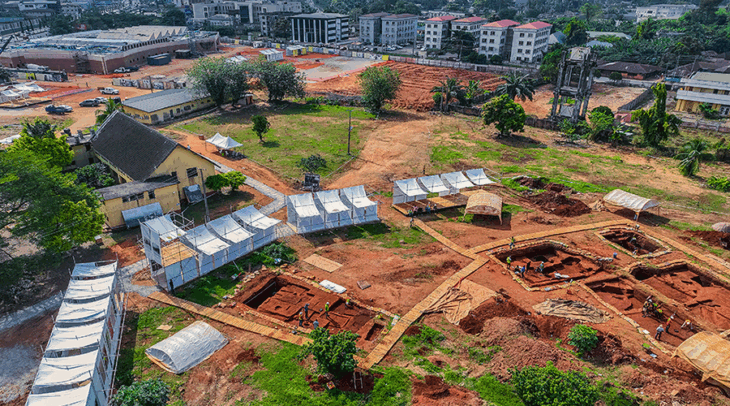
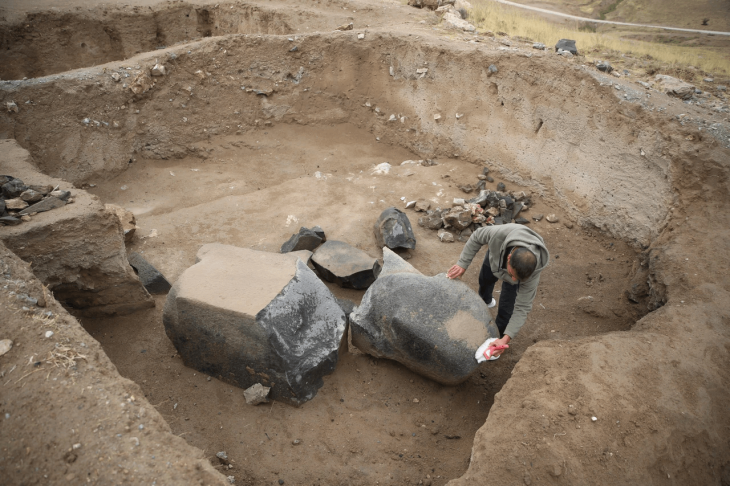
Archaeologists in Izmir, Turkey have made an extraordinary discovery in the ancient city of Metropolis: Approximately 2,000 bronze statue fragments have been found in a section believed to have served as an “ancient scrap yard”.
The excavations are being carried out within the scope of the ‘Heritage to the Future Project’ of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, under the direction of Prof. Serdar Aybek, Professor of Archaeology at Dokuz Eylül University, and in cooperation with the Sabancı Foundation.
Archaeologists have discovered evidence of many civilizations, from the earliest settlements in the Late Neolithic Age to the Classical Age, from the Hellenistic Age to the Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman periods, in the ancient city of Metropolis, also called the “City of Mother Goddess,” where excavations have been going on since 1990.
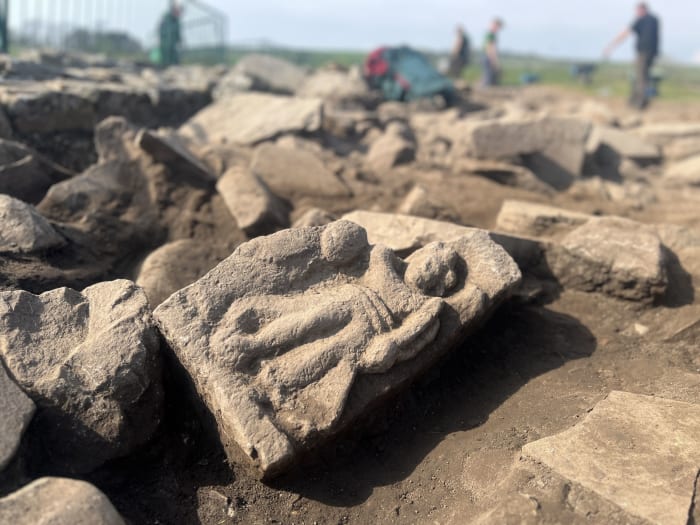
In the ancient city, where many monumental structures were unearthed, these fragments, uncovered in an area believed to have served as an “ancient scrap yard,” offer a unique glimpse into the cultural and religious shifts of the region during the Late Antiquity period.
Professor Serdar Aybek stated that the bronze statue fragments were found in a corner of a space referred to as an “ancient scrap yard,” where they had been broken apart for melting and stored in bulk.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
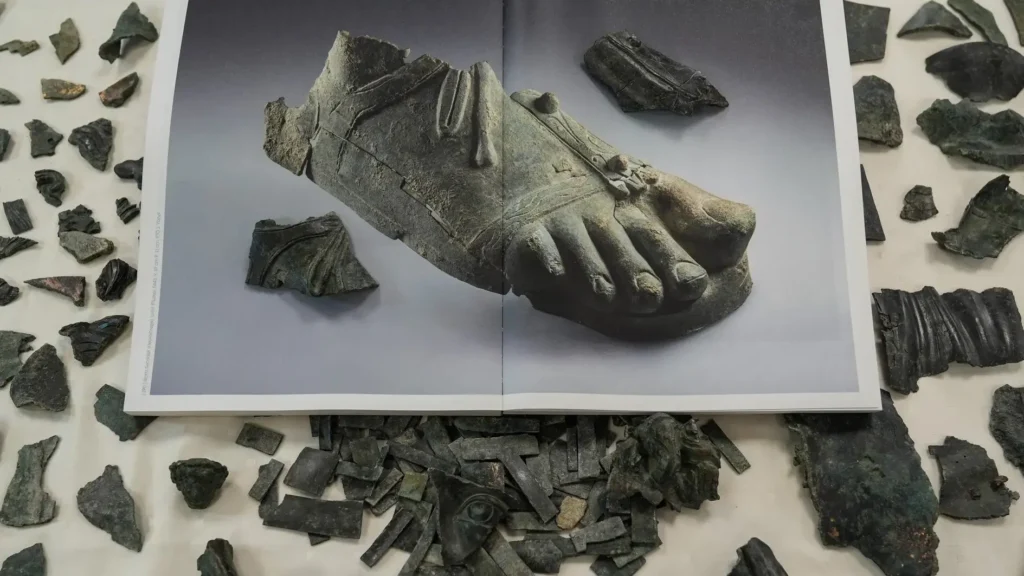

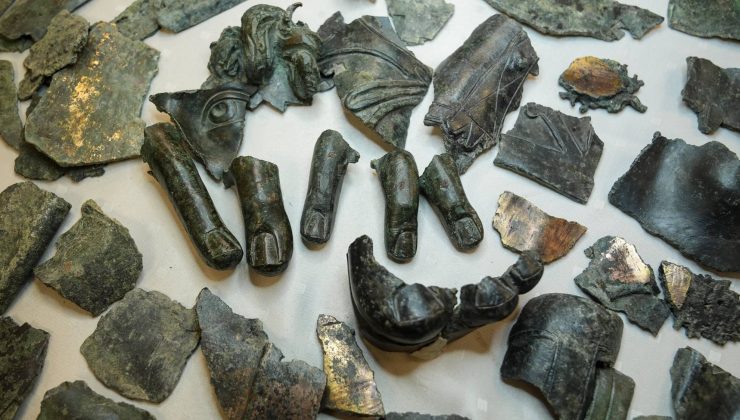
Aybek explained that the findings include statue pieces from the Hellenistic period and figures from the Roman era, describing them as “extraordinary discoveries, even for our field of work. We have uncovered approximately 2,000 bronze statue fragments,” he said.
He highlighted the significance of the bronze statues being broken into pieces, noting, “The collection and recycling of statues in the Late Antiquity provide concrete evidence in Metropolis. Among the findings are parts such as heads, eyes, fingers, and sandals.”
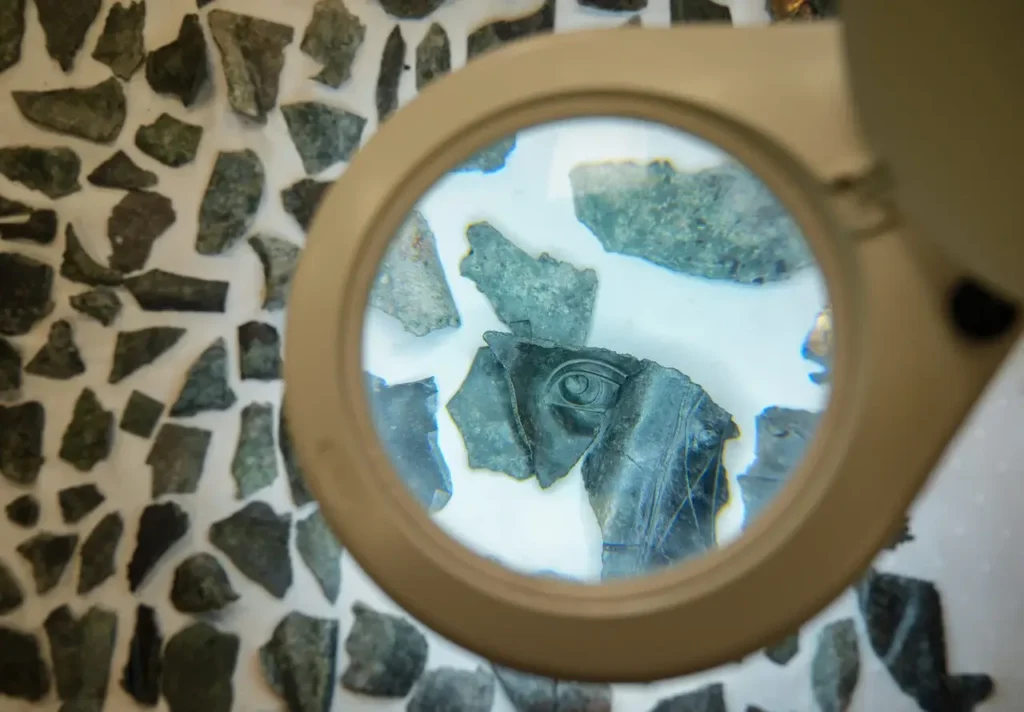

Drawing attention to the dismantling of these statues, Aybek said, “In the Late Antiquity, as mythological beliefs were abandoned in favor of monotheistic religions and Christianity became dominant in the region, bronze statues from mythological and earlier eras were dismantled. Although we do not yet have archaeological evidence to confirm this claim, we can suggest that a significant portion of them was repurposed for minting coins. During that period, rather than producing new materials, bronze groups, mainly consisting of outdated or damaged statues, were broken apart by the ancient scrap yard worker and prepared for melting.”
The fragments might be from the statues built to honor the benefactors listed in the “Metropolitan Apollonios” inscription, according to Aybek, who also underlined the historical significance of bronze statues in antiquity.
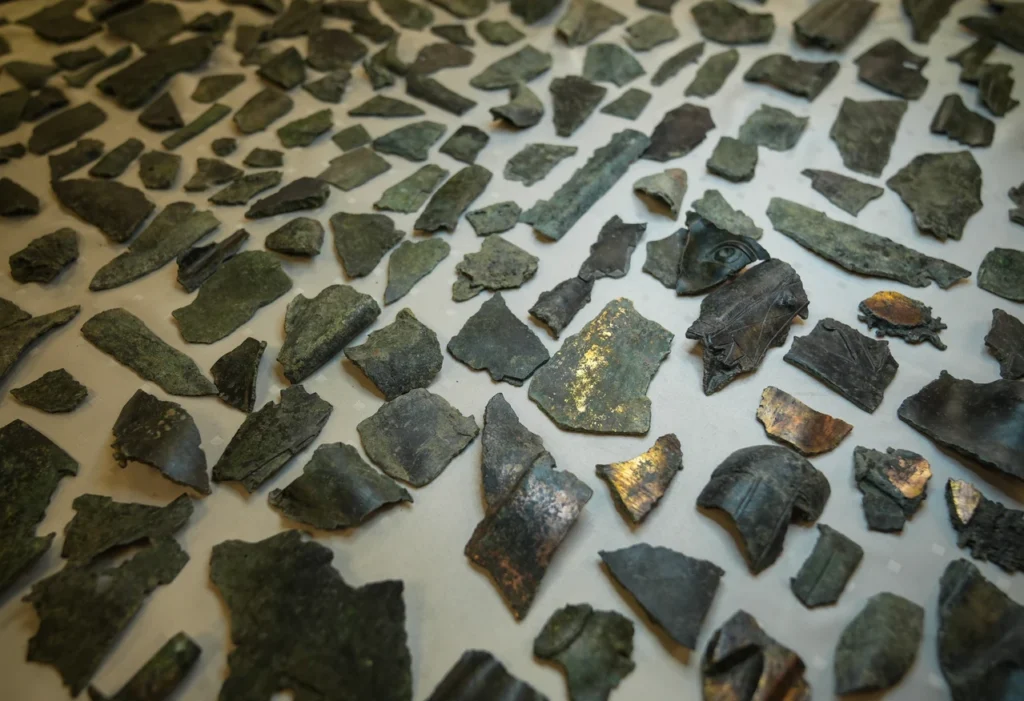

What makes this discovery even more remarkable is the evidence of recycling practices that date back over a millennium.
In addition to the fragmented statues, archaeologists discovered square and rectangular bronze plates that were probably used for statue casting and repair. This implies that, at its height, Metropolis might have served as a center for the creation or repair of bronze statues.
Cover Image Credit: AA