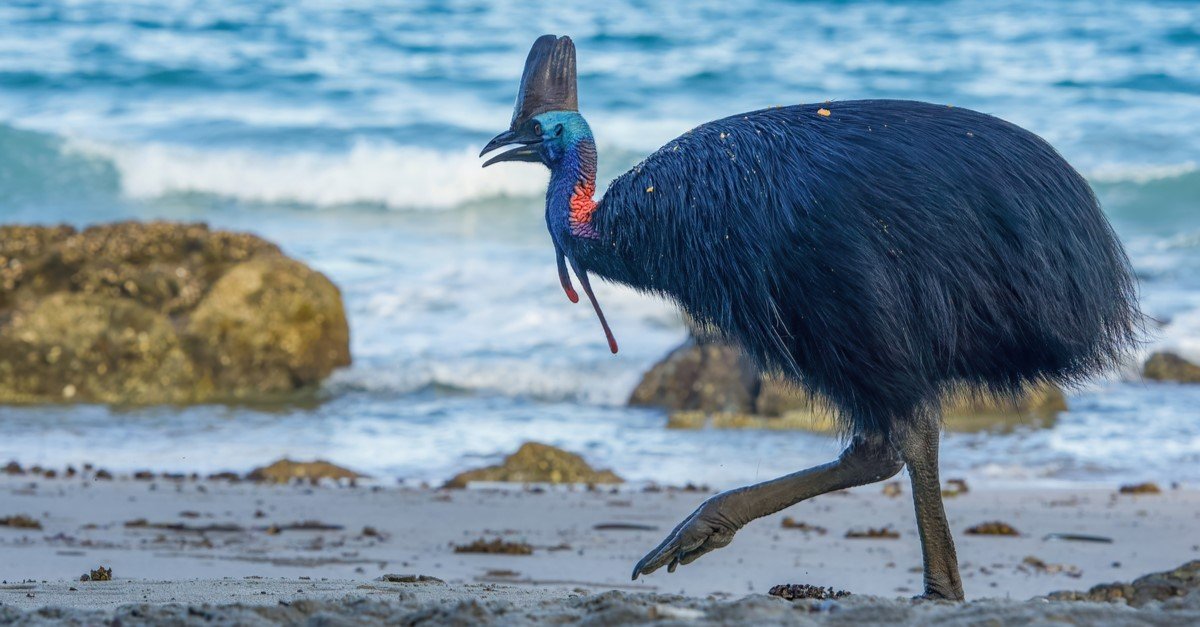
Researchers say the eggshell is an understudied archaeological material that has the potential to clarify past interactions between humans and birds. However, humans may have been hatching and raising young cassowaries, one of the world’s most deadly birds, as early as 18,000 years ago.
After examining eggshells recovered in two locations in New Guinea, the researchers published their findings in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
New Guinea is a significant case study for understanding forager influences on forest landscapes over long periods. Humans had arrived in the area at least 42,000 years ago, and the early population comprised fast exploration of highland habitats.
Although there is evidence that people coexisted with megafaunas like enormous kangaroos, huge wombats, thylacines, and cassowaries for millennia, it is unknown to what degree these animals were a target of early hunting.
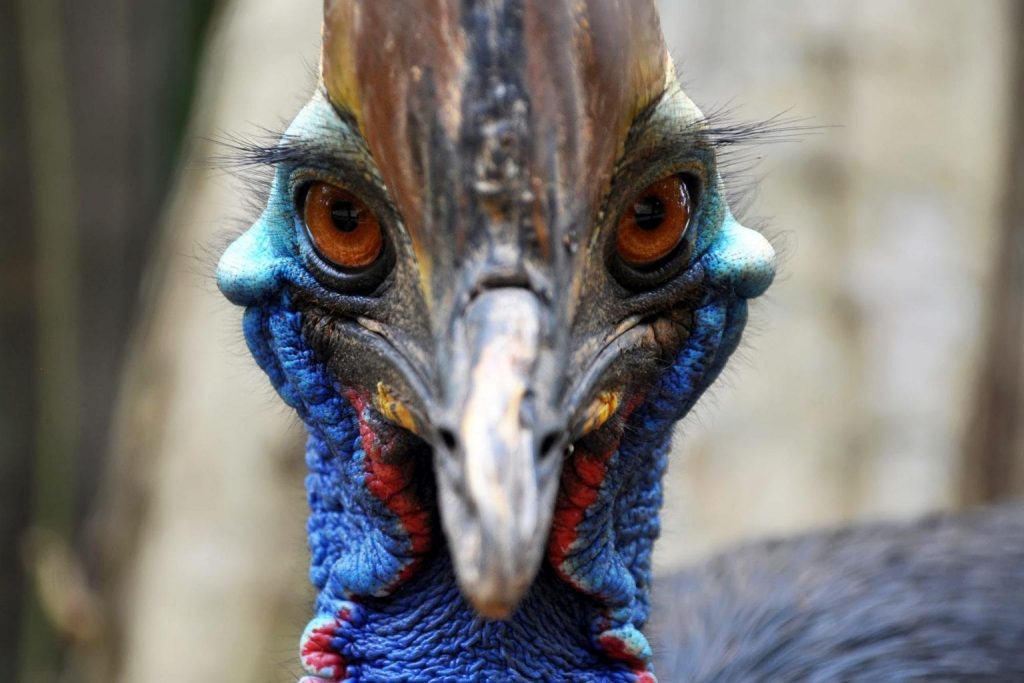

“We investigated how rainforest hunter-gatherers managed resources in montane New Guinea and present some of the earliest documentation of Late Pleistocene through mid-Holocene exploitation of cassowaries,” stated Kristina Douglass, an anthropologist from Pennsylvania State University, and her colleagues.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery may be the earliest example of humans managing avian breeding, thousands of years before the chicken was domesticated.
The scientists looked to legacy eggshell samples from two New Guinea sites, Yuku and Kiowa.
The researchers developed a new method to determine how old a chick embryo was when an egg was harvested.
“I’ve worked on eggshells from archaeological sites for many years. I discovered research on turkey eggshells that showed changes in the eggshells over the course of development that was an indication of age. I decided this would be a useful approach,” Dr. Douglass explained.
The researchers used their method on a total of 1,019 pieces of 18,000- to 6,000-year-old eggs.
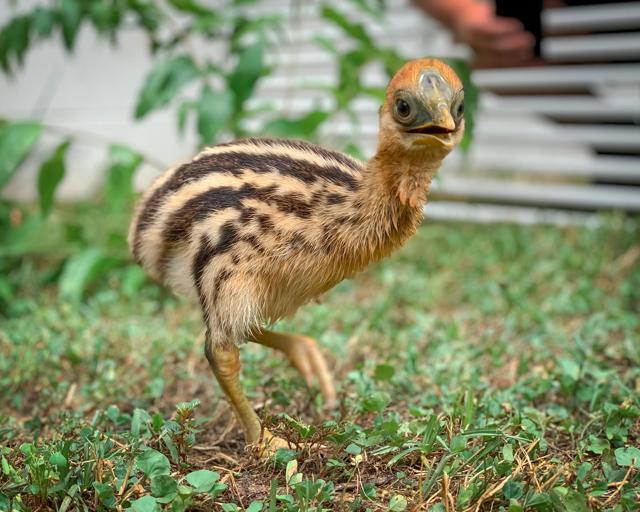

“What we found was that a large majority of the eggshells were harvested during late stages,” Dr. Douglass said.
“The eggshells look very late; the pattern is not random. They were either into eating baluts (a nearly developed embryo chick usually boiled and eaten as street food in parts of Asia) or they are hatching chicks.”
The few cassowary bones found at the sites are only those of the meaty portions — leg and thigh — suggesting these were hunted birds, processed in the wild, and only the meatiest parts got hauled home.
“We also looked at burning on the eggshells. There are enough samples of late-stage eggshells that do not show burning that we can say they were hatching and not eating them” Dr. Douglass said.
To successfully hatch and raise cassowary chicks, the people would need to know where the nests were, know when the eggs were laid, and remove them from the nest just before hatching.
“Back in the Late Pleistocene, humans were purposefully collecting these eggs and this study suggests people were not just harvesting eggs to eat the contents,” Dr. Douglass said.
Finally, Dr. Douglass added: “This really should expand our thinking about domestication as a spectrum. It should get us to think about other examples that may be out there of how people developed these kinds of relationships with animals that are more intimate than we might have guessed at really early times in our history,”