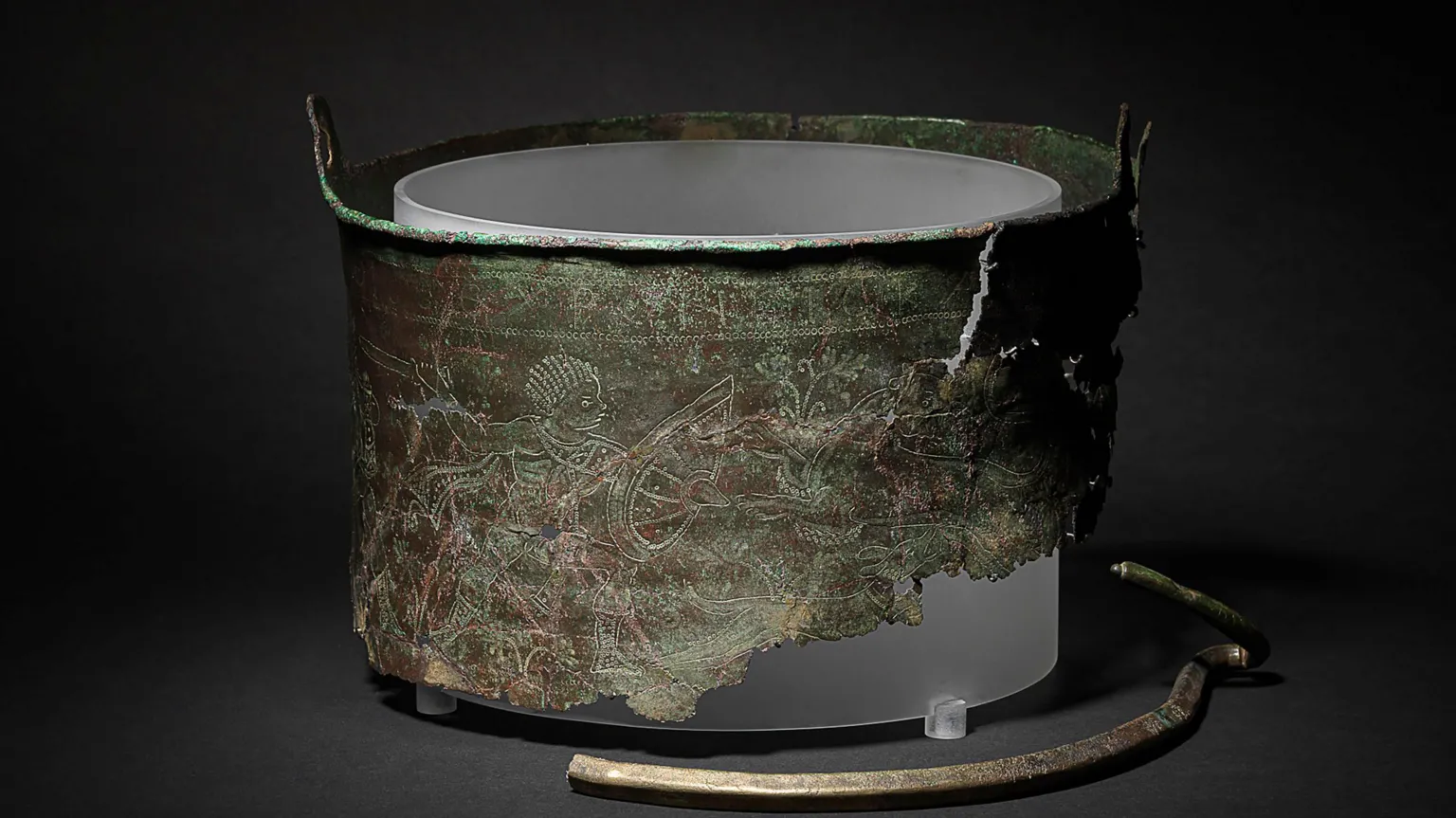
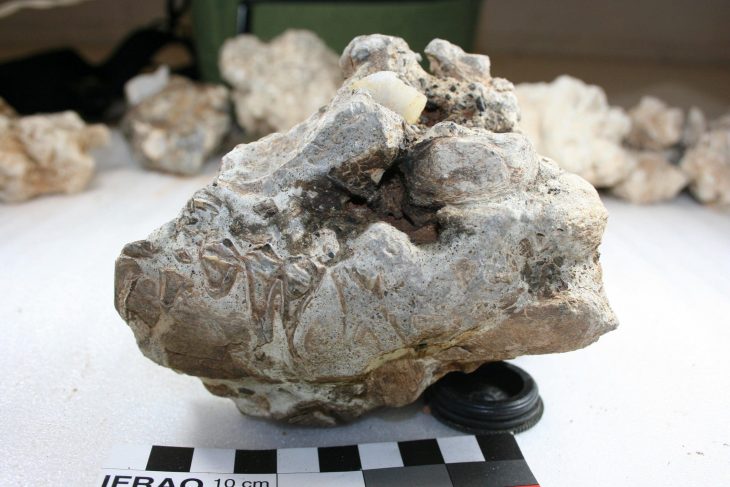
In a remarkable breakthrough at the historic Sutton Hoo site in Suffolk, England, archaeologists have revealed that a 6th-century Byzantine bucket, long shrouded in mystery and once thought to be merely ornamental—was in fact used as a cremation vessel for a high-ranking individual.
Pieced together from fragments unearthed in 1986, 2012, and most recently in 2023, the Bromeswell bucket is now considered a rare example of a cross-cultural burial artifact—an Eastern Mediterranean luxury item repurposed in a Northern European cremation ritual.
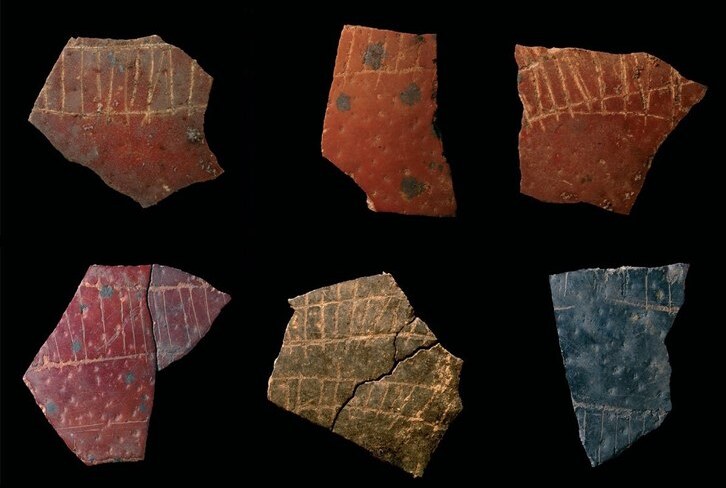
Decorated with an intricate hunting scene of nude warriors and lions, the copper-alloy bucket is believed to have originated from the Byzantine Empire and bears a Greek inscription: “Use this in good health, Master Count, for many happy years.” This sophisticated craftsmanship contrasts sharply with the Anglo-Saxon cremation practices of the time, making the find both culturally and historically significant.
Human and Animal Remains Discovered
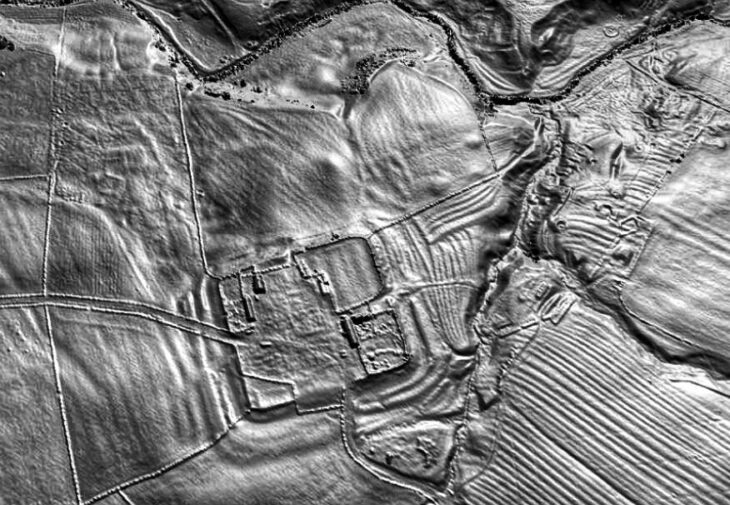
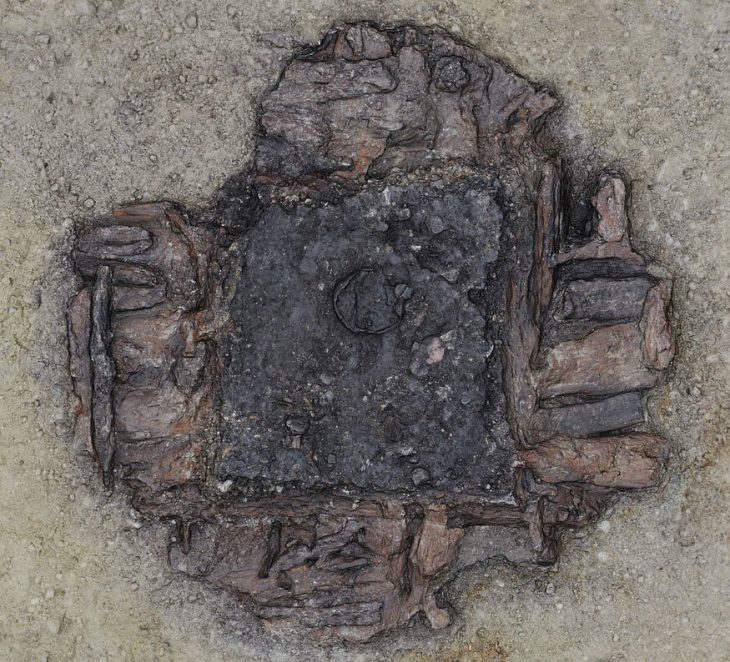
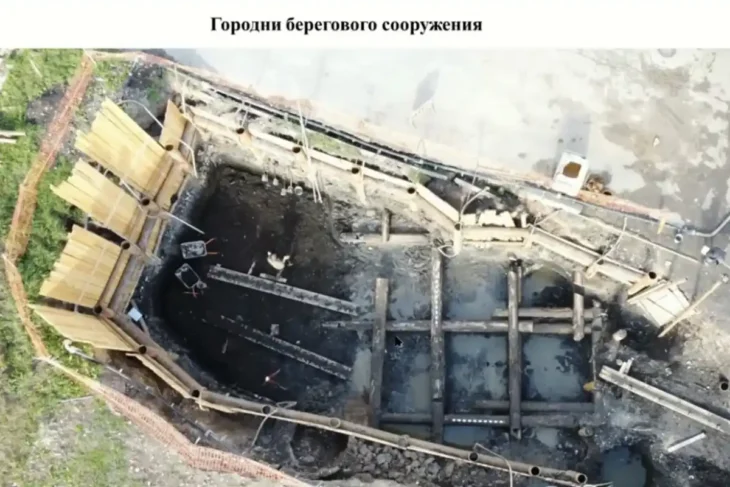
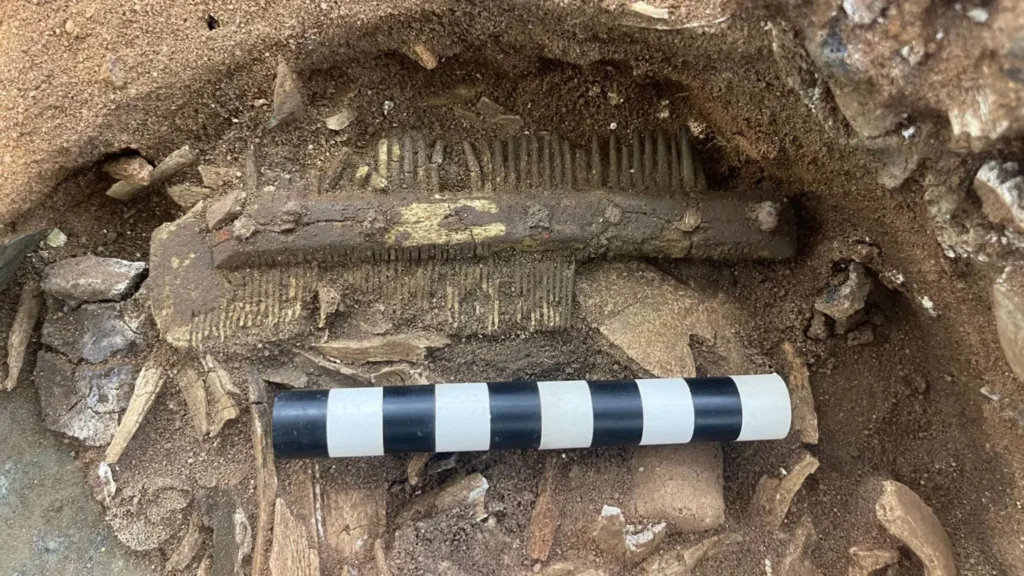
Recent excavations conducted by Time Team, in collaboration with FAS Heritage and the National Trust, uncovered the bucket’s intact base containing cremated human remains, bone fragments from a large animal—likely a horse—and an unburnt antler comb.
Experts believe the inclusion of horse bones signifies high status, as equines were commonly placed on cremation pyres of elite Anglo-Saxons. DNA analysis of the comb may soon offer insights into the individual’s age, sex, and possibly even genetic lineage.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“This bucket would have been a rare and prized possession in Anglo-Saxon times,” said Angus Wainwright, National Trust archaeologist. “Now, we know it was used to contain the remains of an important person within the Sutton Hoo community.”
Solving a Long-Standing Mystery
The discovery concludes a decades-long archaeological puzzle surrounding the bucket’s purpose. According to Dr. Helen Geake, Anglo-Saxon specialist for Time Team, the find is unprecedented: “This is the first known example of such a vessel being used in a cremation burial.”
“It’s a remarkable fusion—a classical, Byzantine artifact used in a Germanic-style cremation. Sutton Hoo continues to defy expectations with its ship burials, horse burials, and now bath-bucket burials,” Geake added.
Cultural Collision in Burial Practice
The Bromeswell bucket exemplifies the rich cultural interplay at Sutton Hoo, a site dating to the early 7th century, associated with the Kingdom of East Anglia. The bucket itself likely predates the famous ship burial by several decades, suggesting a complex and long-standing network of trade and cultural exchange.

CT scans of the artifact reveal concentric rings indicative of a cold-hammering technique—a method typical of Byzantine metalwork, emphasizing the advanced technology behind the object’s creation.
Ongoing Research and Public Display
The National Trust has placed the main fragment of the Bromeswell bucket on display at Sutton Hoo, on long-term loan from the Annie Tranmer Charitable Trust. Time Team has documented the discovery in a special four-part YouTube series, culminating in a “fly on the wall” special airing May 20 at 7 PM.
Further excavations and studies are expected to continue until June, as researchers hope to extract ancient DNA and unlock more secrets from this extraordinary burial.
Cover Image Credit: David Brunetti/National Trust