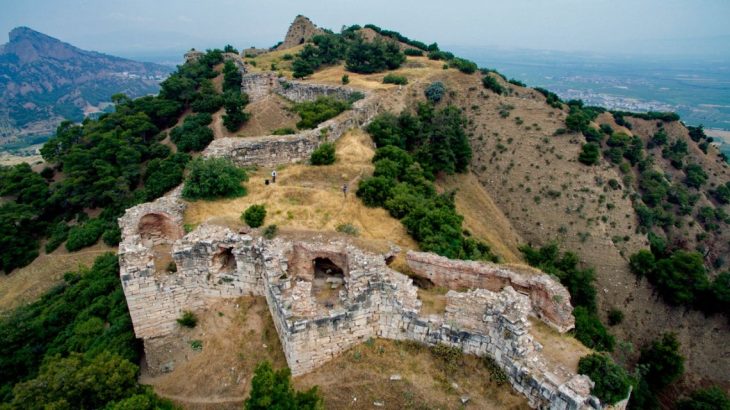
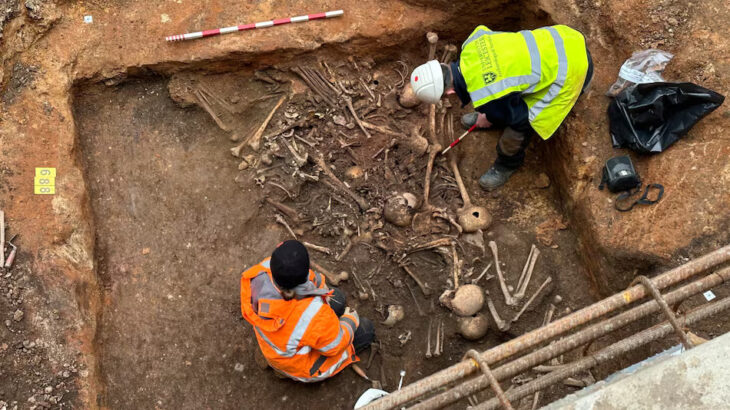
A major archaeological discovery has been made in Manduria, in Italy’s Taranto province, where construction work for new sewer pipelines has revealed a Hellenistic-era chamber tomb dating to the 4th century BCE. The find, supervised by the Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio (ABAP) for the provinces of Brindisi, Lecce, and Taranto, provides new evidence of the Messapian settlement’s sophisticated burial practices and confirms the archaeological importance of this area in southern Italy.
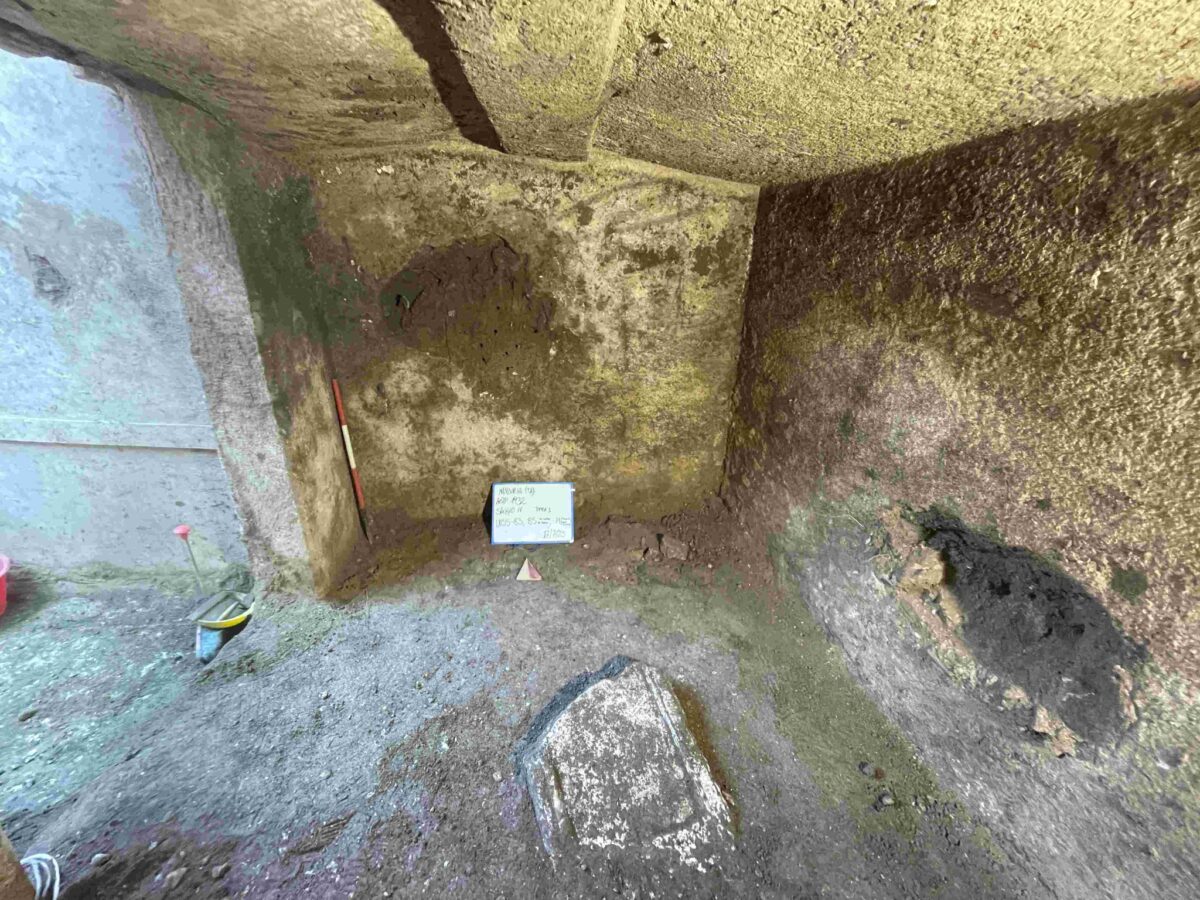
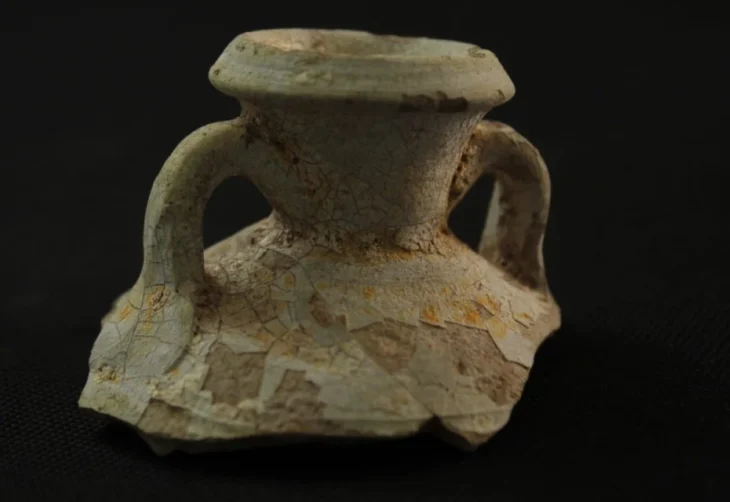
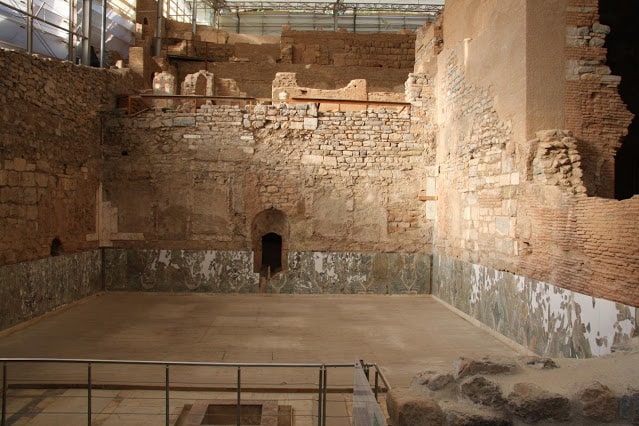
The tomb, located in Via Scarciglia, is part of a small funerary complex and consists of two separate rooms. The first space, interpreted as a dromos or antechamber, preserves traces of red-painted plaster with a raised white band running horizontally along the walls. Excavations here uncovered a rich assemblage of Hellenistic pottery in primary context, including vases, oil lamps, unguentaria, and plates—all firmly datable to the 4th century BCE.
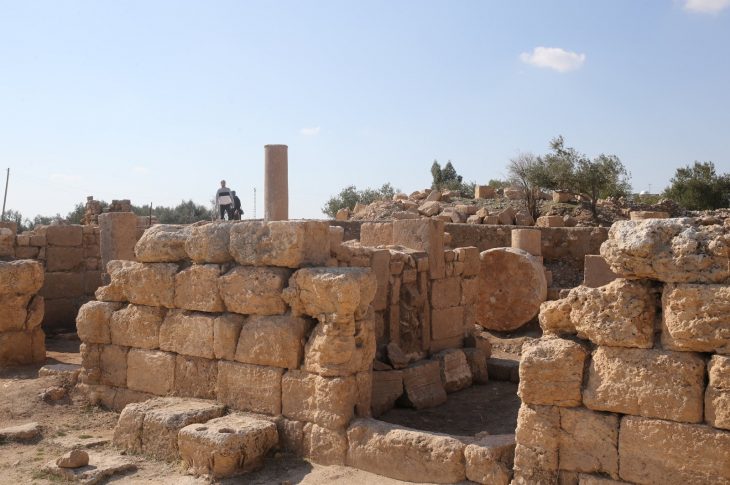
The entrance to the main burial chamber features a moulded stone lintel that reflects careful craftsmanship and suggests the tomb may have belonged to an individual of elevated social status. The entrance was once sealed with a red-plastered double-leaf stone door, fragments of which were recovered during excavation. Inside the chamber, archaeologists identified additional painted plaster remains and four rectangular recesses carved into the southern floor—likely supports for a wooden funerary bed.
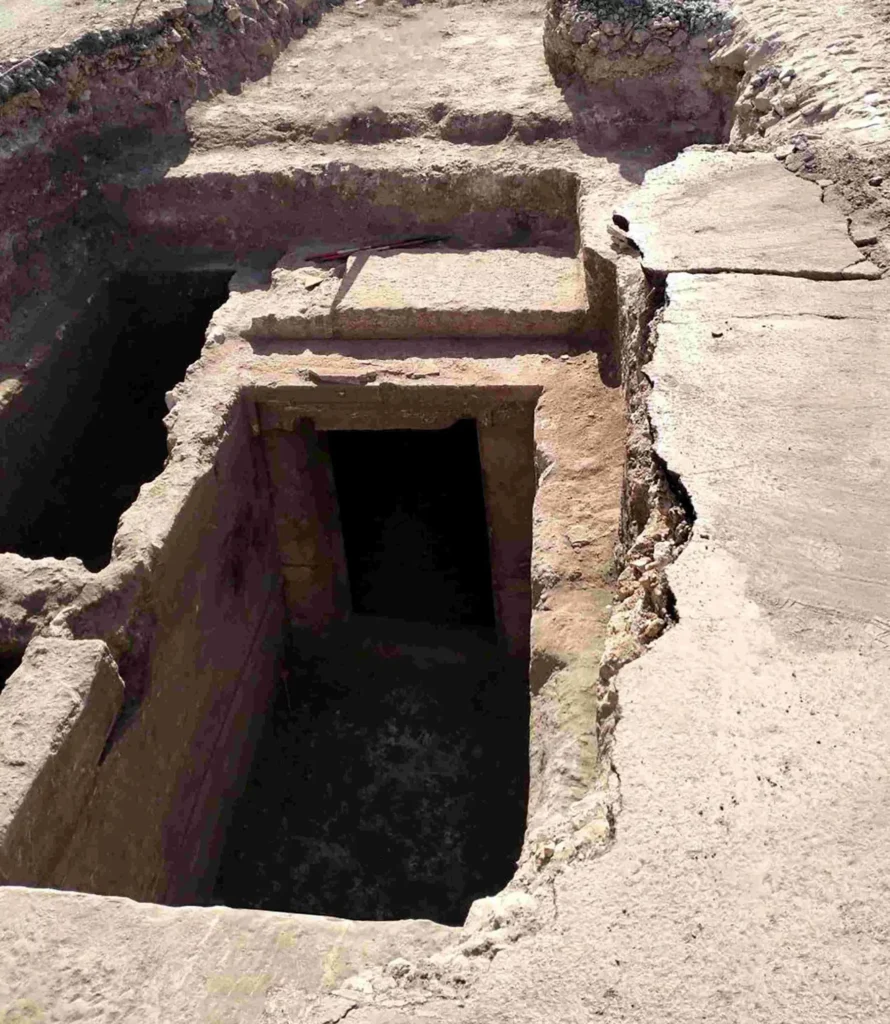

Evidence of Ancient Tomb Robbery
Archaeological investigation revealed that the tomb complex had been disturbed in antiquity. Several holes were cut through the chamber walls, likely in an attempt to reach nearby burials. Through one of these openings, archaeologists discovered a second tomb that had remained sealed externally but was found to be empty, suggesting it was looted in antiquity.
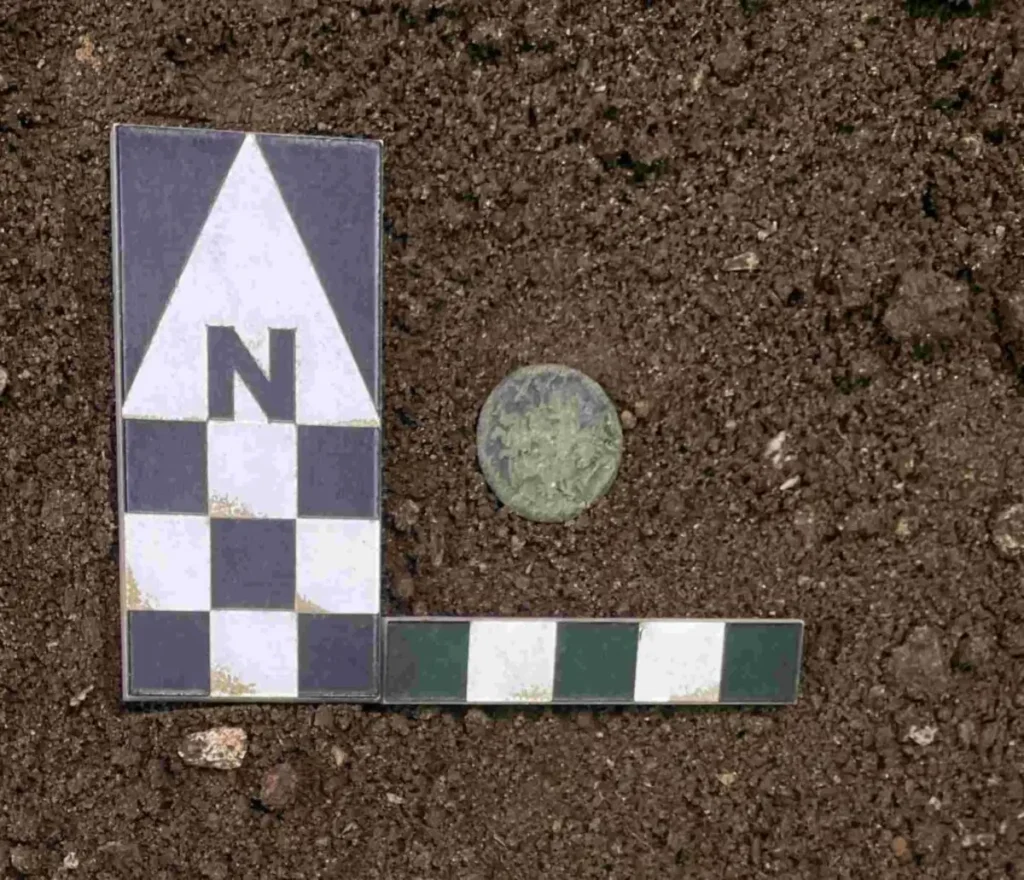
Despite the lack of grave goods, a Roman Republican denarius was recovered from the backfill of this second tomb. This small find indicates that the area continued to be used or visited well into the Roman period, offering a rare glimpse into the region’s changing funerary landscape.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Who Were the Messapians?
The Messapians were an ancient Italic people who inhabited the Salento Peninsula in southern Apulia from at least the 8th century BCE. Thought to have Illyrian origins, they developed a distinct culture marked by fortified hilltop settlements, elaborate burial customs, and unique inscriptions written in the Messapic language, a non-Indo-European tongue.
By the 4th century BCE, Messapian society had been deeply influenced by Magna Graecia, adopting Greek architectural styles, pottery, and funerary traditions while preserving indigenous cultural traits. The discovery of the Manduria tomb adds valuable evidence to this cultural synthesis, illustrating the wealth and cosmopolitan character of Messapian elites during the Hellenistic era.

Expanding Knowledge of Manduria’s Necropolis
This discovery follows earlier findings from late 2024, when the same sewer works exposed a cluster of 11 rock-cut pit graves along Via Scarciglia. Together, these finds confirm that this sector of Manduria functioned as a structured necropolis during the Hellenistic period.
Manduria, historically part of the Messapian culture of southern Apulia, is already known for its imposing city walls and archaeological richness. The newly discovered tomb adds depth to our understanding of Messapian burial customs, which blended local Italic traditions with influences from the wider Mediterranean world during the centuries following Magna Graecia’s expansion.
Collaboration Between Infrastructure and Heritage Protection
The excavation was conducted by Impact Soc. Coop., a specialized archaeological company, under the direct scientific supervision of the Ministry of Culture’s ABAP office. The works were carried out in compliance with Italy’s public procurement regulations, which mandate archaeological oversight during major infrastructure projects.
This successful coordination between the Soprintendenza and Acquedotto Pugliese (AQP), the water utility responsible for the sewer project, demonstrates how modern development can coexist with heritage conservation. AQP emphasized its commitment to cultural preservation, supporting ongoing excavation and documentation efforts to protect the archaeological record while completing essential infrastructure.
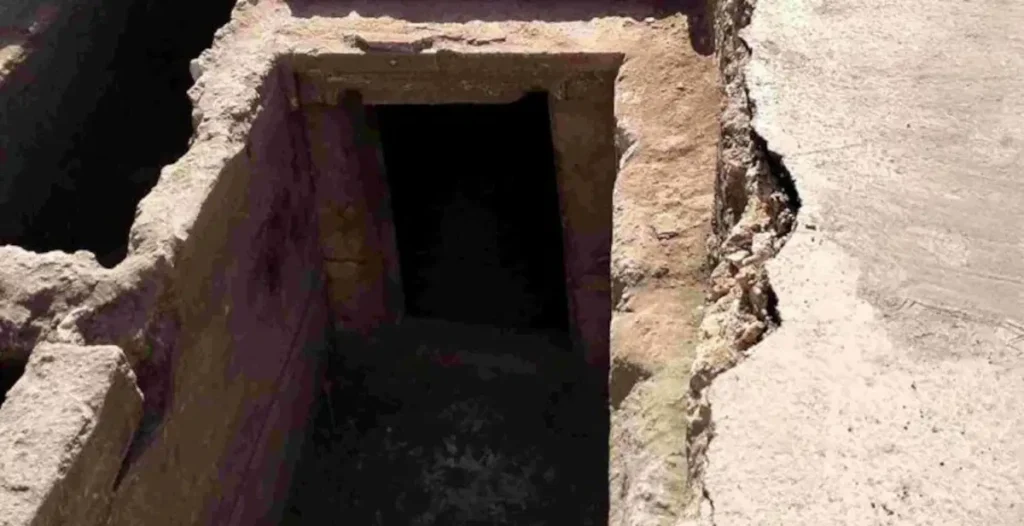

Digital Preservation: A 3D Model of the Tomb
As part of the post-excavation process, experts are conducting a photogrammetric survey of the chamber tomb to create a high-resolution 3D digital model. This cutting-edge documentation method will ensure that the tomb’s architecture, decoration, and context are preserved for future study and potentially made accessible to the public through virtual reconstructions.
Such initiatives highlight the growing role of digital archaeology in Italy, enabling researchers, students, and the public to explore heritage sites even when direct access is not possible.
Soprintendenza archeologia belle arti e paesaggio Brindisi e Lecce
Cover Image Credit: The Hellenistic-period chamber tomb discovered in Manduria. Credit: Ministry of Culture – Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio for the Provinces of Brindisi, Lecce, and Taranto