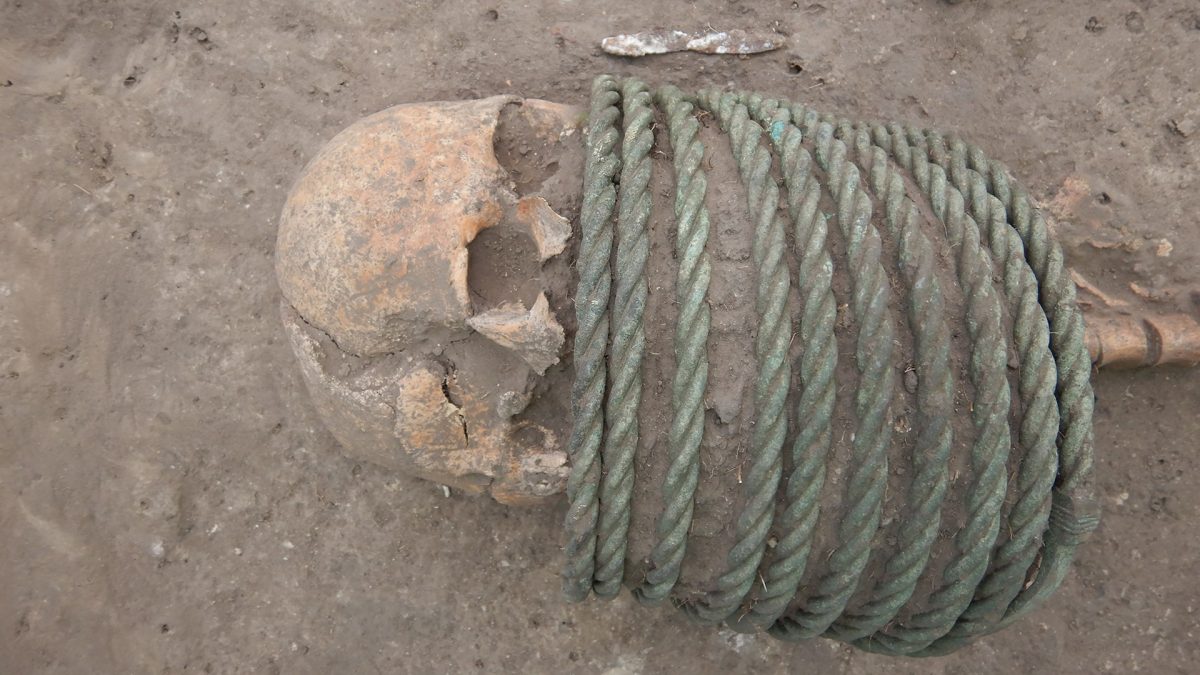
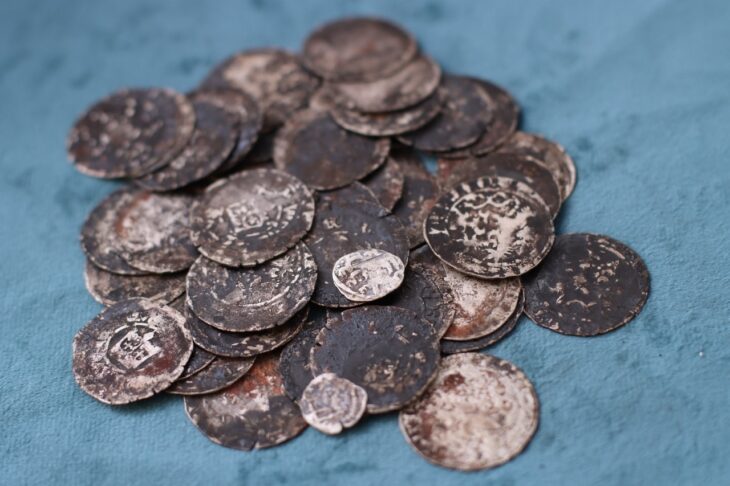
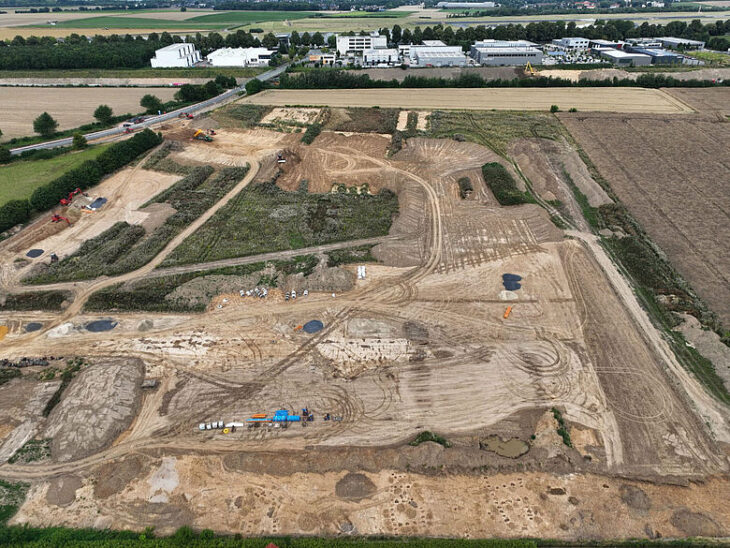
Archaeologists discovered the remains of men buried with weapons such as axes, spearheads, and swords, and women buried with thick twisted bronze neck rings in an 11th-century cemetery near the village of Ostriv, south of Kiev, Ukraine.
Researchers Vsevolod Ivakin and Vyacheslav Baranov presented their study of the remains at the Archaeological Institute of America, which was held Jan. 4-7 in Chicago, according to Live Science.
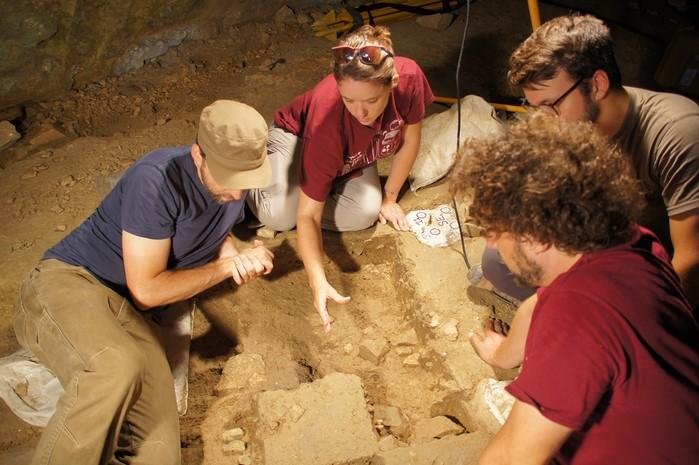
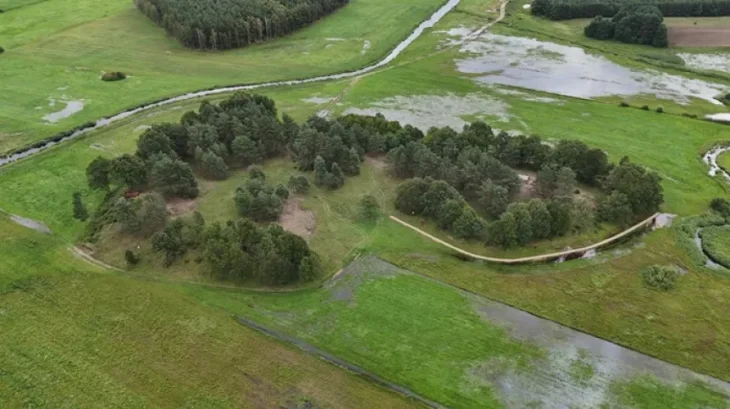
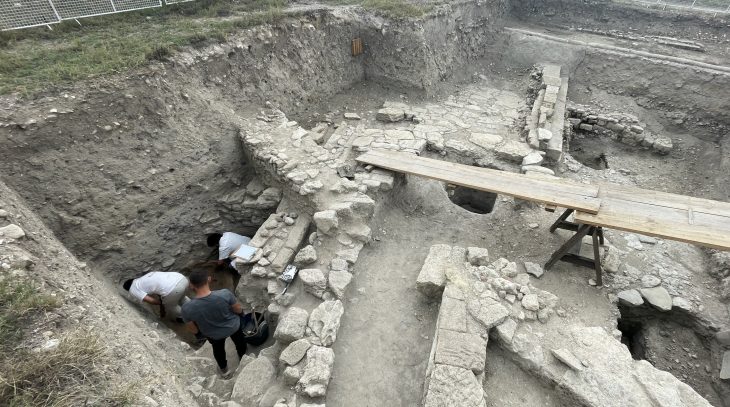
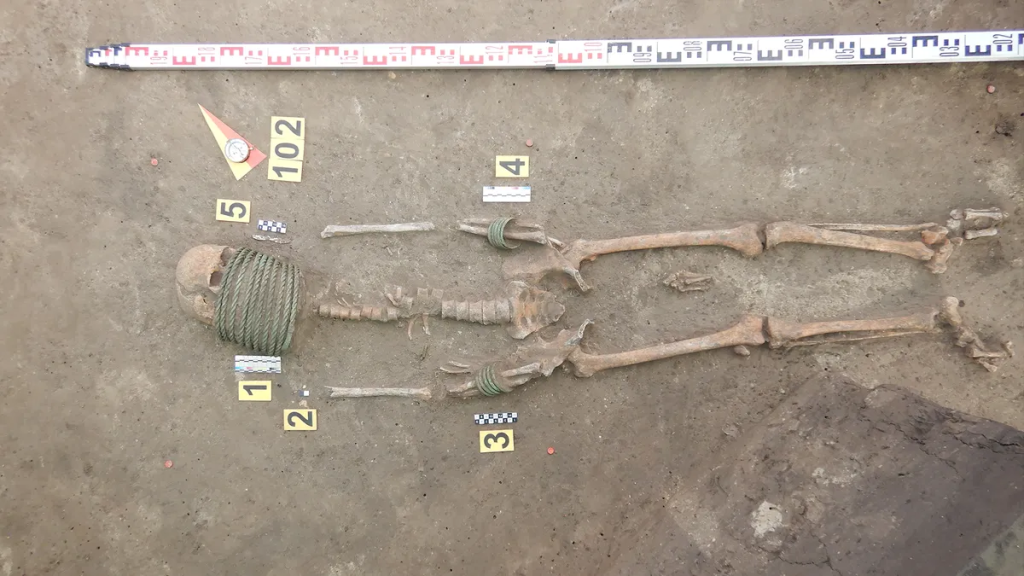
In 2017, the Ukrainian Institute of Archaeology conducted an expedition that discovered the Ostriv graveyard. Between 2017 and 2022, excavations uncovered 107 inhumation burials from the late 10th and 11th centuries. The graves’ uniqueness was quickly apparent. Unlike the unusual funerary practices of the Kyivan Rus during this period, the graves were facing south and west rather than north.
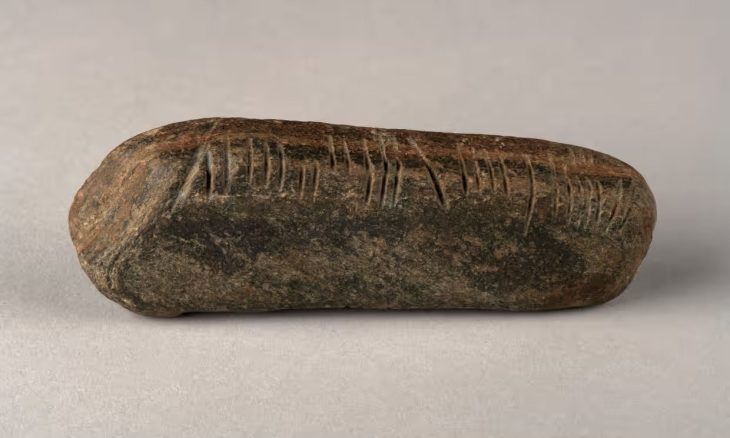
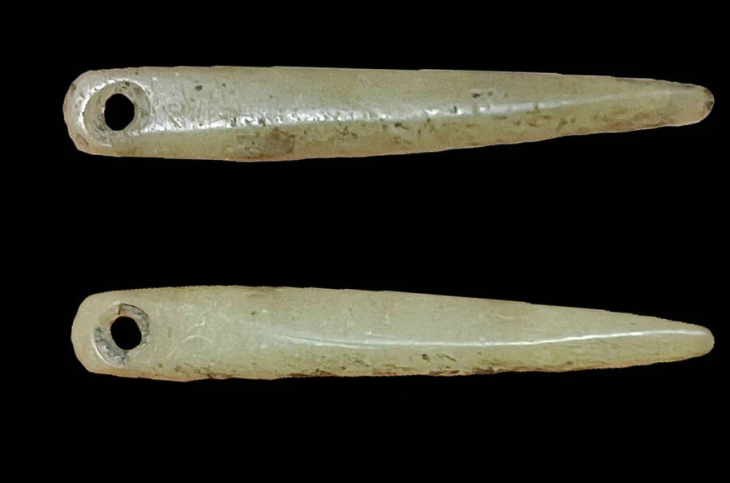
The deceased were laid in supine position (on their backs), with outstretched limbs. In most of the graves, there were remnants of wooden coffins. The remains of funerary food offerings (chicken bones and eggshells) were discovered in the graves and in wooden buckets at the feet of some of the deceased. Some people were buried with extremely valuable items, including slate spindle whorls, jewelry such as bronze neck rings and bracelets, pennanular brooches, cast bronze belt rings, cowrie shell bead necklaces, and weapons such as battle axes, knives, and spearheads.

Though the comparison was not exact, the orientation and funerary furnishings bore a strong resemblance to the practices of tribes in the Western Baltic. Most remarkably, none of the Ostriv graves were cremation burials; the Western Baltic peoples generally burned their dead. Furthermore, Baltic funeral customs do not generally involve buckets.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeologists hypothesize that these key differences may be attributed to restrictions placed on traditional funerary practices by the Christian dukes of Kyiv, primarily Volodymyr the Great (r. 980-1015) and Yaroslav the Wise (r. 1019-1054), and by the process of Christianization of the Baltic settlers of the region during the 11th century. A stone altar found in the cemetery could have been used for Christian or pagan rituals, or a mixture of the two.
Research continued at the site until 2022 but the excavation has been paused due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Cover Photo: Vyacheslav Baranov