The Acropolis of Athens and its monuments, the greatest architectural and artistic complex bequeathed to the world by ancient Greece, is one of the most visited and best-known archaeological sites in the world, yet researchers continue to uncover new information about it.
A new publication in the American Journal of Archaeology, by Merle Langdon (University of Tennessee) and Janric van Rookhuijzen, tells a historical detective story of a lost temple on the site of the Parthenon. It all began with the discovery of ancient graffiti.
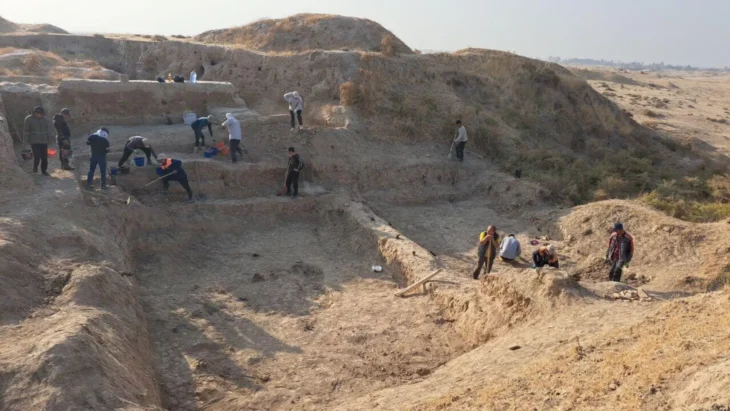
Over 2000 rock carvings on marble rocks, which date to the 6th century BC, provide an unexpected window into the daily lives and worries of the shepherds who once roamed these areas. The carvings are located in the hills to the north and east of Vari in Attica.
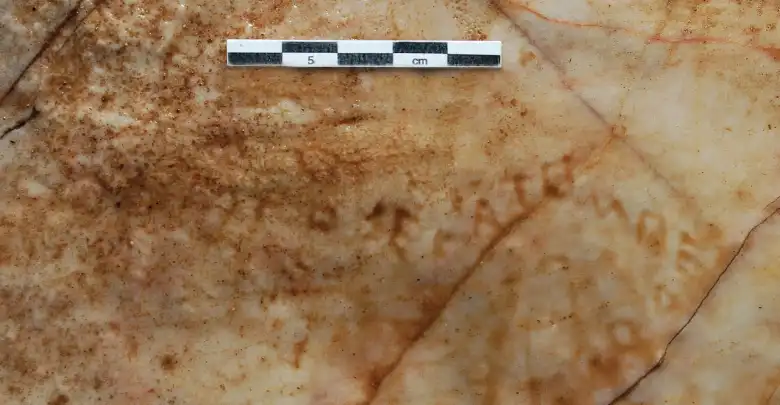
Among these, one unique inscription has captured the attention of archaeologists: a drawing of a temple with the inscription “Hekatompedon”, signed by an individual named Mikon.
The newly discovered work is a rough rock-cut drawing of a building. Though the details of the drawing are not fully understood, it can be identified as a temple due to the columns and steps.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Snaking around the building there is a Greek inscription reading To Hekatompedon … Mikonos (The 100-foot building … of Mikon). Mikon is not otherwise known, but he was most likely a shepherd who made the graffito while grazing his flocks. The version of the Greek alphabet used is very ancient, making it clear that the drawing was made as early as the 6th century BCE.
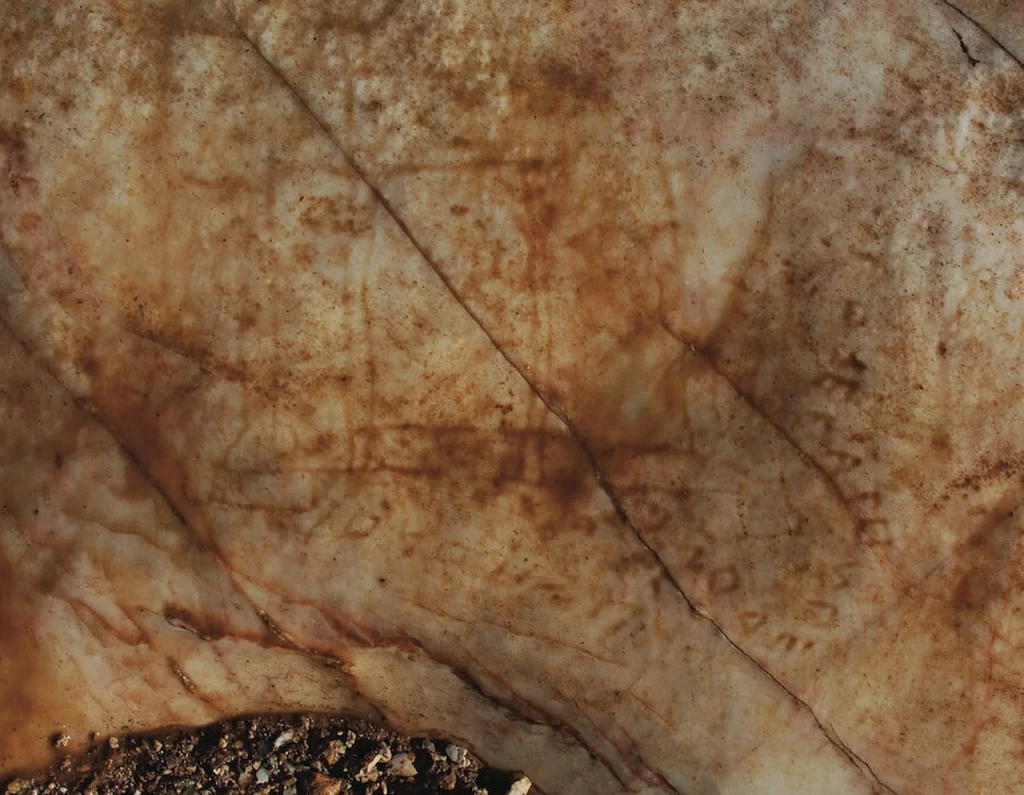

Except for a few rare exceptions like the Temple of Apollo in Thermos, pentastyle buildings—that is, buildings with five columns—are uncommon in Greek architecture. The drawing depicts the façade of a building with at least five columns. Protruding elements and horizontal lines suggest a sketch of a two-step krepis or an entablature with acroteria.
Of is the inscription’s word Hekatompedon, a Greek name meaning “100-footer”, referring to a structure of enormous size. The term “Hekatompedon” was used both literally and figuratively to describe enormous structures. In a religious context, it usually refers to large temples.
It is likely that Mikon wanted to depict a building on the Acropolis of Athens. However, because the alphabet he used can be firmly dated to the 6th century BCE, the drawing must be at least 50 years older than the Parthenon, which was begun around 450 BCE.

Despite being extremely old, the Parthenon was not the first temple. Though archaeologists have bitterly disagreed over their dates, appearances, and precise locations on the hill, it has long been believed that even older temples once stood on the Acropolis. Another historical event that makes comprehension difficult is the destruction of all the structures that once stood atop the Acropolis by a Persian army that invaded Athens in 480 BCE during the Greek-Persian Wars.
Before the Periclean structures on the Acropolis were built, Mikon’s inscription sheds light on the meaning and application of the term Hekatompedon. The so-called Decrees of the Hekatompedon, inscriptions dated to 485/4 BC, mention rooms within it used to store treasures. Greek temples normally served as the storage of treasures offered to the gods. These documents confirm, therefore, that the term was already used to designate a specific and sacred part of the Acropolis.
Archaeologists believe that Mikon’s drawing’s recently discovered graffito holds great significance. Given that Mikon referred to his sketched temple as a Hekatompedon, it is probable that the decree’s use of the term Hekatompedon also applied to a temple. Indeed, the Parthenon that stands on the hill today was once called the Hekatompedon.
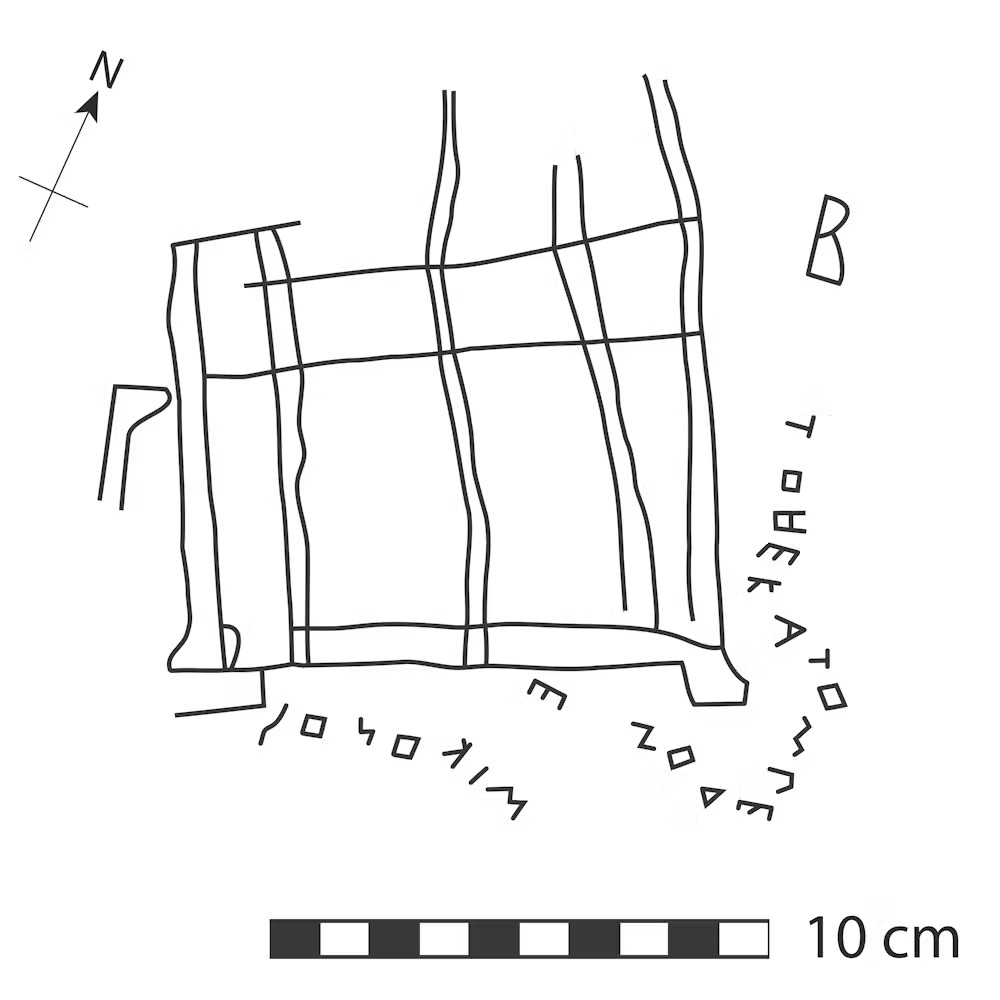
According to archaeologists, Mikon’s graffito is a unique document from the second half of the 6th century BC that represents the earliest epigraphic attestation of the term Hekatompedon. The use of the definite article τό implies that a specific building is represented, probably on the Acropolis of Athens. The engraving can provide information for future studies on the architectural history of the Acropolis in the archaic period, as it sheds new light on the term Ἑκατόµπεδον used in the second Hekatompedon decree of 485/4 BC. In particular, it reinforces the view that this term referred to a temple, with a probable, though uncertain, location on the south side of the Archaic period Acropolis.
Additionally, they add, that beyond its archaeological importance, the inscription is also significant because it shows that, contrary to what is normally thought, shepherds could read and write, even at this early date when literacy in the Greek world was still spreading.
Cover Photo: Classic view of Acropolis of Athens Alexander Popkov