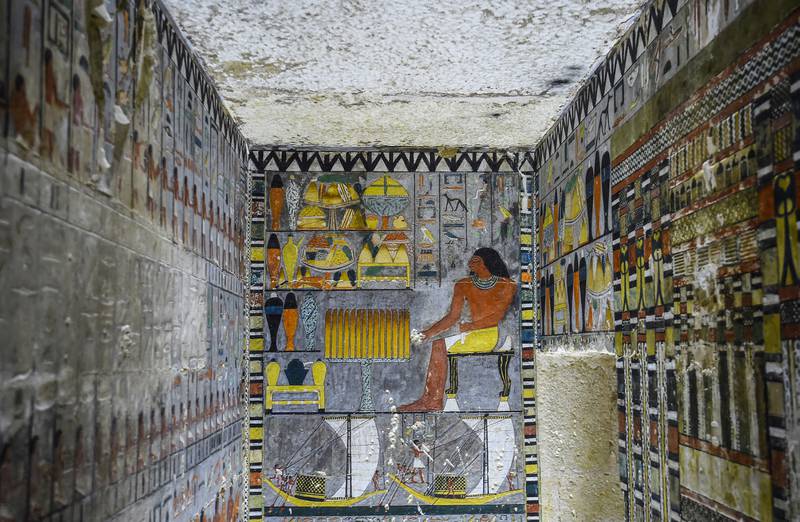
The mummified corpse of an ancient Egyptian nobleman named Khuwy, discovered in 2019, showed the ancient Egyptians were carrying out sophisticated mummifications of their dead 1,000 years earlier than previously thought.
The mummified body of a high-ranking aristocrat named Khuwy, discovered in 2019, was proven to be far older than previously thought, making it one of the oldest Egyptian mummies ever unearthed. It has been dated to the Old Kingdom, demonstrating that mummification processes were highly advanced 4,000 years ago.
The discovery was featured in a 2020 episode of National Geographic’s Lost Treasures of Egypt.
Dr. Salima Ikram, a professor of Egyptology at the American University in Cairo and one of the primary researchers in the recent study, told The National that “circumstantial evidence” suggested the mummy dated from the Old Kingdom.
The intricacy of the body’s mummification method and materials – particularly its very fine linen dressing and high-quality resin – was supposed to have taken 1,000 years to produce.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
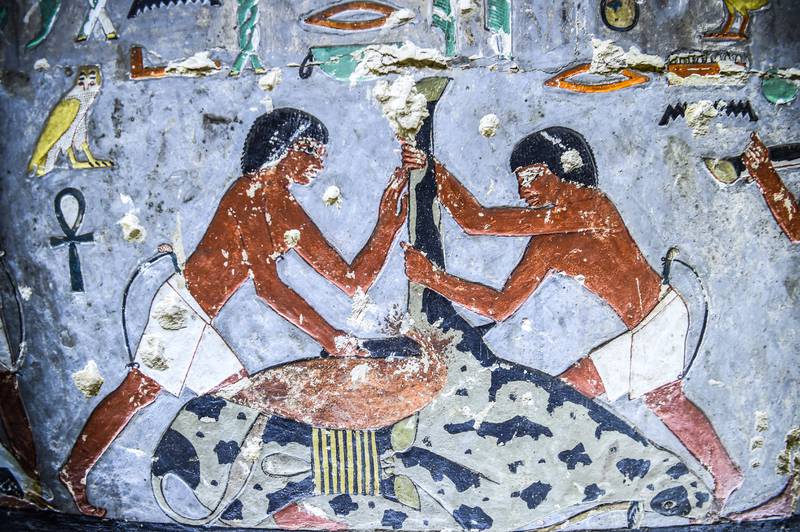

Hieroglyphs on the tomb wall provided evidence for the mummy’s ancient antiquity.
These suggest that it was the final resting place of Khuwy, a high-ranking official of the Fifth dynasty (which lasted 150 years, from the early 25th century BC to the mid 24th century BC) and a royal family related. Pottery and canopic jars – receptacles used during the mummification process to hold body parts – were discovered in the tomb believed to have been created in the Old Kingdom as well.

Professor Salima Ikram, head of Egyptology at the American University in Cairo and a leading expert on the history of mummification, told the Observer: “This would completely turn our understanding of the evolution of mummification on its head. The materials used, their origins, and the trade routes associated with them will dramatically impact our understanding of Old Kingdom Egypt.
“If this is indeed an Old Kingdom mummy, all books about mummification and the history of the Old Kingdom will need to be revised.”
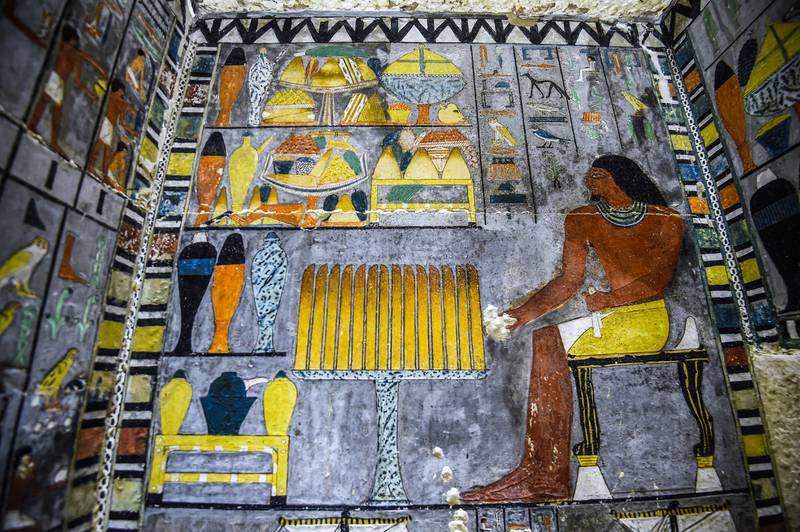

The tomb complex, Dr Ikram said, features a layout that is characteristic of the architecture of royal pyramids built during the Fifth dynasty.
Despite the strong case suggesting that the mummy does indeed date back to the Old Kingdom, Dr Ikram and her colleagues are conducting further tests which will confirm whether the remains are indeed those of Khuwy.
Dr. Ikram said that everything about the discovery points to the funerary practices of many later dynasties.
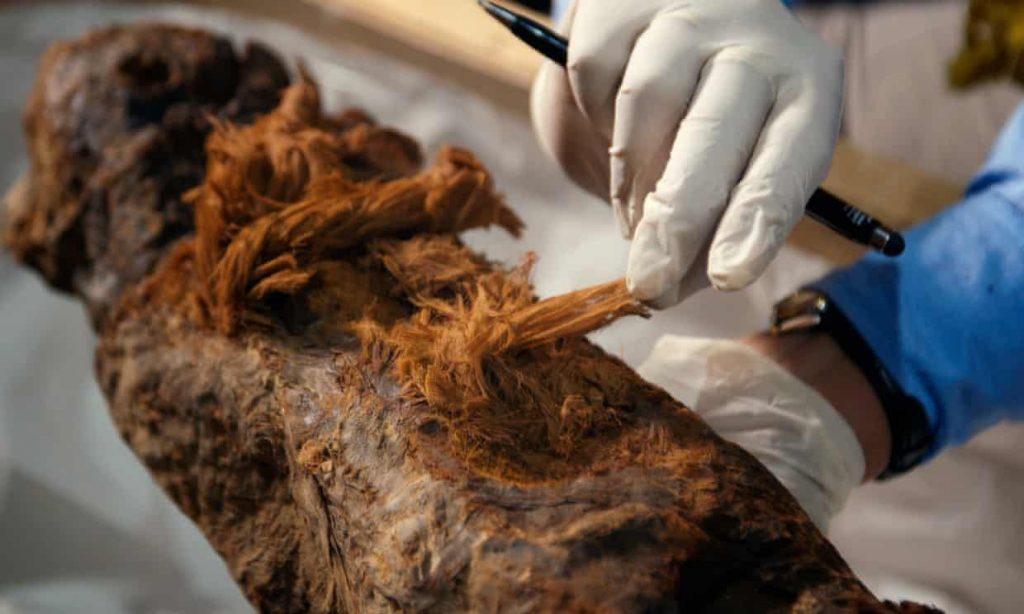

Ikram says in the program: “It’s extraordinary. The only time I’ve [seen] so much of this kind of good quality linen has been in the 21st dynasty.” The 21st dynasty of Egyptian Pharaohs reigned more than 1,000 years after Khuwy lived.
“The resin used to preserve the body would have been imported from the Near East, from Lebanon most likely.”
The existence of these materials in Egypt at the time would mean that trade with neighboring empires was much more extensive than previously thought.
It is among major discoveries to be revealed in National Geographic’s documentary series, Lost Treasures of Egypt, starting on 7 November. The mummification discovery will feature in episode four – entitled Rise of the Mummies – on 28 November.