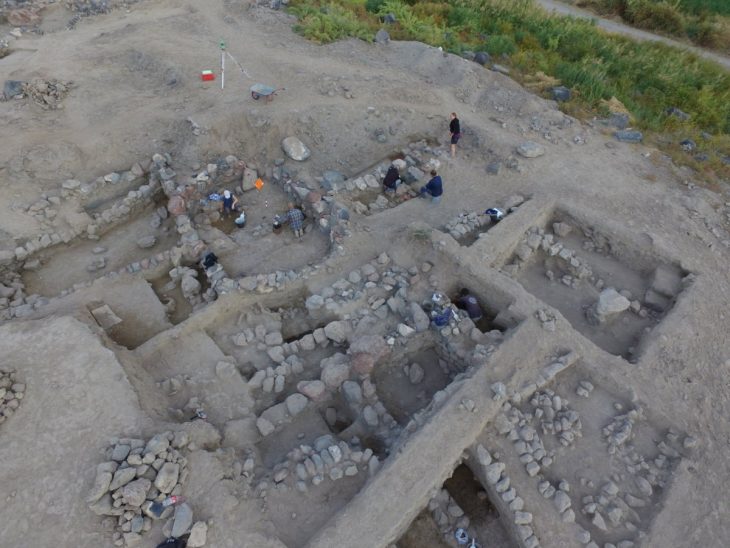
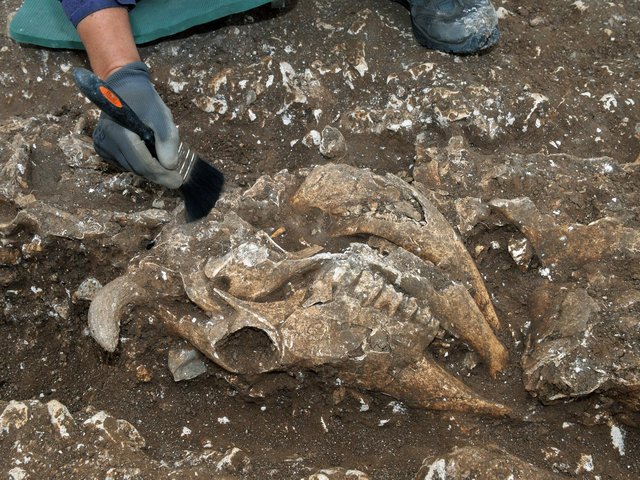
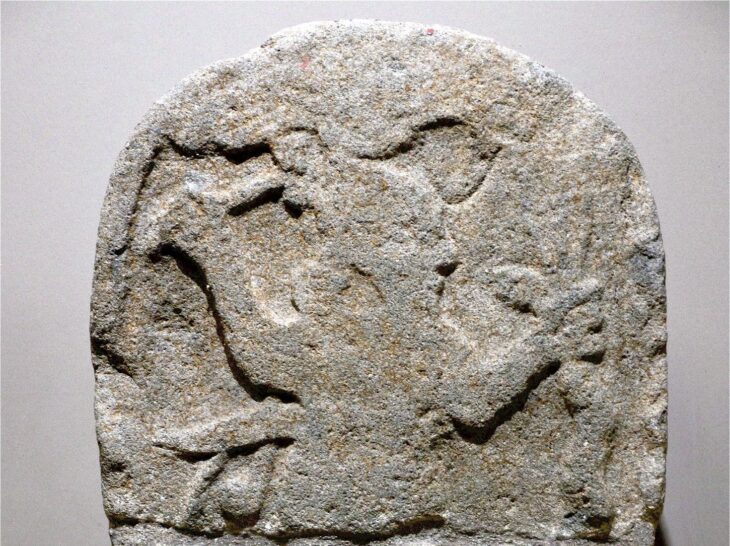
The Saudi Commission for Tourism and National Heritage has announced the discovery of a 2,550-year-old inscription etched on basalt stone in northern Saudi Arabia in the name of Nabonidus, Babylon’s last ruler. It is the longest cuneiform inscription ever discovered in the nation, with 26 lines.
The commission stated in a statement that an etching at the top of the inscription depicts King Nabonidus holding a scepter with four other motifs that include a serpent, a flower, and a representation of the moon, adding that these symbols are likely religious in nature.
The inscription was discovered near Al Hait, Saudi Arabia’s Hail Region. The commission said that in ancient times Al Hait was known as Fadak and this area was home to many ancient remains.
This archaeological find will be added to previous finds of stone inscriptions and obelisks mentioning King Nabonidus, who ruled from 556 to 539 B.C., in a variety of sites between Tayma and Hail. The discovery demonstrates the growth of cultural and commercial interaction between the Arabian Peninsula and Mesopotamian civilizations.
The Babylonian Empire during Nabonidus’ reign, stretched from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea, he captured a portion of what is Saudi Arabia and eventually decided to dwell in Tayma, a city in what is now Saudi Arabia, until approximately 543 B.C.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
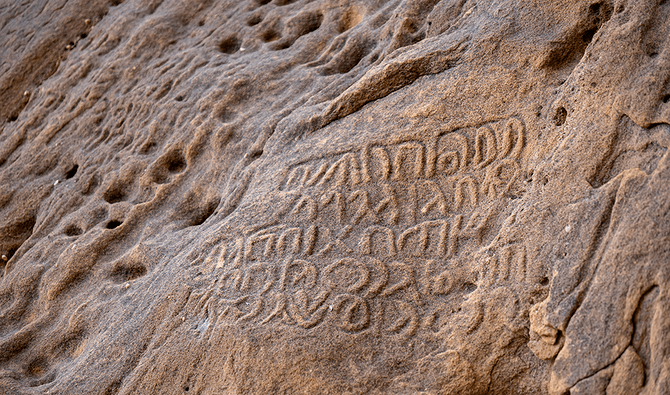
Nabonidus went into exile at Tayma, some 160 miles north of Al Hait, four years after ascending to the throne of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, possibly as a consequence of a coup, as his inscriptions expressly disclaim any royal heritage.
Historians disagree on why Nabonidus decided to reside in what is Saudi Arabia for such a long time. The cause for his self-imposed exile from political and religious authority is unknown, although disputes with the clergy and elite over his attempts to change Babylon’s god hierarchy and declare the moon preeminent above all others are believed to have played a part.
At the conclusion of Nabonidus’ reign, the Babylonian Kingdom was attacked by the Persian Empire, led by King Cyrus the Great; Babylon was conquered by the Persians in 539 B.C., and the Babylonian empire fell. It is unknown what happened to Nabonidus following the fall.
According to Arabnews, details of the discovery will be released after specialists have more time to analyze. It will be linked to previous results that have been documented in the northwest of the Kingdom.
Cover Photo: The top of the inscription from the last king of Babylon shows engravings showing Nabonidus and four symbols. (Photo: Courtesy Saudi Press Agency)
















