Archaeologists have discovered two lost medieval cities in the eastern mountains of Uzbekistan that were important hubs on the ancient Silk Road. More importantly, these lost twin cities may have sustained themselves in a frightening landscape of metallurgy and trade.
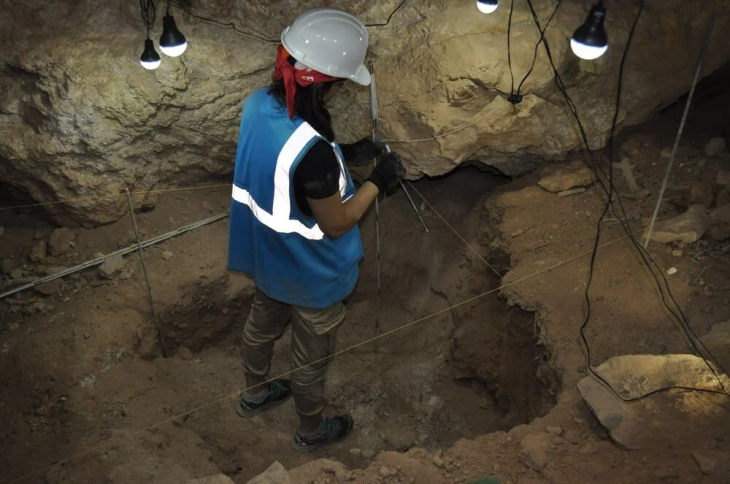
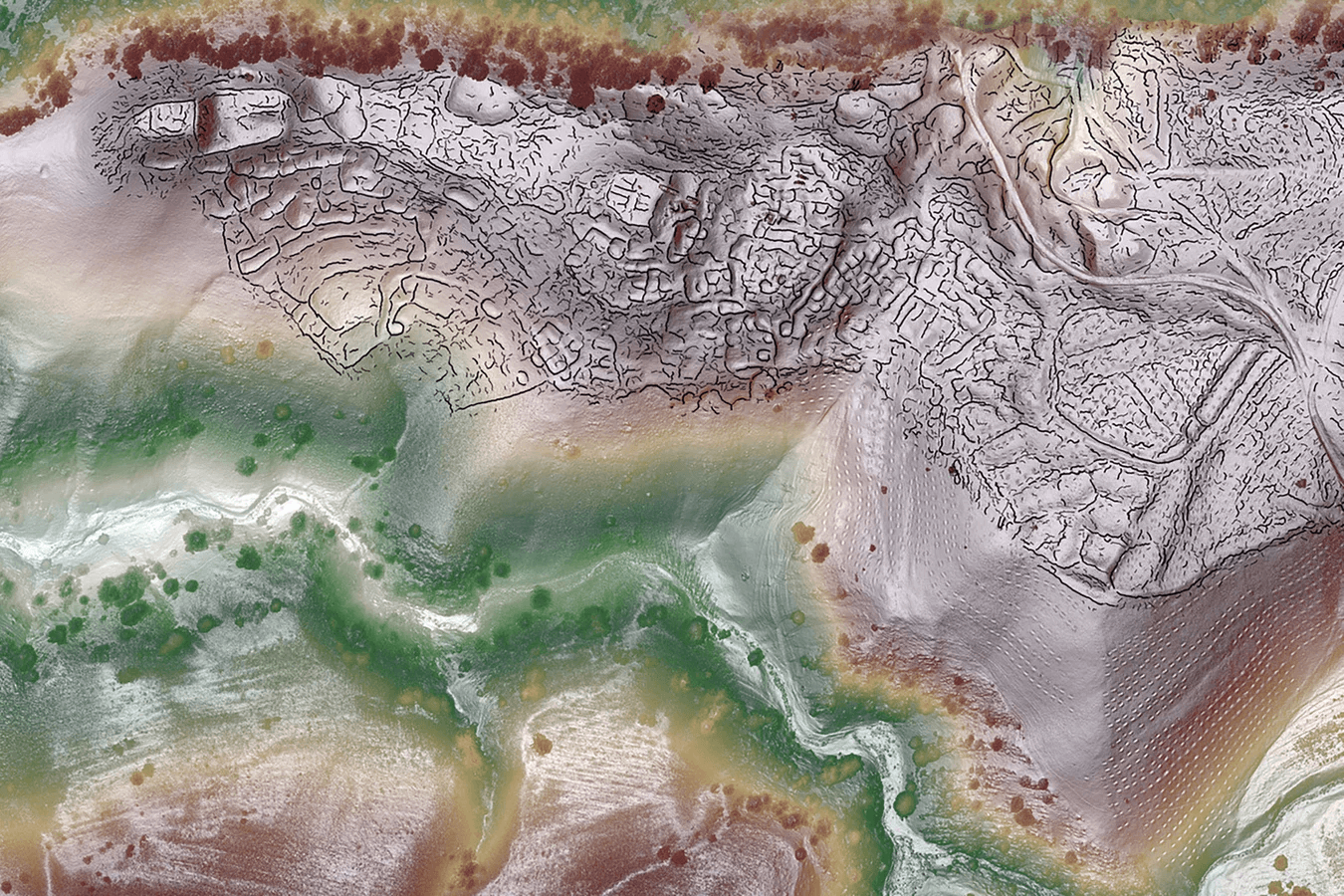
The settlements, which are thought to have flourished between the sixth and the eleventh centuries, were discovered using remote sensing with lasers mounted on drones at an elevation of over 2 km above sea level. Merely 3% of the global populace currently resides above this elevation. Cusco, Peru, and Lhasa, Tibet, are two uncommon examples.
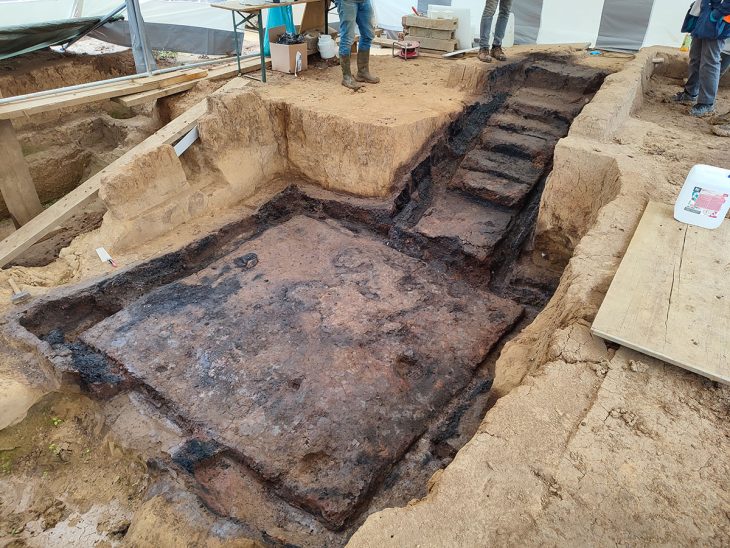
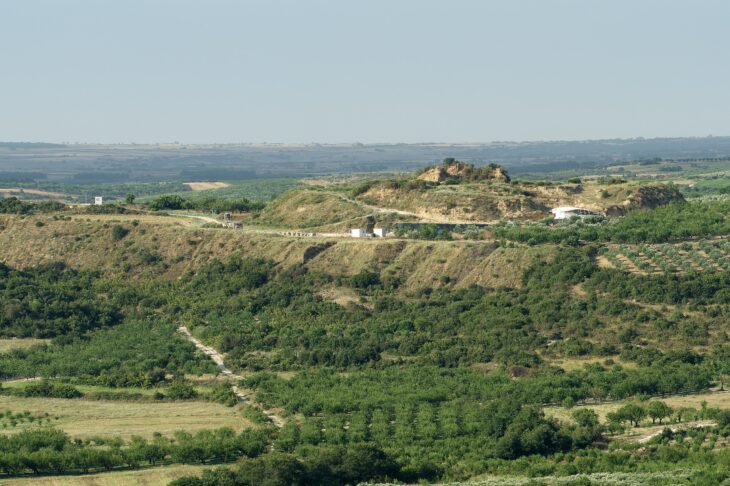
One of the cities – Tugunbulak, sat more than 2,000m (6,600 ft) above sea level. The Tugunbulak was about 120 hectares in area and was estimated to have been home to tens of thousands of people, making it comparable in size to Samarkand at the time.
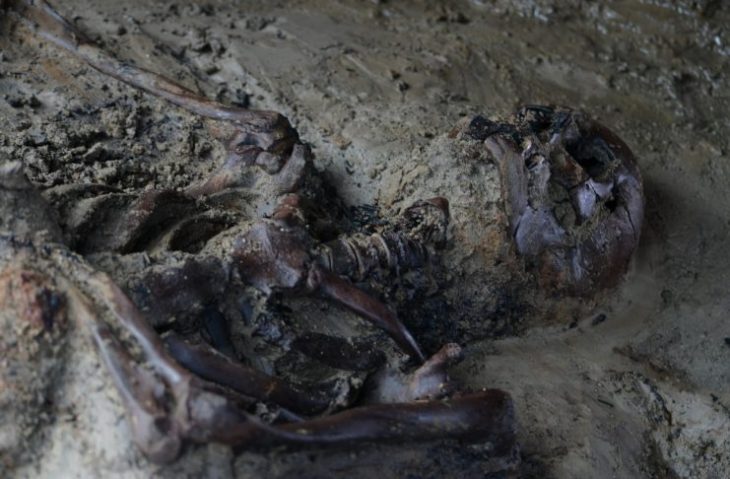
The second city, Tashbulak, was smaller. It did, however, attract researchers due to its large cemetery, which contained 400 graves of men, women, and children. Among them are some of the oldest Muslim burial sites in the region.
The researchers team believes Tugunbulak and the smaller city, Tashbulak, were bustling settlements between the 8th and 11th centuries, during the Middle Ages when the area was controlled by a powerful Turkic dynasty.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
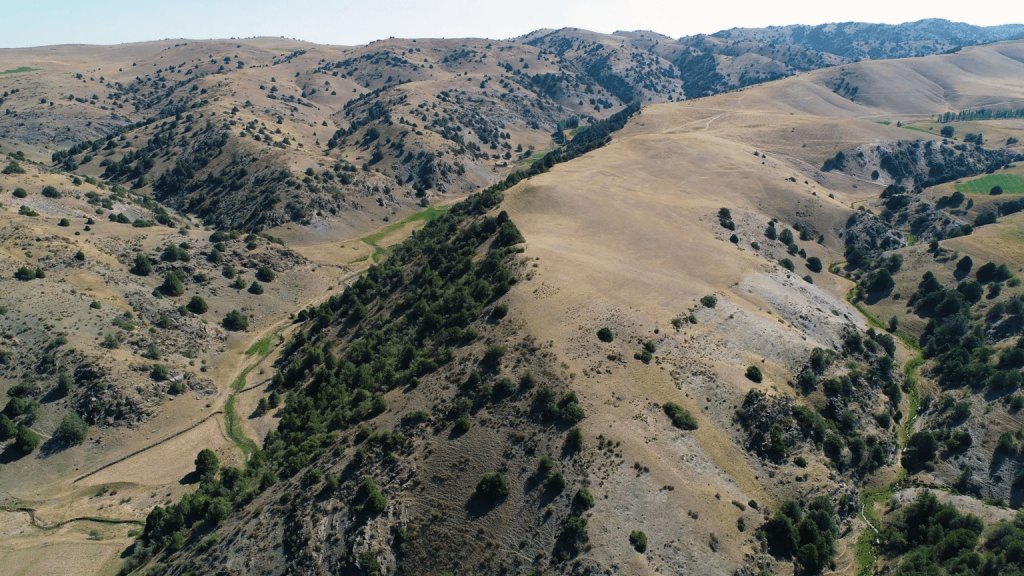

The discovery, led by Farhod Maksudov, director of the National Archaeological Centre of Uzbekistan, and Michael Frachetti, an archaeologist at Washington University in St Louis, was published this week in the scientific journal Nature.
Historical records allude to cities in the region, Michael Frachetti said BBC, but the team did not expect to find a 12-hectare medieval city some 2,200m above sea level.
The discovery is significant for understanding the evolution of ancient civilizations in mountainous regions. Such large, well-planned, and fortified settlements from that time are uncommon at high altitudes. The discovery demonstrates that political and industrial centers along the Silk Road were not limited to well-known cities like Samarkand, but rather spread widely, including into difficult-to-reach mountainous areas.
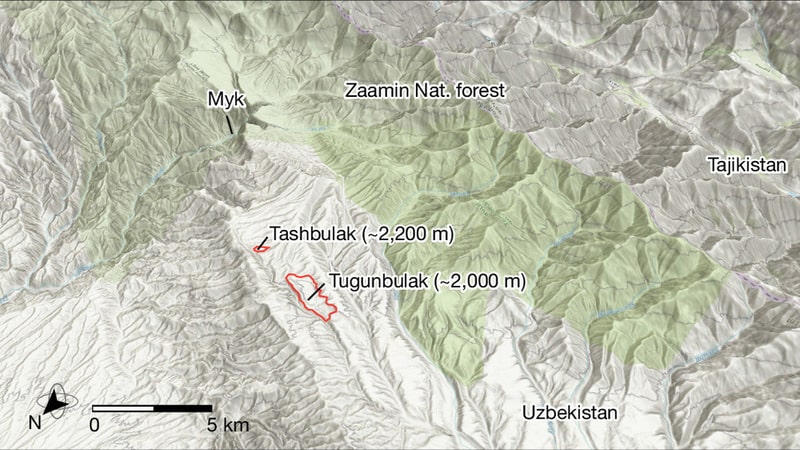
Conventional Silk Road maps show that trade routes that traverse the Eurasian continent generally steer clear of the Central Asian mountains. It is believed that the true trading destinations were low-lying cities like Samarkand and Tashkent, which have the irrigation and arable land needed to sustain their thriving populations. On the other hand, the nearby Pamir mountains, where Tashbulak and Tugunbulak are located, are rugged and mostly nonarable because of their elevation.
For this reason, the research is very important in terms of shedding light on the lifestyles of nomadic communities.
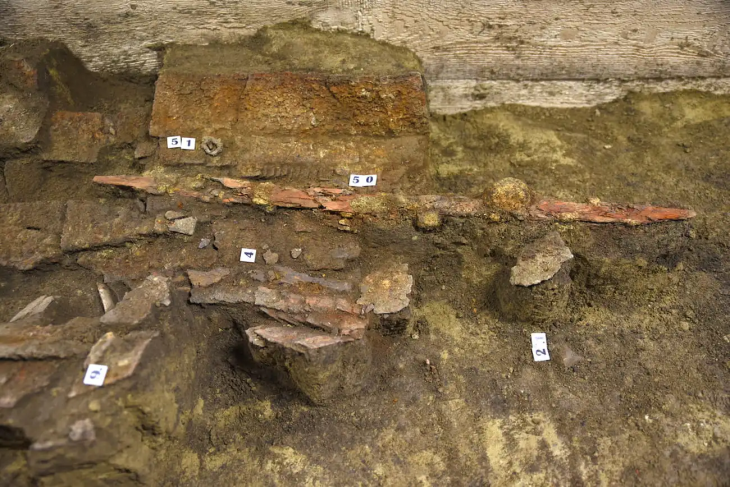
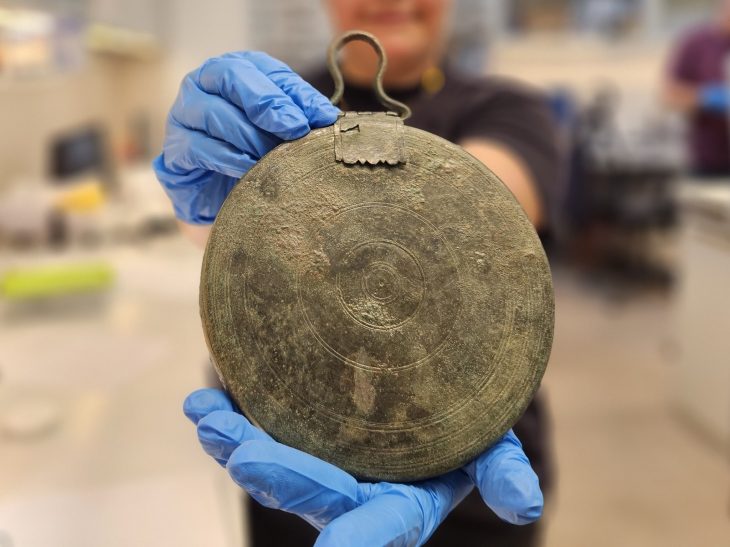
According to the researchers, people may have decided to settle in Tugunbulak and Tashbulak in order to take advantage of the strong winds that would fuel the fires needed to smelt iron ores, which were abundant in the area. Production kilns have also been discovered during preliminary excavations.
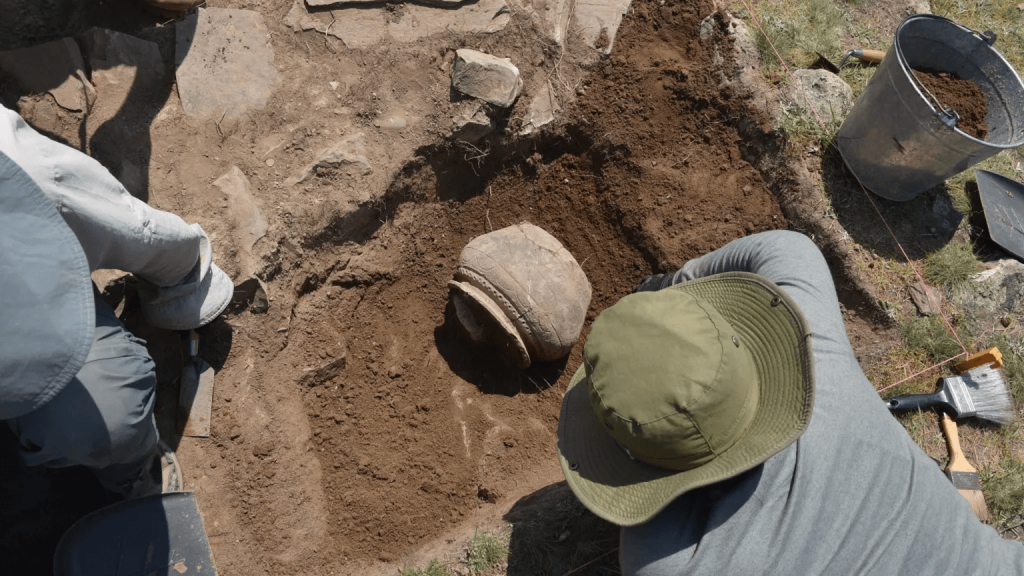

However, researchers suspect that this choice may have led to the collapse of communities. This area used to be covered by a thick juniper forest, but these could have been cut to facilitate iron production. “The area became environmentally very unstable because of the flash floods, because of the avalanches,” Farhod Maksudov, said.
Source: Large-Scale Medieval Urbanism Traced by UAV-Lidar in Highland Central Asia,” by Michael D. Frachetti et al., in Nature. Published online October 23, 2024
Cover Image credit: A lidar view of Tugunbulak, the site of a nearly 300-acre medieval city in Uzbekistan, with crest lines. SAIElab/J. Berner/M. Frachetti