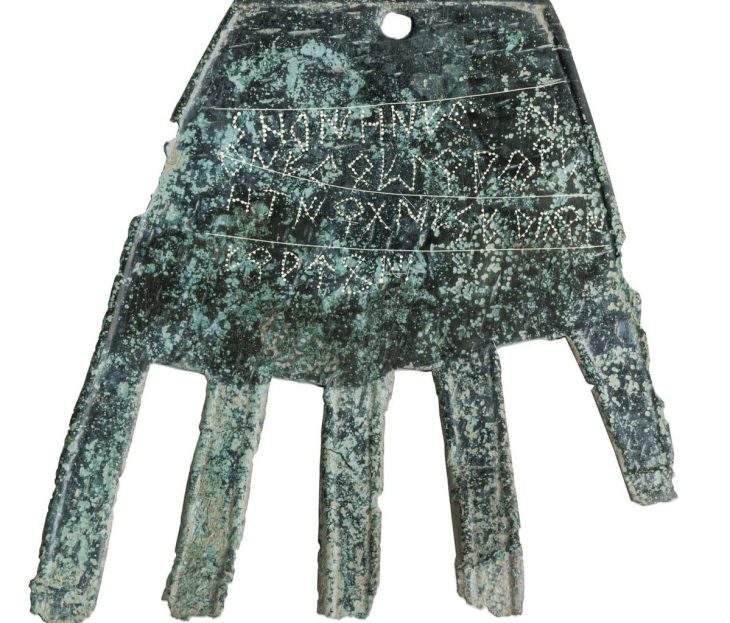
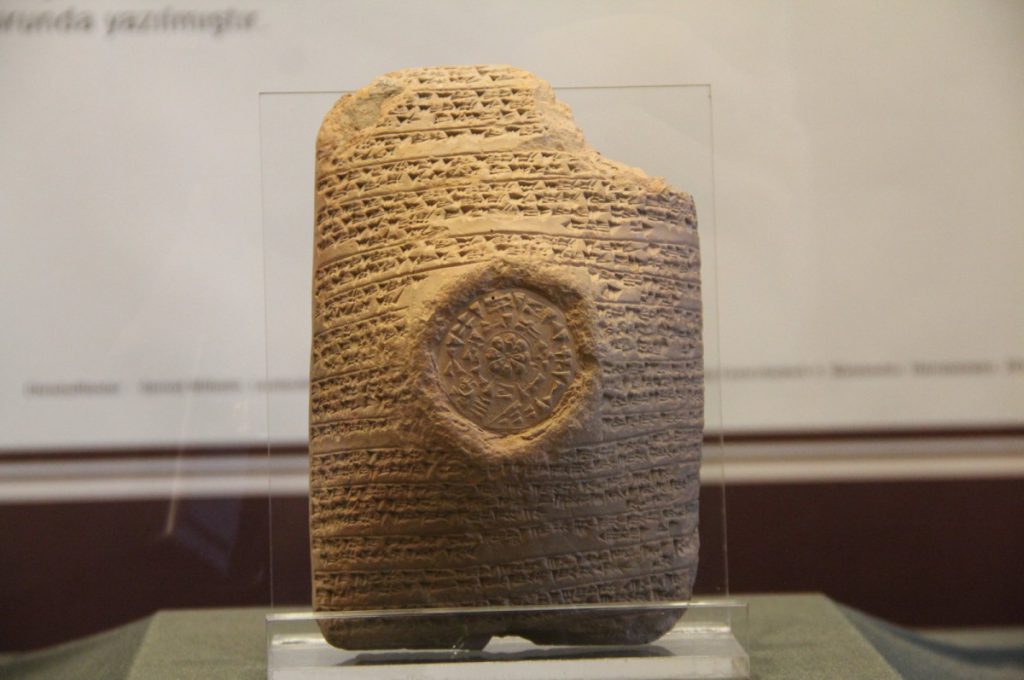
Thanks to a project implemented in Türkiye, 1,954 ancient Hittite tablets are being read for the first time using artificial intelligence (AI).
The project’s initial phase, which involved reading, scanning, and digitizing Hittite cuneiform tablets kept in the collections of the Çorum Museum, the Istanbul Archaeology Museum, and the Ankara Anatolian Civilizations Museum, has been finished.
This outstanding project will aid researchers in quickly and easily analyzing ancient documents, speeding up the process of decipherment within the framework of the project run in collaboration with Ankara University and the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums.
500 Hittite cuneiform tablets were translated at the start of the project by photographing them in high resolution and scanning them with 3D technology. According to the results of the testing, the AI’s success rate was 75.66%.
The data obtained from the deciphered tablets will be shared with the scientific world by Hittitologists. Also, the public will be able to view the cuneiform clay tablets once the translation phase is finished in the soon-to-be-opened Hittite Digital Library.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Ankara University researcher and project coordinator Özlem Sir Gavaz emphasized that the project is the first of its kind in the world and said: “It has a great meaning that Boğazkale tablets were discovered in Çorum. We initiated such a project for the first time in the world to read Hittite tablets with AI. Were there any examples before? Yes. In Chicago, Toronto and Tel Aviv University. Those directly related to AI were on the Babylonian and Akkadian tablets. There was no project to digitize Hittite tablets and then integrate them with AI. Therefore. We are quite proud of it.”

The project, called “3D Scanning of Cuneiform Tablets in the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations and Reading Boğazköy Tablets with AI,” is also supported by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, Ankara University and the Cultural Heritage and Museums.
Project coordinator Gavaz also explained that they tried to decipher the Hittite language manually, but this method proceeds more slowly and is prone to errors, while AI works in a shorter time and with a low margin of error.
Zeynel Karacagil, another coordinator of the project, explained that the project has two main pillars, the first of which is the digitization of the Hittite cuneiform tablets and the second is the process of reading them with AI.
Explaining that they started the AI process with 1,954 high-resolution photographs, Karacagil said: “In the first phase, the reading of the tablets was planned on 500 of them. There are some situations when AI captured some characters with 95% success while some of them were 50%. The fact that some tablets are broken or deformed and other factors have an effect on the results. But we are trying to solve high-resolution photos with different algorithms. The rate of 75.66% in the first phase is a great success for the academic community and our country. It is the first time that cuneiforms in Hittite have been translated in this manner. It is a source of pride for us to achieve such success for the first time with our local and national researchers. We are also breaking the perception that only foreigners can work in the field of AI.”
He also expressed that they have created 3D scans of the tablets and digital archives within the scope of the project and that they are planning to enable AI to read more tablets in the future. Currently, with approximately 2.5 million point shots, 86 of the tablets have been scanned in this respect.