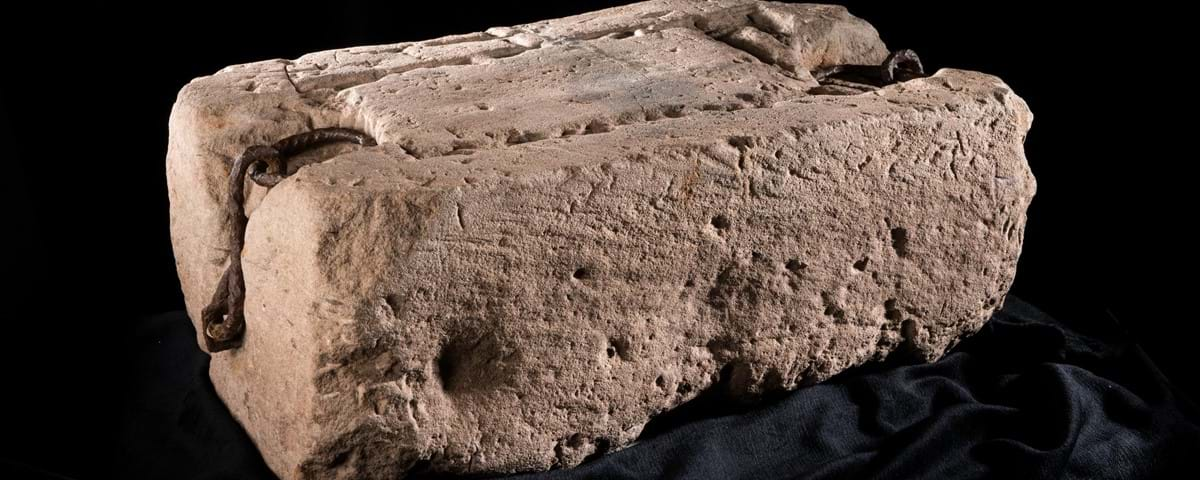
New research has revealed previously unrecorded markings that appear to be Roman numerals on the Stone of Destiny, considered one of Scotland’s most sacred national treasures.
The Stone of Destiny, which is also known as the Stone of Scone was first used to approve the crowning of kings in Scotland more than a thousand years ago. Honoring the traditions of the past, King Charles III has chosen to transport this sacred stone to Westminster Abbey in London for his coronation in May, where it will be placed inside a special coronation chair that was constructed to hold and support the heavy stone approximately 700 years ago.
The details were discovered when experts examined a 3D-printed replica of the stone created as part of the King’s enthronement preparations the next month.
Historic Environment Scotland used digital scanning technology to create a 3D model of the sacred object, and this procedure has revealed previously hidden or unobserved details on the stone’s rough and uneven surfaces.
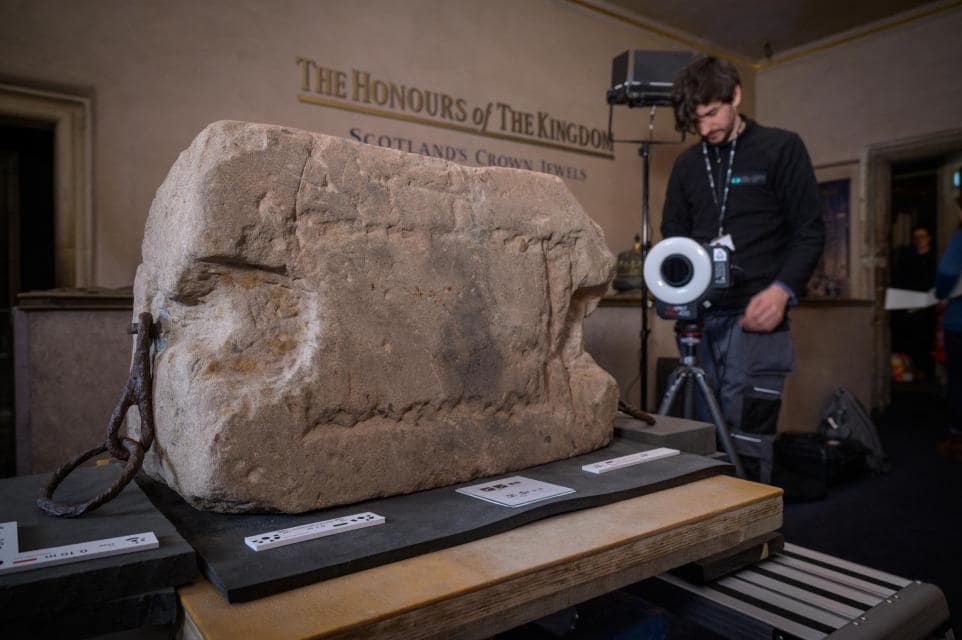

“It’s very exciting to discover new information about an object as unique and important to Scotland’s history as the Stone of Destiny,” said HES head researcher Ewan Hyslop in an interview with the Scotsman. “The high level of detail we’ve been able to capture through the digital imaging has enabled us to re-examine the tooling marks on the surface of the Stone, which has helped confirm that the Stone has been roughly worked by more than one stonemason with a number of different tools, as was previously thought.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The discovery of previously unrecorded markings is also significant, and while at this point we’re unable to say for certain what their purpose or meaning might be, they offer the exciting opportunity for further areas of study.”
New investigations have revealed previously unrecorded markings with the appearance of Roman numerals on the Stone of Scone’s surface.
The digital imaging has also improved visibility of the geological features of the Stone, such as cross-bedding, which is indicative of the geological conditions in which the sandstone was formed and which is characteristic of sandstone of the Scone Sandstone Formation.
The Stone of Destiny is usually displayed at Edinburgh Castle and has significant historical significance in Scotland. Its origins are unknown, but it is rumored to have biblical roots and to have played a role in the enthronement of Scottish kings for more than a century before its first recorded use in 1057, when Macbeth’s stepson Lulach was proclaimed king at Scone in Scotland.
Cover Photo: Historic Environment Scotland