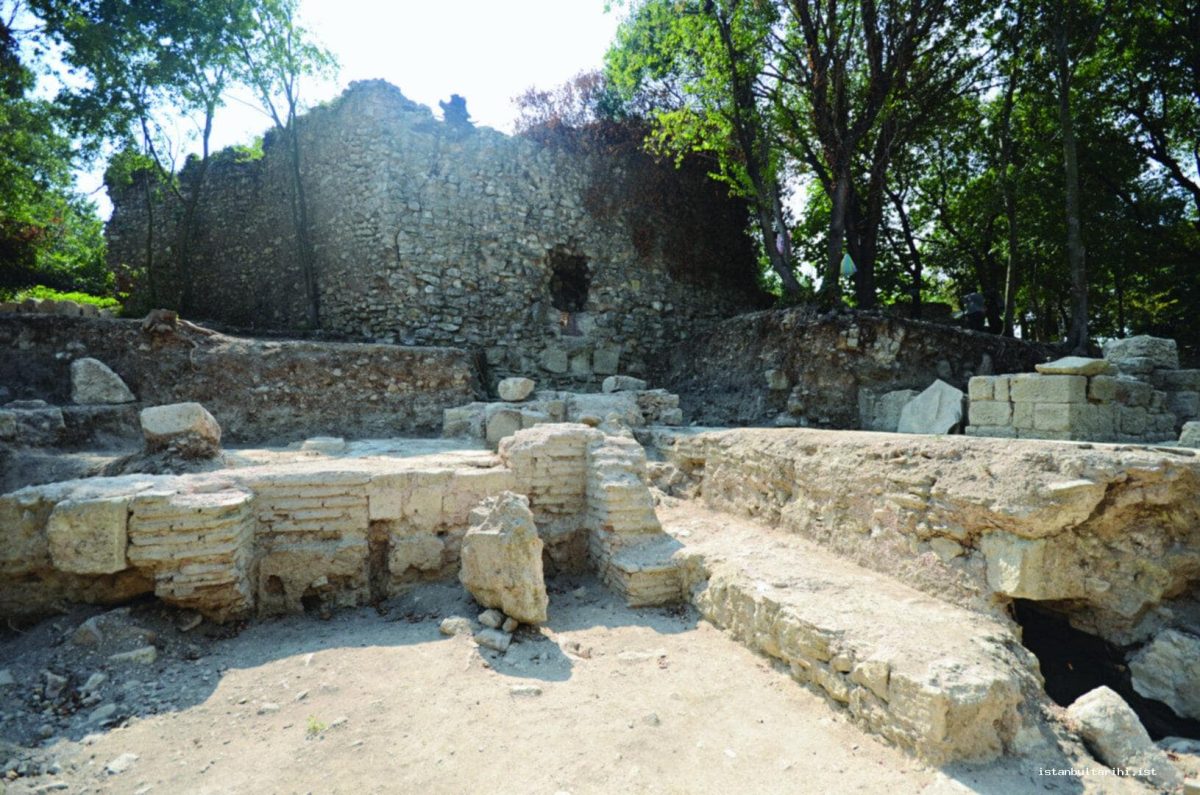
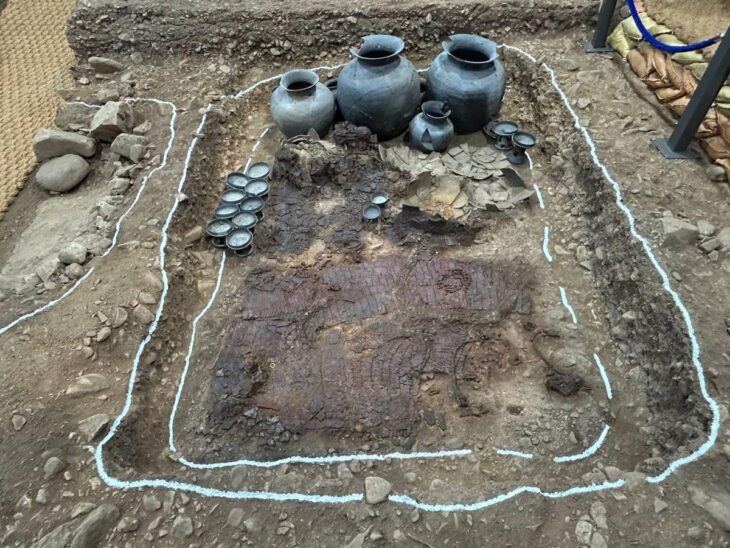
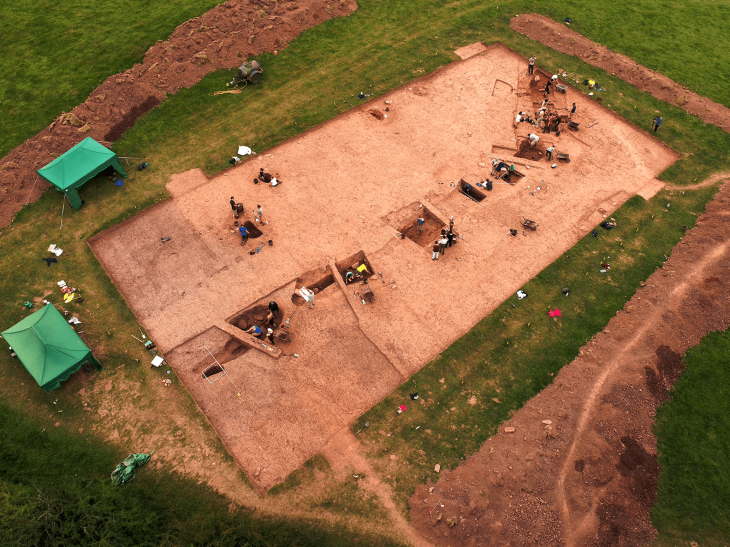
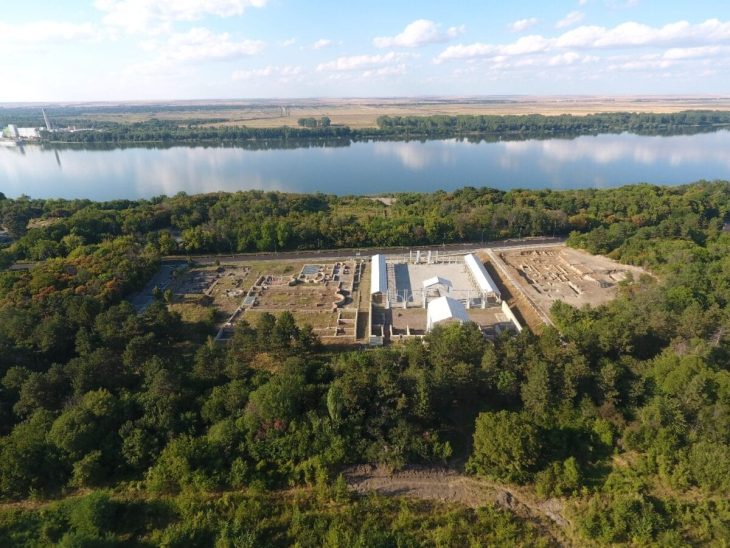
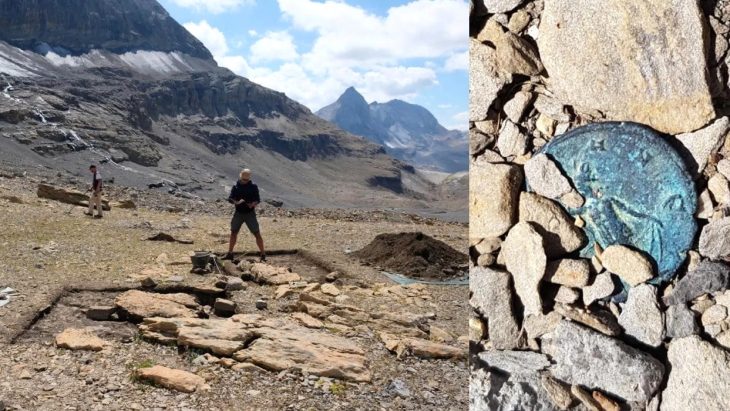
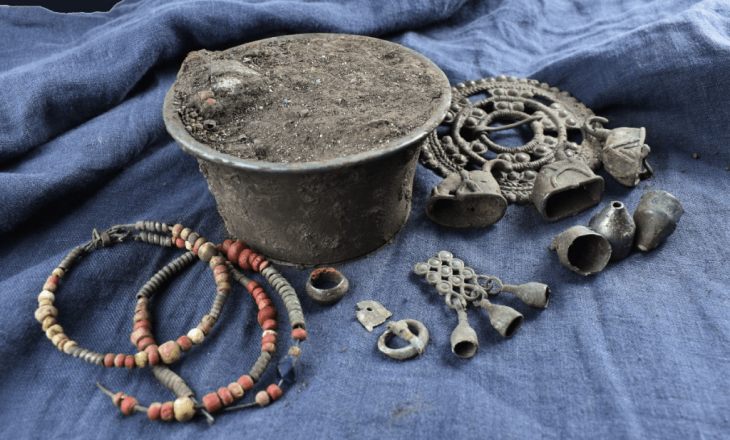
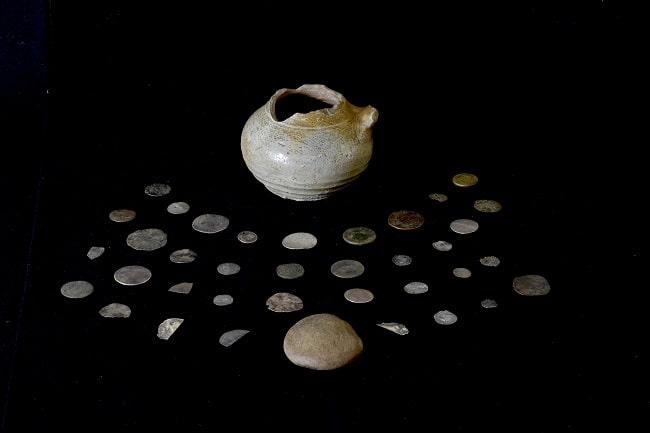
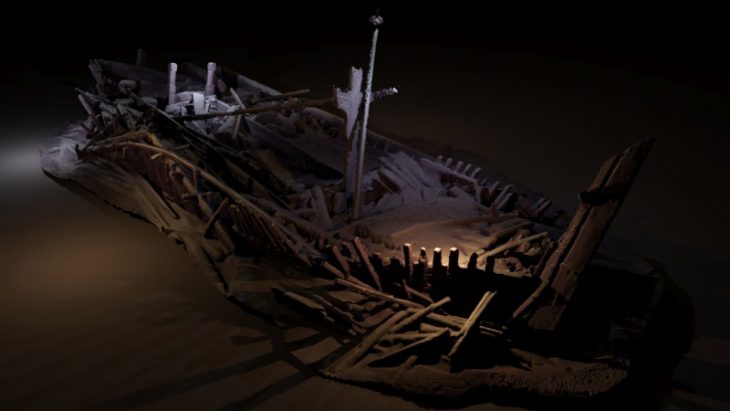
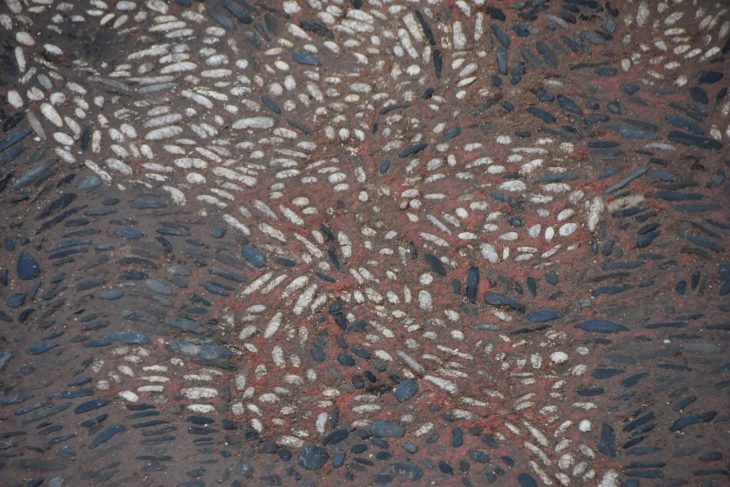
The excavations in the ancient Greek city of Bathonea, located in the Küçükçekmece Lake basin in the Avcılar district of Istanbul, with the discovery of underwater architectural remains of the second ancient lighthouse in Turkey after the ancient city of Patara.
The excavations in Bathonea, are being done by the Culture and Tourism Ministry and Kocaeli University under the supervision of Professor Şengül Aydıngün, aiming to reveal and preserve the historical and archaeological heritage.
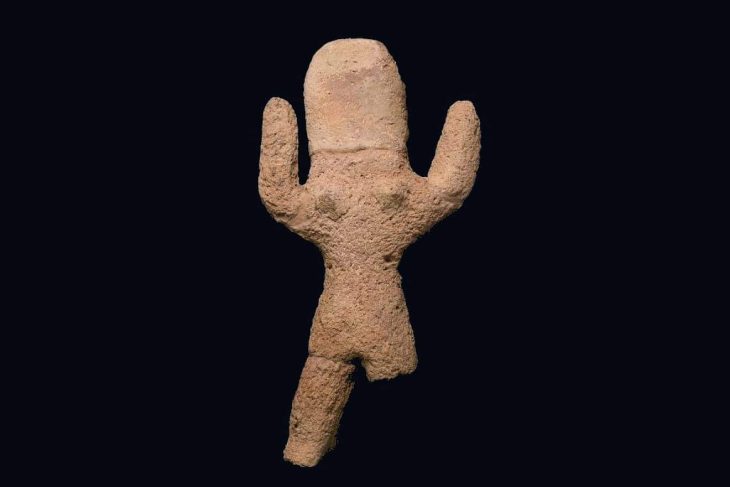
The early Hittite traces found in the excavations of the Ancient City of Bathonea, where many unknown important structures of Istanbul and issues waiting to be enlightened, are brought to light, are described as the biggest discovery in the studies. With this discovery in the excavations, Hittite traces were found for the first time on the European continent.
The Bathonea ancient city also bore traces of the Thracian/Phrygian tribes, the existence of which was contested until these findings proved they migrated from the Bosporus to Anatolia 3,000 years ago.
Professor Şengül Aydıngün, the head of the excavations, said, “From the first year we entered this field in 2008, Bathonea attracted the attention of the world. Officials from the American Archaeological Institute visited us. We showed them some very small remnants in the field and the following year, they put them on the list of the world’s best discoveries. Actually, Bathonea is not an ancient city but a port city. In the past, when Istanbul was founded, there was the city of Byzantium. Then Constantinople was founded. Just like today, Avcılar was a town connected to the center. It was a port settlement that provided great services to the city.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
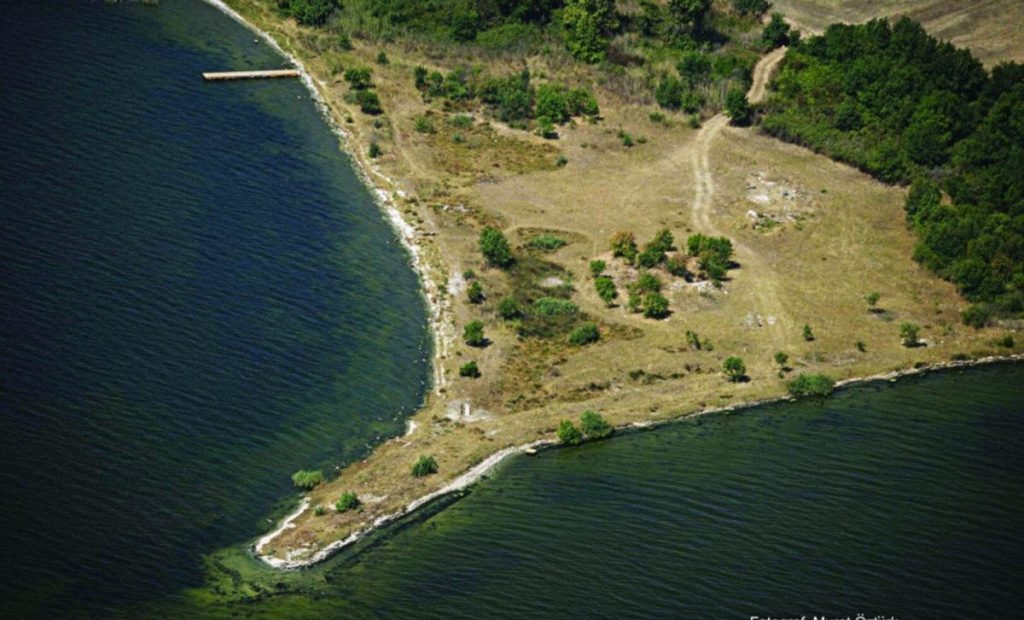

“We can say that the Bathonea excavations host one of the largest scientific teams in our country, composed of internationally powerful scientists.”
“In addition, I would like to underline the great importance of physical labor in archaeological excavations, and we express our gratitude to every worker who wields a shovel, throws soil, and carries wheelbarrows; their contributions are very valuable. We also express our thanks once again to Mercedes-Benz, with whom we are delighted to be together, and we hope this beautiful collaboration continues for many years.”
The social benefit programs it carries out as a supporter of the Bathonea Ancient City excavations, Mercedes-Benz Türk plays an essential role in uncovering and preserving the historical and archaeological heritage of Istanbul.
During the excavations in Bathonea, traces of two ancient harbors called “Large” and “Small,” dated to the Hellenistic and Roman periods, and an ancient lighthouse, have been discovered.
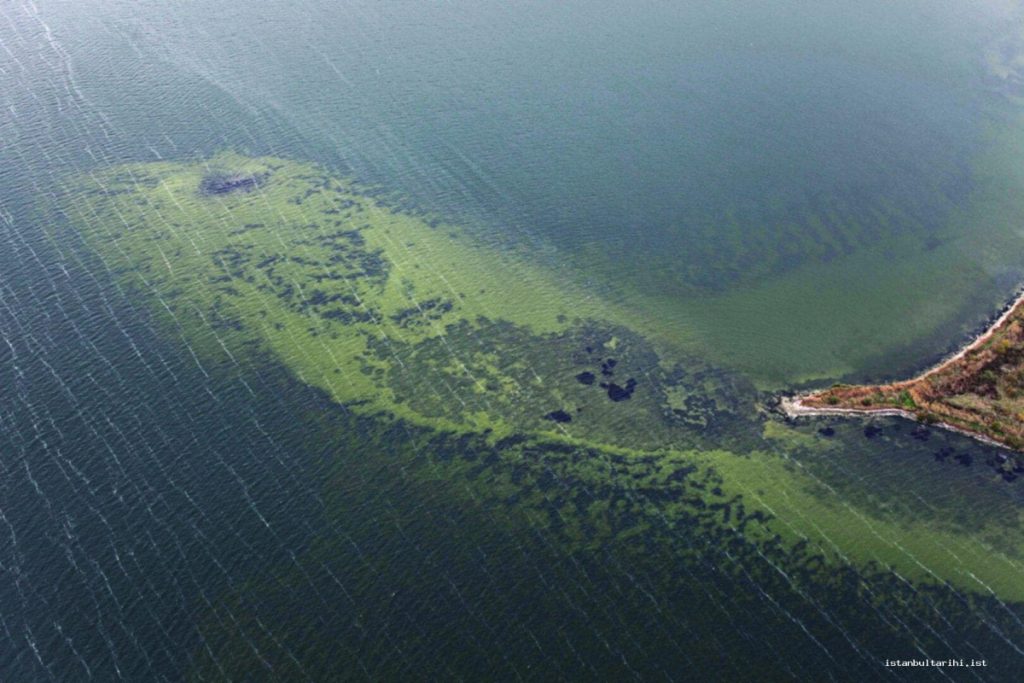

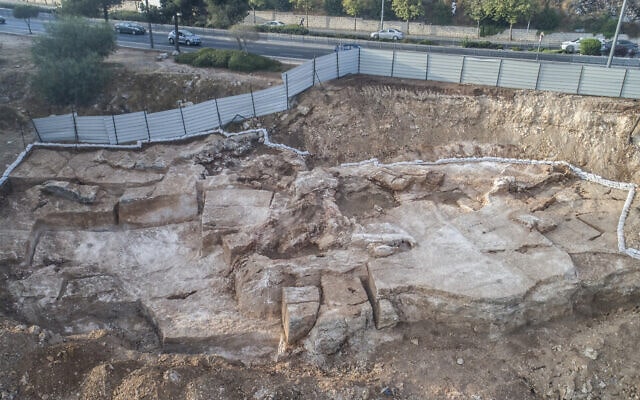
Excavations have begun since 2011-2012, revealing ancient harbor structures, a large open cistern believed to have been commissioned by Emperor Constantine the Great (A.D. 330), the remains of a castle, a large palace complex with mosaic-covered floors, underground water channels, and ancient roads.
Also, traces of a Viking neighborhood have been unearthed in the ancient city. “We unearthed seven clues that indicated the Vikings once lived here,” said Blazei Stanislawski, a Polish Viking expert who joined the team after he first learned that Vikings lived in Bathonea.
Small objects, ceramics, and amphoras discovered within these structures have revealed evidence of intense maritime trade between various ancient centers from the western to eastern Mediterranean (Spain, Italy, Sicily, Morocco, Egypt, Lebanon, Phoenicia, Syria, and the Aegean Islands) from the sixth to sixth centuries B.C.
The Journal of the American Archaeological Institute, the British Independent Newspaper, and the Heritage Key included the excavation site in the “Top 10 List of the World’s Most Important Archaeological Discoveries” in 2009.