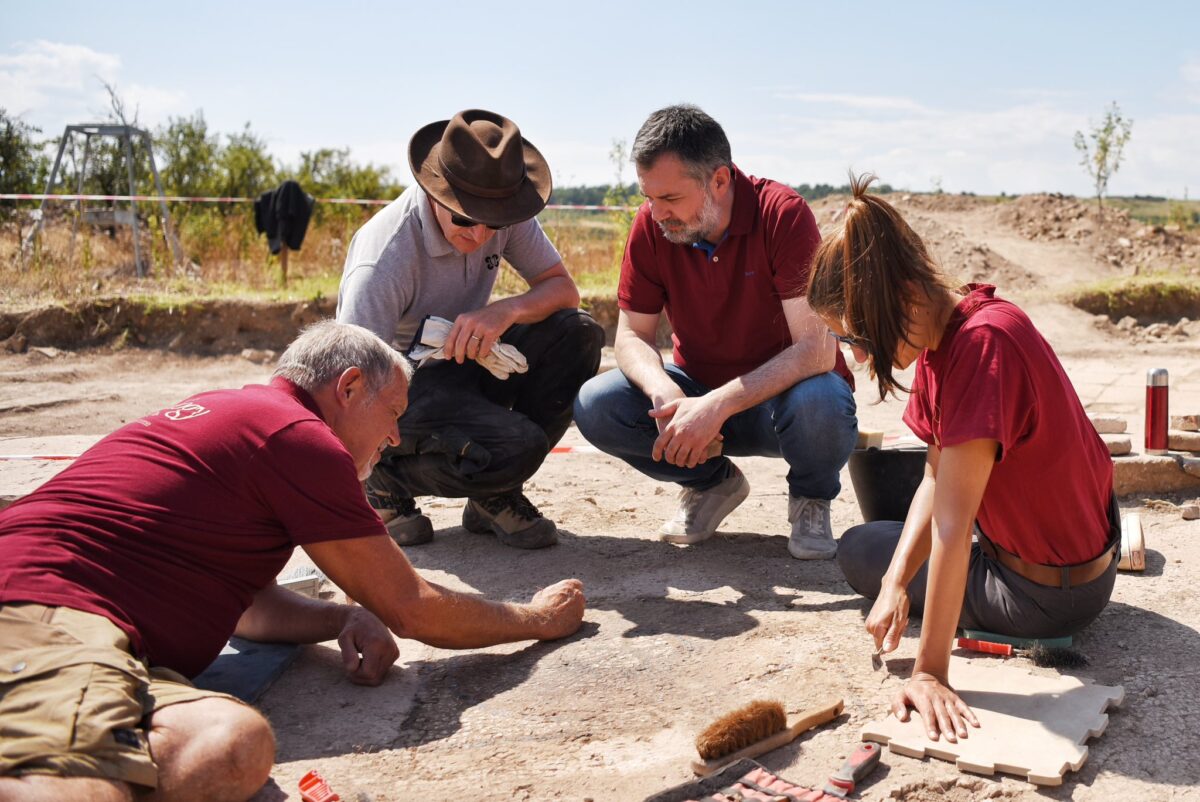
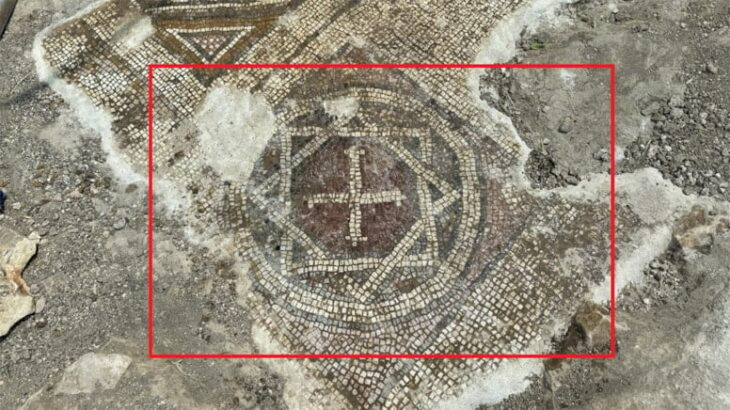
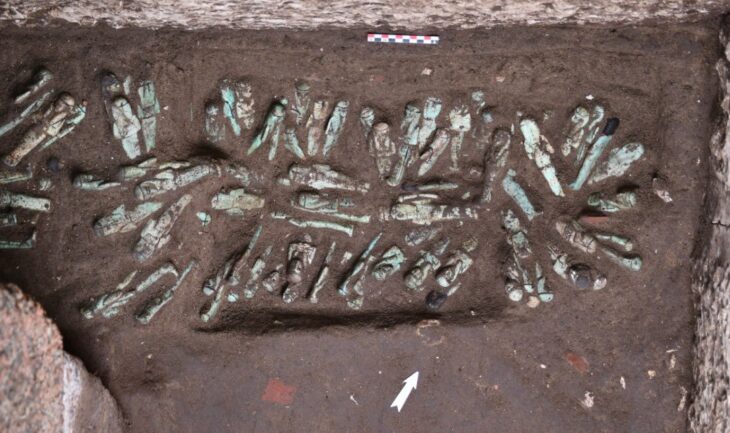
In a discovery that sheds new light on Kosovo’s ancient roots, the country’s Minister of Culture, Hajrulla Çeku, announced via his official Facebook page the unearthing of a rare Byzantine-era inscription at the Ulpiana archaeological site — a dedication to Emperor Justinian and Empress Theodora, and the second of its kind ever found.
The inscription, dedicated to Emperor Justinian and his wife, Empress Theodora, marks a significant milestone in the ongoing exploration of Kosovo’s rich cultural heritage.
Minister Çeku shared the news through a Facebook post, stating:
“The first inscription mentioned the founding of the city of Iustiniana Secunda as a Dardanian city. The second one shows the construction of the episcopal basilica. These are the only known dedications of Justinian, the emperor with origins from this region.”
The newly discovered inscription sheds light on the religious and architectural history of Ulpiana, a once-thriving Roman and Byzantine city located near present-day Gračanica. According to Çeku, this is the only known basilica construction inscription directly linked to Justinian in this area, further strengthening the city’s historical connection to the famed emperor.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Ulpiana: Jewel of Dardania
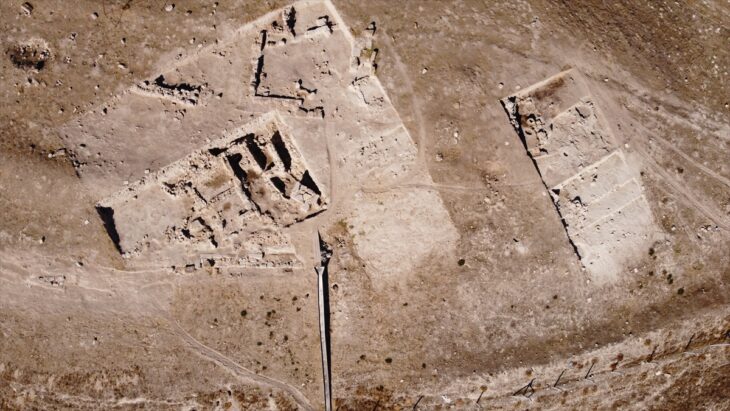
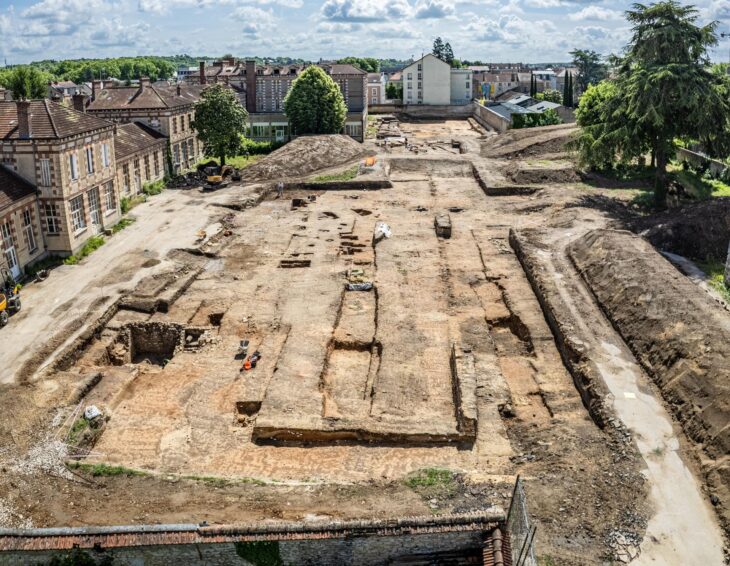
Ulpiana, often referred to as “Justiniana Secunda,” was one of the most important urban centers in the Roman province of Dardania. Flourishing from the 1st to the 6th century AD, the city played a strategic and administrative role in the region.
After a devastating earthquake in the early 6th century, Ulpiana was rebuilt under the orders of Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565), who sought to restore and fortify key settlements across the empire. The first inscription discovered previously confirmed Justinian’s efforts in refounding the city, naming it “Iustiniana Secunda” — a name that reflects its renewed status under imperial patronage.
This second inscription provides fresh evidence of the emperor’s commitment not only to civic reconstruction but also to religious and spiritual infrastructure, notably the construction of an episcopal basilica. Its dedication to both Justinian and Theodora also highlights the couple’s joint legacy and influence in the region’s religious life.
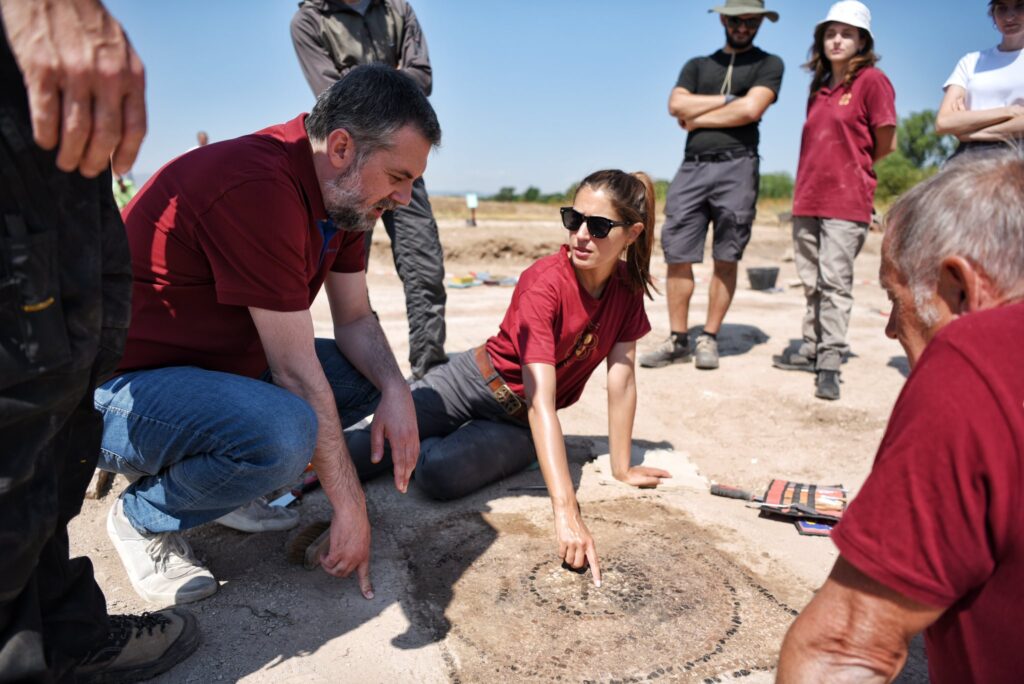

Significance of the Discovery
These inscriptions are not just archaeological curiosities; they are rare primary sources that connect Kosovo’s modern identity with its ancient Dardanian roots. Emperor Justinian, best known for codifying Roman law (Corpus Juris Civilis) and commissioning the Hagia Sophia, was himself of Illyrian—or possibly Dardanian—origin, making the findings in Ulpiana personally and politically symbolic.
Archaeologists working on-site emphasize that no other dedications of this kind have been discovered elsewhere, making these inscriptions uniquely significant. They not only confirm Justinian’s direct involvement in the city’s development but also place Ulpiana on the historical map as a key center of early Christian life in the Balkans.
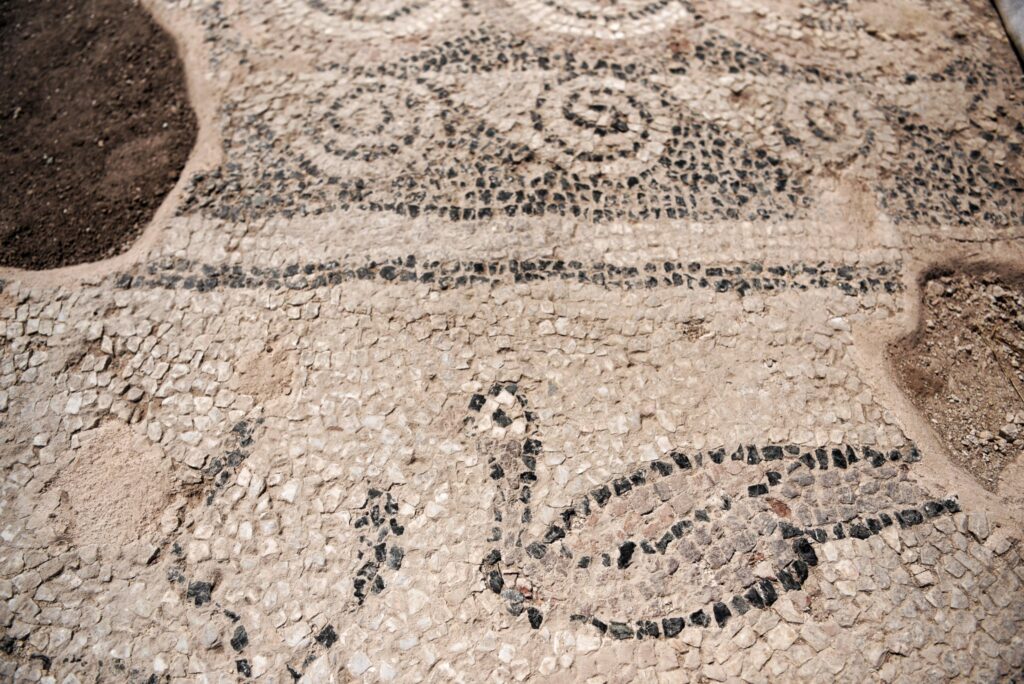

Preservation and Future Research
Minister Çeku highlighted the government’s serious commitment to preserving cultural heritage. “The preservation and protection of archaeological heritage has never been treated with this seriousness,” he noted.
Recent expropriations of public property have enabled uninterrupted excavation in Ulpiana and the nearby site of Dresnik. Conservation efforts are underway, supported by international collaborations and capacity-building initiatives. These include detailed site management plans, academic research, and future publications aimed at documenting Kosovo’s archaeological legacy.
“The work being done here is not just about unearthing stones,” Çeku wrote. “It is about uncovering our story — and making sure it endures.”
The discovery of the second inscription in Ulpiana is more than a historic footnote — it is a bridge between past and present, shedding light on Kosovo’s ancient heritage and reaffirming its cultural significance on the global stage.
As archaeological efforts intensify, Ulpiana is poised to become a cornerstone in the study of Late Antiquity in the Balkans, offering invaluable insight into the lives of emperors, cities, and civilizations long past.
Cover Image Credit: Hajrulla Çeku – Facebook