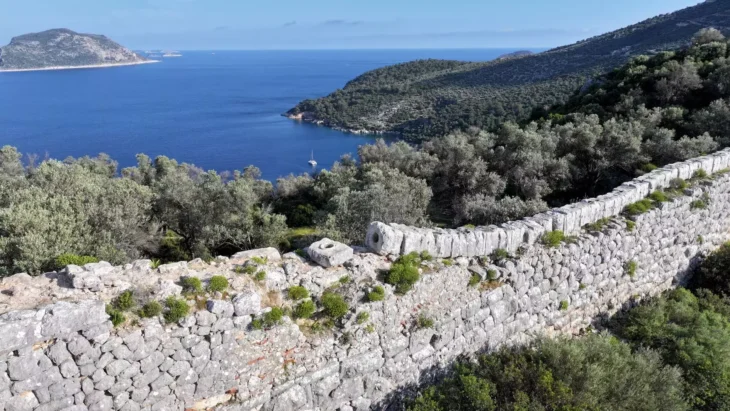
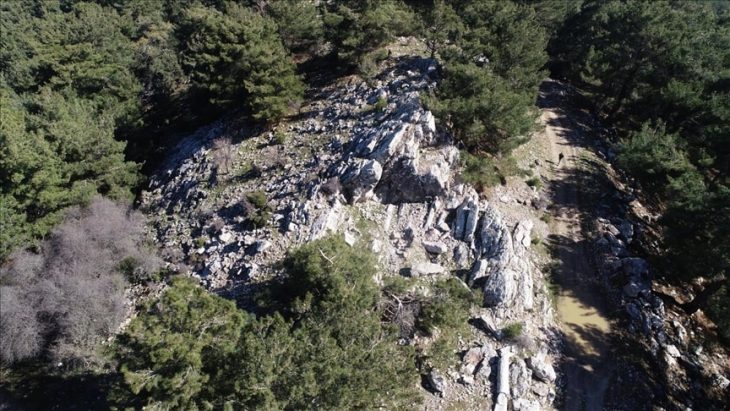
A total of 24 well-preserved Chinese bianzhong (chime bells) in two sets from the Spring and Autumn period (770-476 BC) were unearthed in the ruins of Ancient Capital City of the Zheng and Han States in Xinzheng, Central China’s Henan.
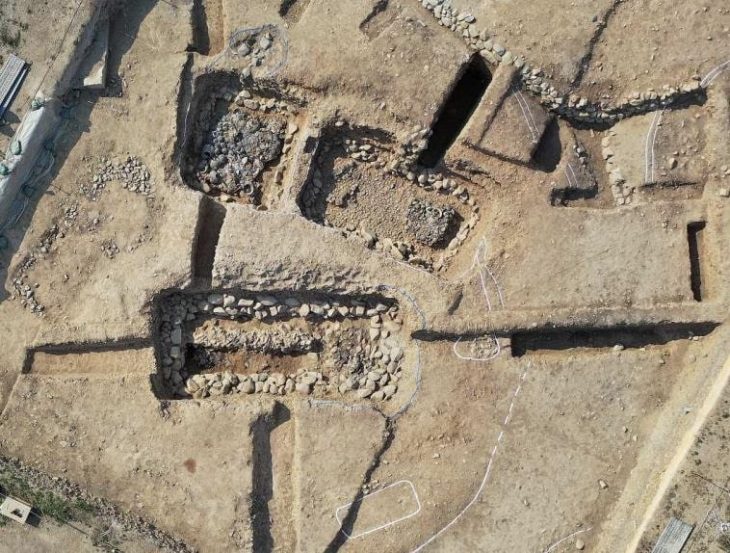
This rare discovery of significant academic value was found in a sacrificial pit near the ruins of a palace.
Bianzhong are an ancient Chinese musical instrument consisting of a set of bronze bells, played melodically. These sets of chime bells were used as polyphonic musical instruments. They were hung in a wooden frame and struck with a mallet.
Although tuned bells have been created and used in many cultures for musical performances, Bianzhong are unique among all other types of cast bells in several ways. They have a lens-shaped (rather than circular) section, a distinctive “cutaway” profile on the bell mouth, and 36 studs or bosses symmetrically placed around the body in four groups of nine on the outer surfaces of the large bells.
This special shape gives Bianzhong bells the remarkable ability to produce two different musical tones, depending on where they are struck. They are also known as “One bell, two sounds”.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“The bianzhong symbolizes rank and power, and represents a high achievement in both the art and culture of ancient China,” Guan Ping, a Beijing-based historian, told the Global Times.
“The bianzhong were used at the kingdom palace as part of the ritual system. The discovery will help experts to examine cultural development in the Spring and Autumn Period and the Warring States Period,” Guan added.
“Music is strongly linked to rituals, and in ancient China, it played an important part in the ritual and music system to maintain social order,” Guan explained.
Yu Jie, a staff member at the Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, said that the bianzhong sacrificial pit at the site is 2.6 meters long from east to west, 1.4 meters wide from north to south, and 0.8 meters deep.
“There are three rows of bell frames in the pit, with a total of 24 chime bells. The chime bells are well preserved, without any signs of looting, and the wooden frame is clearly visible,” Yu explained, adding that the frame can be “dated back to the middle and late Spring and Autumn Period”.
The Zhou Dynasty (1046BC- 256BC) was the first dynasty to lay down rules of rites and music, with sets of such instruments used in ceremonies, galas, and performances.
In recent decades, bianzhong have been found in various locations throughout China. In 1978, the discovery of bianzhong inside the tomb of the aristocrat Yi of Zeng in Suizhou, Central China’s Hubei Province, became world famous. The bells have a total of 3,755 characters and are inlaid with gold. In 1981, another bianzhong set was discovered near Yi’s tomb.
The ancient city ruins where the recent discovery was made cover an area of 16 square kilometers. In addition, archaeologists also discovered two tombs near the palace ruins area. The tombs are in the shape of vertical pits, and complete bronze ritual vessels were unearthed.