In a paper published today, Oxford-led researchers reveal their discovery of a 3,000-year-old victim—attacked by a shark in the Seto Inland Sea of the Japanese archipelago.
According to the study published in the Journal of Archeological Science: Reports, this body is the oldest direct evidence of a shark attack on a person, and an international research team meticulously reconstructed what happened using a combination of archeological science and forensic procedures.
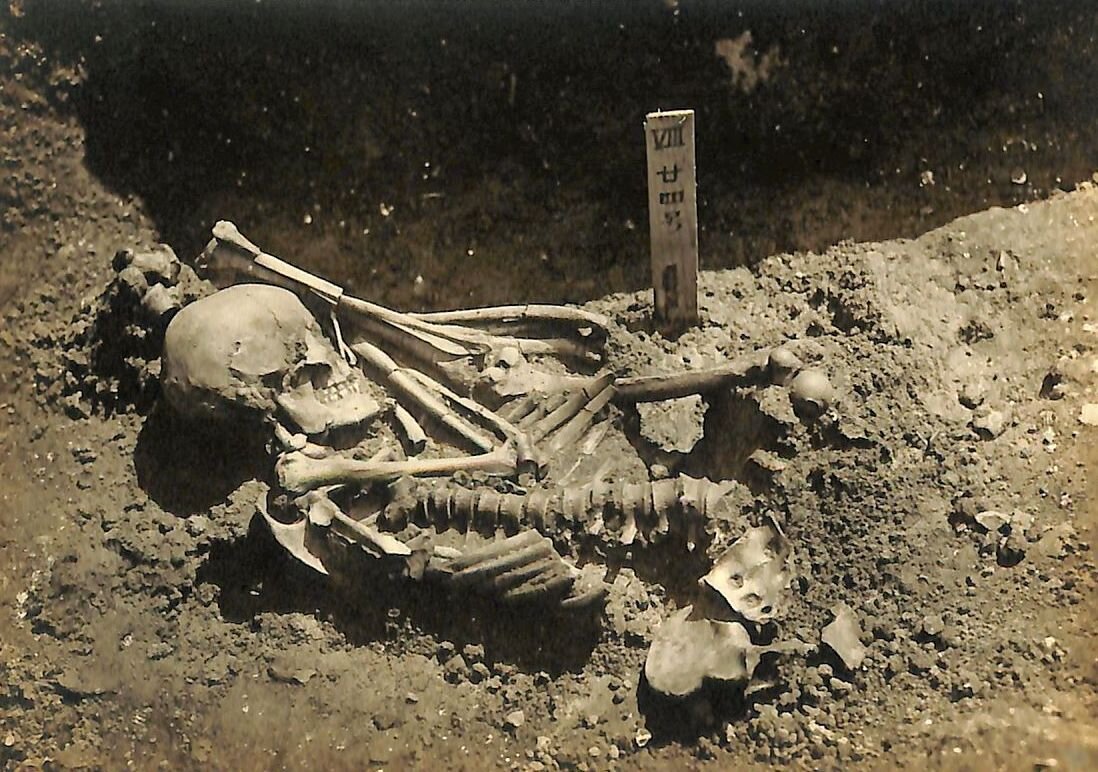
The victim was discovered by Oxford academics J. Alyssa White and Professor Rick Schulting while studying evidence for violent trauma on the skeletal remains of archaic hunter-gatherers at Kyoto University. They found No. 24, an adult male plagued with severe injuries, from the previously excavated Tsukumo site.
“We were initially flummoxed by what could have caused at least 790 deep, serrated injuries to this man,” say the Oxford pair. “There were so many injuries and yet he was buried in the community burial ground, the Tsukumo Shell-mound cemetery site.”
They continue, “The injuries were mainly confined to the arms, legs, and front of the chest and abdomen. Through a process of elimination, we ruled out human conflict and more commonly-reported animal predators or scavengers.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Because ancient examples of shark reports are exceedingly rare, they looked for evidence in forensic shark attack cases and collaborated with expert George Burgess, Director Emeritus of the Florida Program for Shark Research. The multinational team also put together a recreation of the incident.
The scientists determined that the person died between 1370 and 1010 BC, more than 3,000 years ago. The victim’s wound distribution clearly suggests that he was alive at the time of the attack; his left hand was shorn off, probably as a defensive wound.
Individual No. 24’s body had been recovered soon after the attack and buried with his people at the cemetery. Excavation records showed he was also missing his right leg and his left leg was placed on top of his body in an inverted position.
According to the pair, “Given the injuries, he was clearly the victim of a shark attack. The man may well have been fishing with companions at the time, since he was recovered quickly. And, based on the character and distribution of the tooth marks, the most likely species responsible was either a tiger or white shark.”
Co-author Dr. Mark Hudson, a researcher with the Max Planck Institute, says, “The Neolithic people of Jomon Japan exploited a range of marine resources… It’s not clear if Tsukumo 24 was deliberately targeting sharks or if the shark was attracted by blood or bait from other fish. Either way, this find not only provides a new perspective on ancient Japan, but is also a rare example of archeologists being able to reconstruct a dramatic episode in the life of a prehistoric community.”
Click to read the article. Cover Photo: Kyoto University