In a groundbreaking archeogenetic study, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, in collaboration with an international team, have analyzed the remains of over 700 individuals from the Early Middle Ages. The comprehensive genetic analysis focused on two significant burial sites, Mödling and Leobersdorf, revealing unexpected insights into the ancestry of these ancient populations.
The study uncovered a striking contrast between the two communities: individuals from Leobersdorf predominantly exhibited East Asian genetic markers, while those interred in Mödling primarily had European ancestry. Remarkably, both groups coexisted in close proximity for at least six generations.
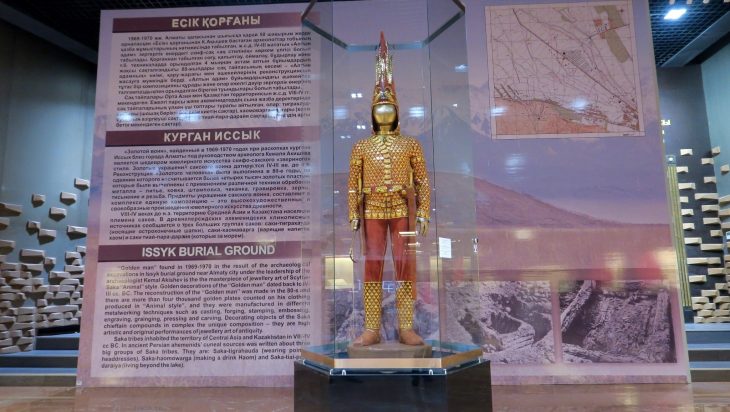
This research, part of the European Research Council project HistoGenes, highlights the complex relationship between genetics and culture. The findings stem from an extensive genetic examination of burial grounds dating back to the 8th century CE, during the Avar period. The Avars had arrived in the 6th century from the East Asian Steppes and settled in East Central Europe among a mixed population.
Despite the rich archaeological context, questions lingered regarding the origins of the individuals buried at these sites. Were they descendants of the Avar conquerors, or did they represent a blend of the local population integrated into Avar society? The analysis of 500 graves in Mödling and nearly 150 in Leobersdorf provided clarity, revealing significant genetic differences that had previously gone unnoticed.
Ke Wang, a geneticist and lead author of the study, remarked, “The genetic difference between these groups was very clear and consistent for most individuals at the sites.” Prior to the genetic analysis, the archaeological evidence suggested little distinction between the two communities, which shared similar lifestyles and cultural practices. Walter Pohl, a historian from the Austrian Academy of Sciences, noted, “Cultural integration apparently worked despite major genetic differences, and these people were obviously regarded as Avars.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The historical context aligns with anthropological and archaeological evidence, indicating that this period was one of relative peace in the Vienna Basin, despite the Avars’ warrior reputation. Doris Pany-Kucera, an anthropologist at the Natural History Museum Vienna, stated, “We find no battle injuries on the skeletons, and there are hardly any signs of deficiencies.” Additionally, weapons were rarely found in the graves.
The meticulous sampling strategy and advanced genetic analysis allowed researchers to identify numerous familial connections among the deceased. Zuzana Hofmanová, a geneticist involved in the study, explained, “The large number of genetic relationships between the individuals allowed us to reconstruct contemporary six-generation-long pedigrees at each site.” Notably, very few individuals lacked biological ties to others in their burial ground, yet no consanguineous relationships were found, even among distant relatives.
Intriguingly, the study revealed that almost none of the mothers had local ancestors, suggesting they originated from other regions and communities. The two groups maintained distinct ancestries through selective partner choices, with women in Leobersdorf likely descending from East Asian communities, while those in Mödling were of European descent. Despite these differences, both communities shared similar status symbols and cultural practices, leading archeologist Bendeguz Tobias to conclude, “Most likely both considered themselves Avars.”
Such extensive studies of burial grounds remain rare in the field of archeogenetics. Johannes Krause, director at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, emphasized the significance of the findings, stating, “Mödling burial ground is one of the largest ever analyzed genetically, and such results hold a lot of potential for future research across various disciplines.”
This research not only sheds light on the complex interplay of genetics and culture in ancient societies but also opens new avenues for understanding the dynamics of historical populations in Europe.
Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
Wang, K., Tobias, B., Pany-Kucera, D. et al. Ancient DNA reveals reproductive barrier despite shared Avar-period culture. Nature (2025). doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08418-5
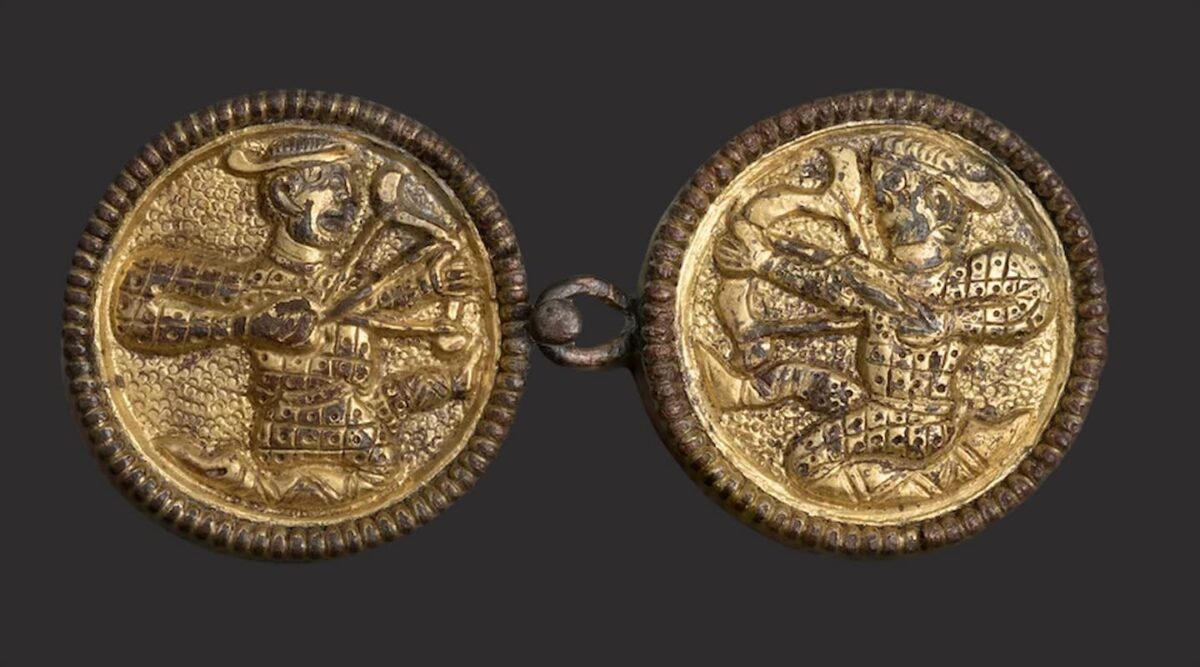
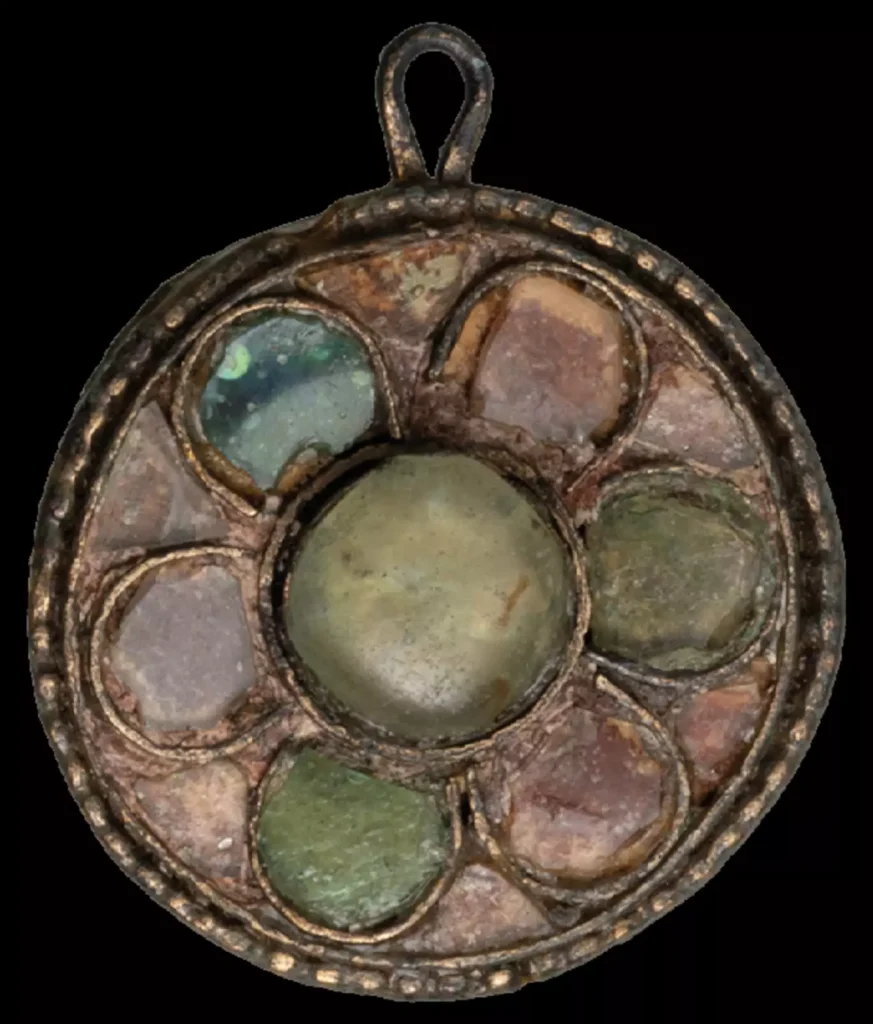
Cover Image Credit: An Avar-period cloak clasp from a female grave at Moedling, Austria. Archers were associated with a higher social status. Credit: Benedict Seidl