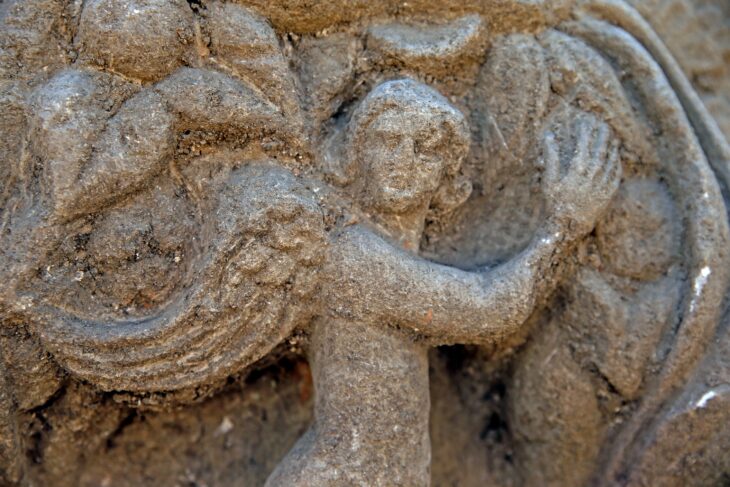
Archaeologists have unearthed two new temples in the Doric style in Paestum, an ancient Greek colony in southern Italy.
The temples were part of Magna Graecia (Great Greece), a thriving group of ancient Greek cities in southern Italy that date back to the eighth century BC. When the Romans conquered the ancient Greek colony of Poseidonia in 273 BC, they renamed the city Paestum.
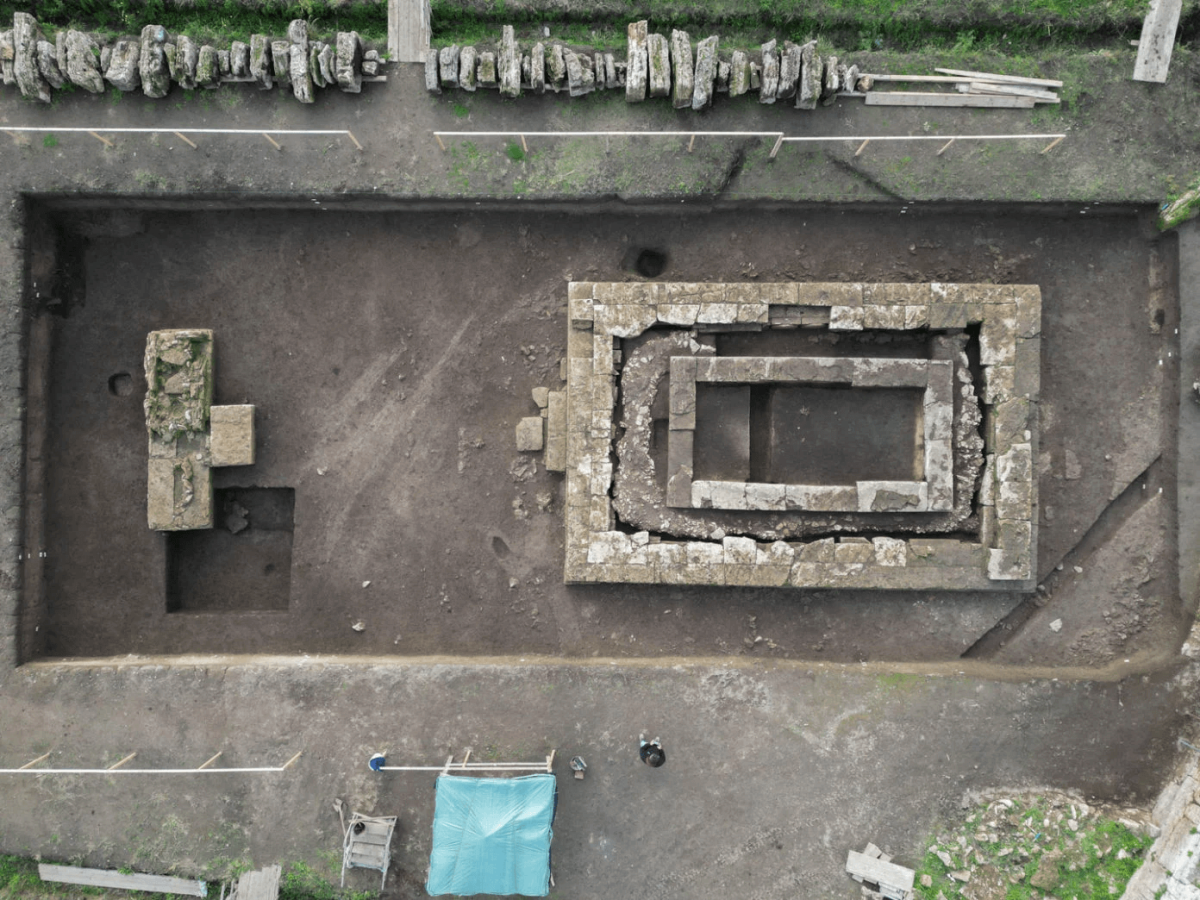
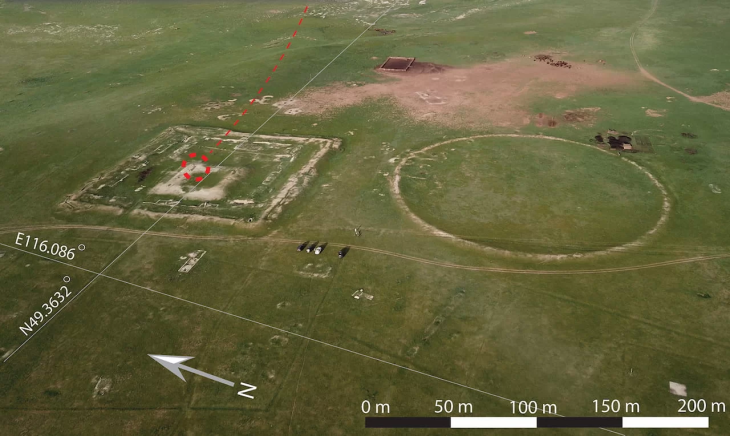
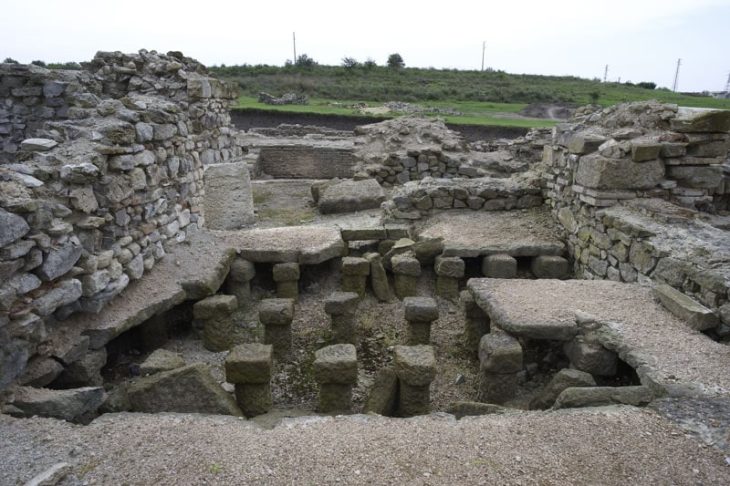
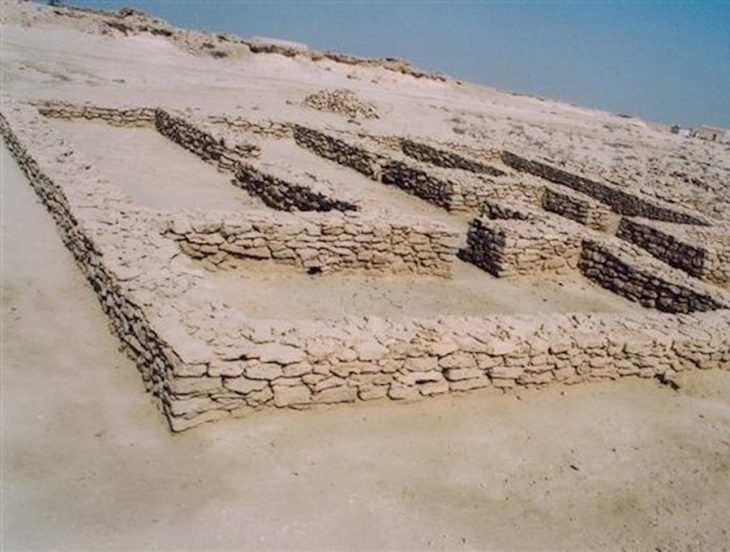
Experts discovered two superimposed Greek temples of the Doric order next to its ancient walls, a few meters from the Mediterranean Sea, in addition to those already known, such as Hera’s or Poseidon’s, two of the best preserved from antiquity.
The first, located in 2019 but investigated three years later, has been dated to the first decades of the 5th century BC and, due to its characteristics and dimensions, represents “a unique case in Doric religious architecture.”
The remains of the temples were uncovered at the archaeological site of Paestum, which is located on the western coast of southern Italy in the province of Salerno in the region of Campania, the country’s Ministry of Culture announced.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to the ministry, the latest discovery adds to our understanding of the ancient settlement and the evolution of Doric architecture in Poseidonia and Magna Graecia as a whole. The findings significantly expand our knowledge of the city’s layout, for example.
Tiziana D’Angelo, the director of the Archaeological Park of Paestum and Velia, described the discoveries as “exceptional” in a press release, saying they provide key new evidence that will help to reconstruct the ancient history of Poseidonia.
Today, Only some parts of the stylobate, the surface that supports the columns, and the crepidoma, the stepped platform on which the entire building rests, are preserved. The temple measured 11.60 meters long by 7.60 meters wide surrounded by columns (4×6). It had six columns on the long sides and four on the short. These dimensions and architectural features are unique for a Doric temple.
However, research has led to the discovery of a second temple from the sixth century BC that is “more modest” in size but has “similar” characteristics and may be older.
Archaeologists consider the possibility that this sanctuary collapsed at some point and was replaced by a new temple on top a century later, in a period of strong growth of the ‘polis’.
The Italian Minister of Culture, Gennaro Sangiuliano, acknowledged that these discoveries confirm that “There is still much to excavate and investigate” after “years of inertia” in Paestum, a UNESCO World Heritage site since 1998.
Paestum is thought to have been founded around 600 B.C. by settlers from Sybaris, the most populous city in Magna Graecia. Paestum, originally known as Poseidonia by the Greeks, thrived for approximately two centuries before being conquered by the Lucanians—an Italic tribe—around 400 B.C. The settlement was later conquered by Rome and renamed Paestum in 273 B.C.
Cover Photo: Ministura della Cultura Italia