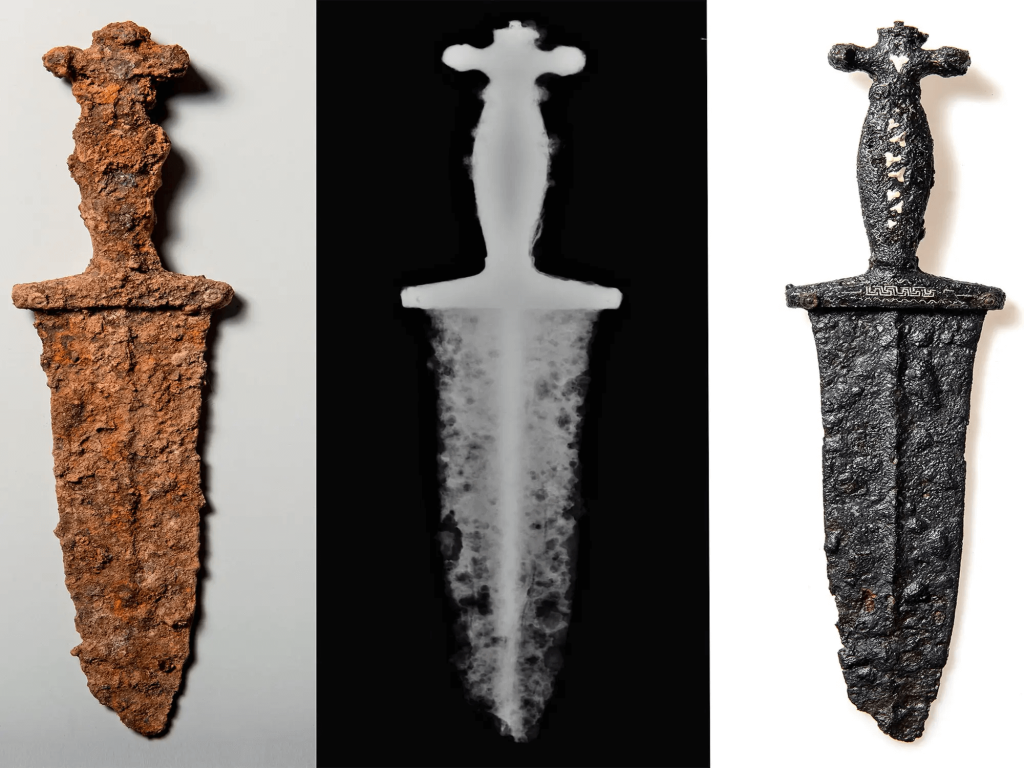
In Switzerland, a volunteer archaeologist and dental student Lucas Schmid discovered in 2019 a 2000-year-old silver and brass dagger. It was a vital clue in the story of a long-forgotten battle between the Roman Empire and tribal warriors.
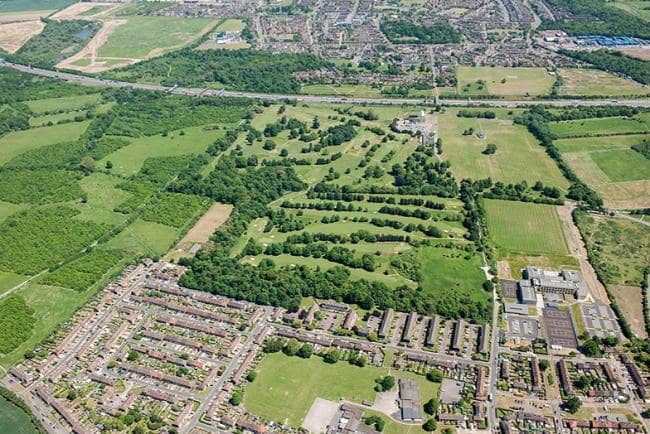
Lucas Schmid unearthed the dagger in the mountainous Graubünden region of Switzerland, an area believed to be the site of a lost battlefield where Imperial Roman soldiers fought Rhaetian warriors in approximately 15 BC.
His discovery sparked an excavation of the area that revealed a trove of ancient military artifacts.
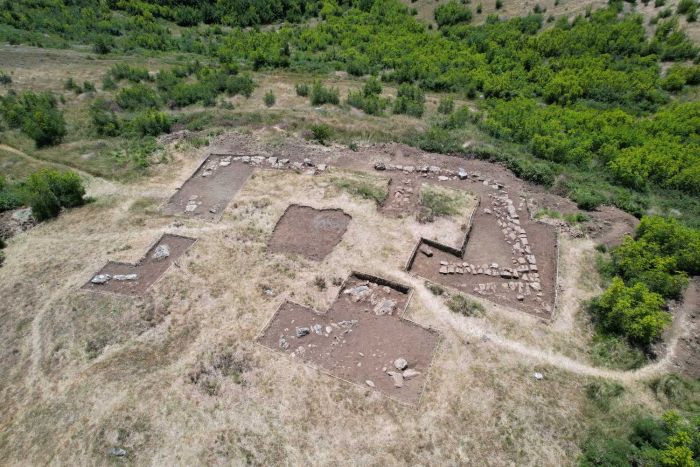
Now, a team of scientists and students have mapped a 2,000-year-old Roman battlefield representing the last stand of the Suanetes tribe, and the collapse of the region to the Roman Empire.
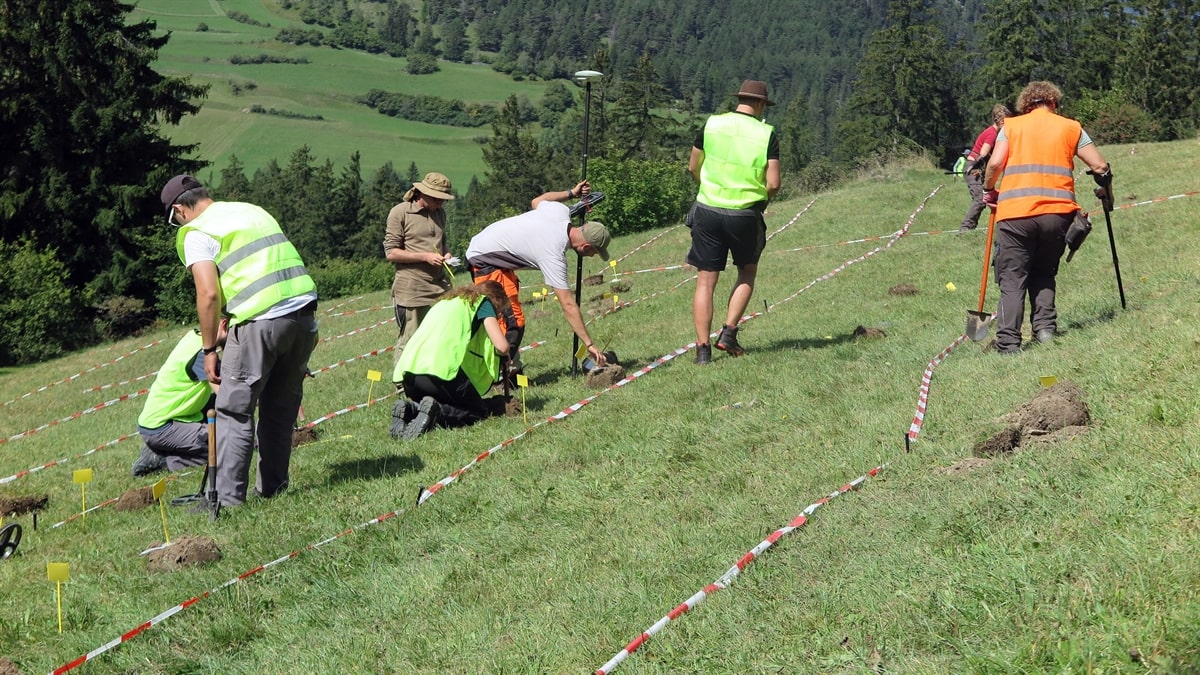
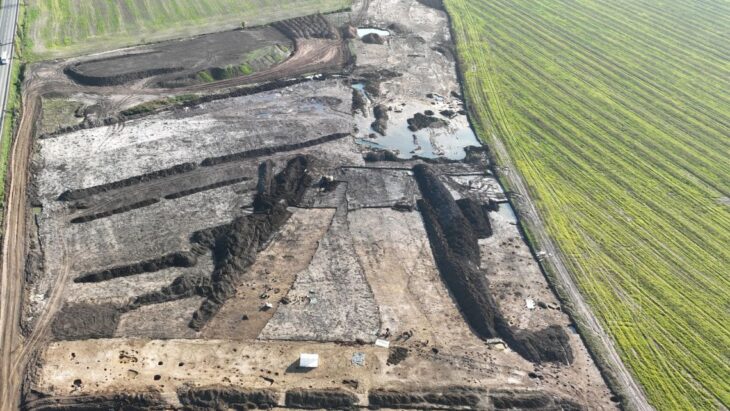
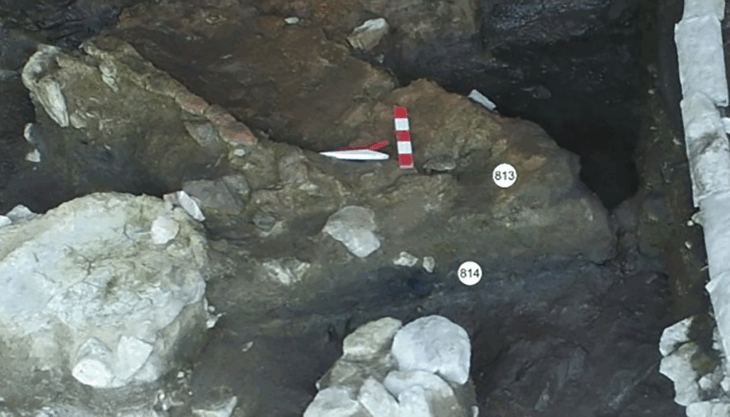
Students and researchers from the universities of Basel and Zurich, together with volunteer detectorists, search a Roman battle site near the Crap-Ses gorge in canton Graubünden. Over the past two years, experts have unearthed thousands of Roman military artefacts littering a hillside in southeast Switzerland.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Elegant columns, villas, amphitheaters, and other remains of ancient settlements can be found all over Switzerland, bearing witness to life under the Romans. But up to now, no battle sites had been identified and researched on Swiss territory.
The Swiss researchers believe a 2,000-strong task force from the third, tenth, and twelfth Roman legions clashed with 500-1,000 local fighters at the top of the hill, which is located near the Crap-Ses gorge between the towns of Tiefencastel and Cunter.
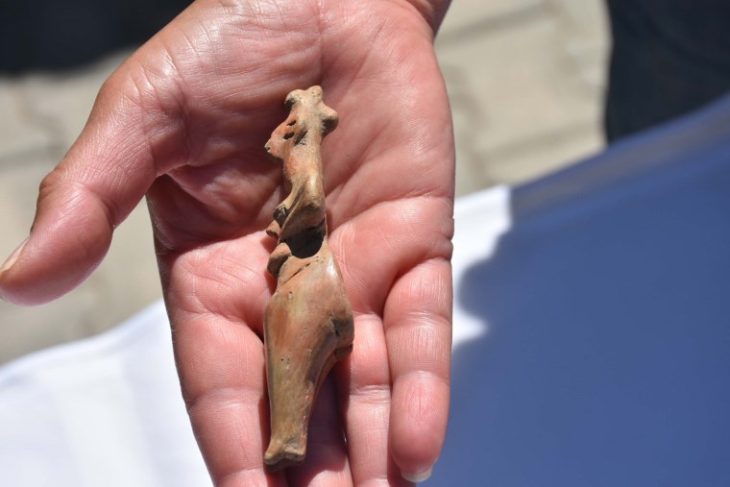
Schmid’s find led to the discovery of hundreds of other ancient artifacts. A new investigation of the site, run by a team from the Archaeological Service of Graubünden, the University of Basel (Switzerland), unearthed spearheads, lead slingshots, brooches, parts of shields, coins, and hobnails from Roman soldiers, Live Science report.
This autumn alone, around 250-300 objects a day were recovered during a three-week dig.

In his conversation with Live Science, Peter-Andrew Schwarz, an archaeologist at the University of Basel, said that the excavation of the site also recently unearthed a Roman coin minted between 29 BC and 26 BC during the reign of Emperor Augustus.
The Romans conquered the area of present-day southern Ticino in Switzerland’s Italian-speaking region at the beginning of the third century BC. After about seventy-five years, they had taken over the Rhone Valley, which included Geneva, southern France, and the route that connected Italy and Spain.
Through the establishment of colonies, primarily in western Switzerland, Roman rule was progressively reinforced. But their reign over the Alps was lengthy. Throughout the first century BC, Roman troops repeatedly advanced into the mountains. Roman historians, propose several justifications for these campaigns, including the need to establish a transit route to Germany, raise additional tax revenues, and put an end to disturbances and traveler attacks and raids.
Finding objects are now being displayed for the first time by the Archaeological Service of Graubünden (ADG), The Smithsonian reported.
Cover Photo: Archaeological Service Graubünden