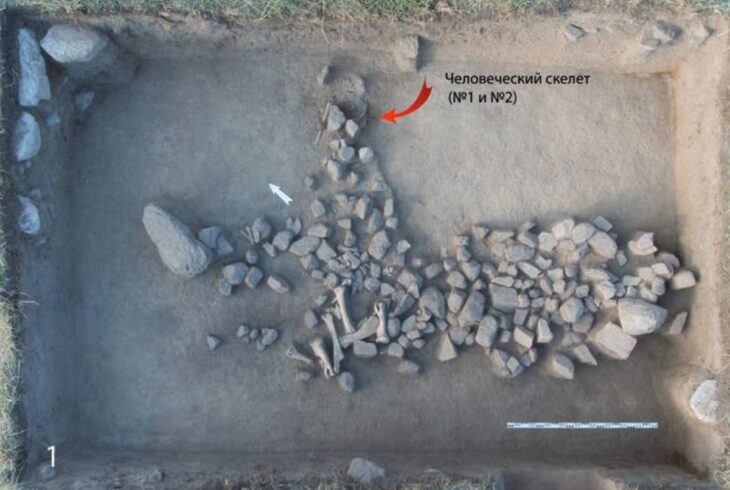
Archaeologists have uncovered a “richly decorated” remarkable Roman villa complex during excavations at Brookside Meadows in Grove, a village in Oxfordshire, England.
The complex evolved and included several buildings from the late first and second centuries, as well as four enormous columns or post bases, which were among the largest from the Roman era in Britain.
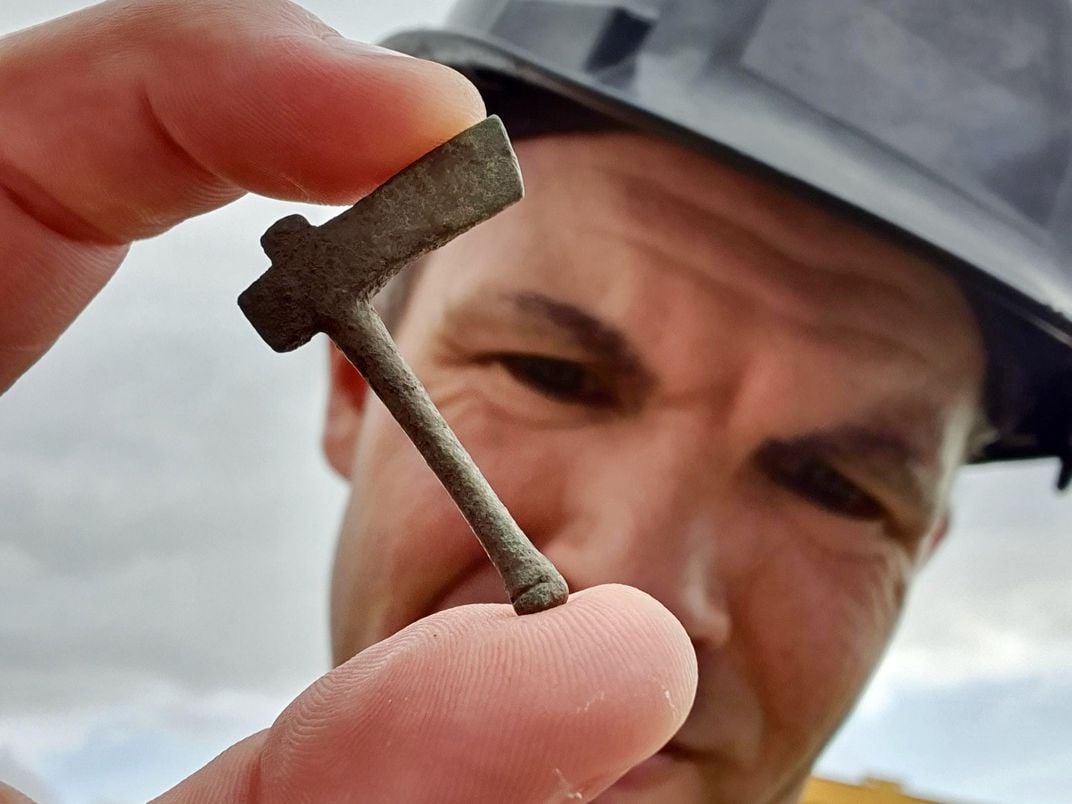
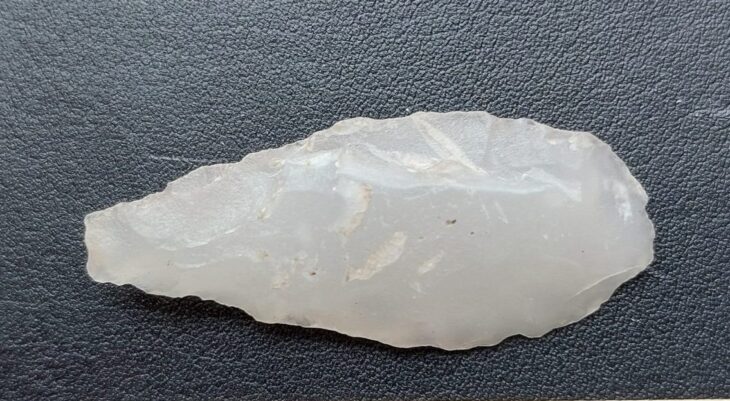
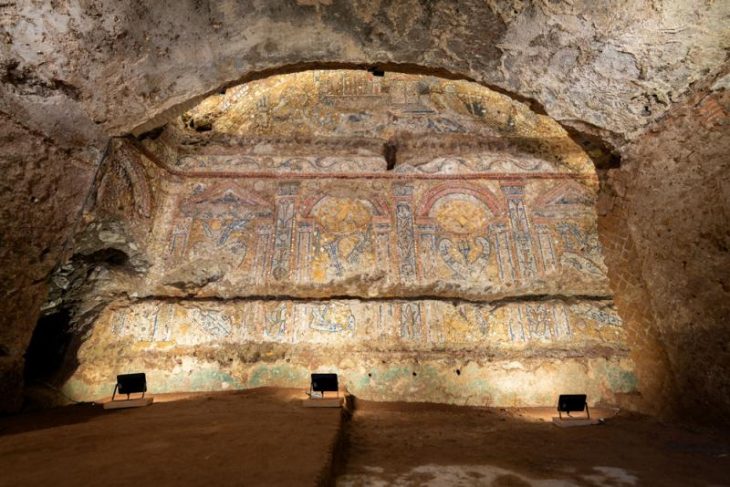
The villa complex, discovered in a landscape dating back to the Bronze Age, is adorned with intricately painted plaster and mosaics. Among the discoveries are fragments of a monumental hall-like structure known as an “aisled building,” with hints of internal colonnades. The site also contained strange artifacts, such as miniature axes and scrolls, which could have once been used in rituals.
“The sheer size of the buildings that still survive and the richness of goods recovered suggest this was a dominant feature in the locality if not the wider landscape,” says Louis Stafford, a senior project manager at Red River Archaeology Group (RRAG), in the statement.

The villa had a central hall that served as a link between several rooms. Site director Francesca Giarelli tells CNN that it was probably constructed before the adjacent aisle buildings, which were larger constructions that might have been added as the owners’ wealth increased. One of the complex’s buildings likely had multiple levels.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
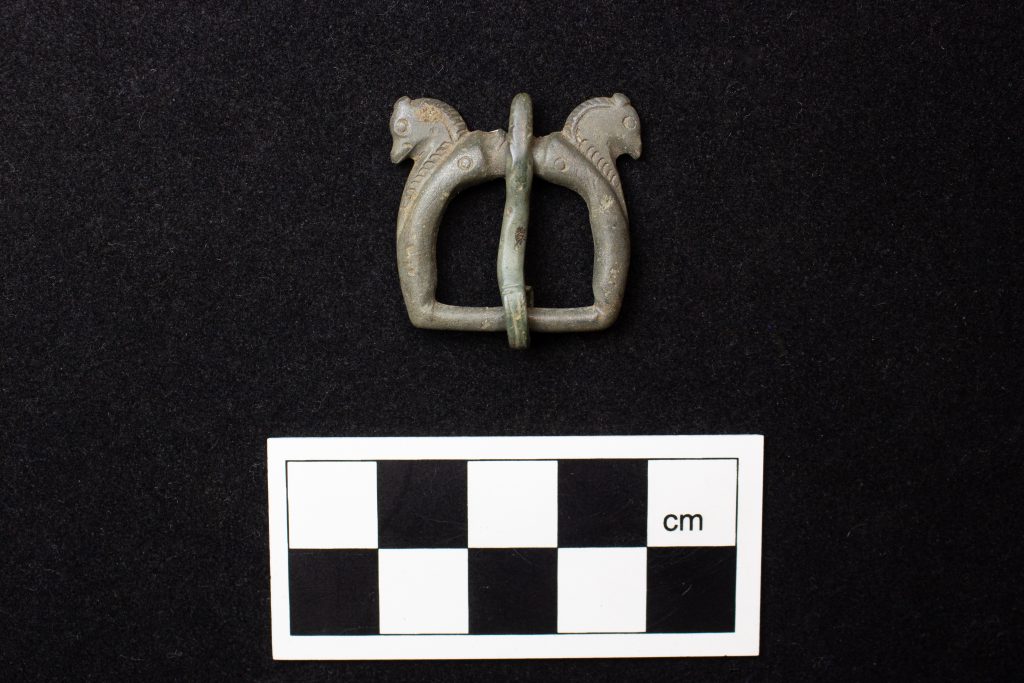
The artifacts found depict a vivid picture of Roman life, ranging from sophisticated painted plaster with floral motifs to mosaic tesserae, hypocaust box flue tiles, and a plethora of coins, rings, and brooches. A horse-headed belt buckle from 350-450 C.E. provides insight into late Roman and early Anglo-Saxon interactions, highlighting the site’s historical significance. The artifacts suggest that Romans occupied the area through the fourth or fifth century C.E.

Villas were more than just places to live during the Roman Empire’s rule in Britain, which lasted from 43 to roughly 411 C.E., Giarelli tells CNN. Villa owners were frequently in charge of keeping up with crops, repairing roads, and stockpiling food.
The villa also included repurposed areas, such as an oven made of melted Roman building material that was used to dry cereals and hops. This is a reflection of a phenomenon seen in other opulent Romano-British villa complexes, where function was prioritized over ostentatious displays of wealth as agricultural processing and manufacturing became more important.

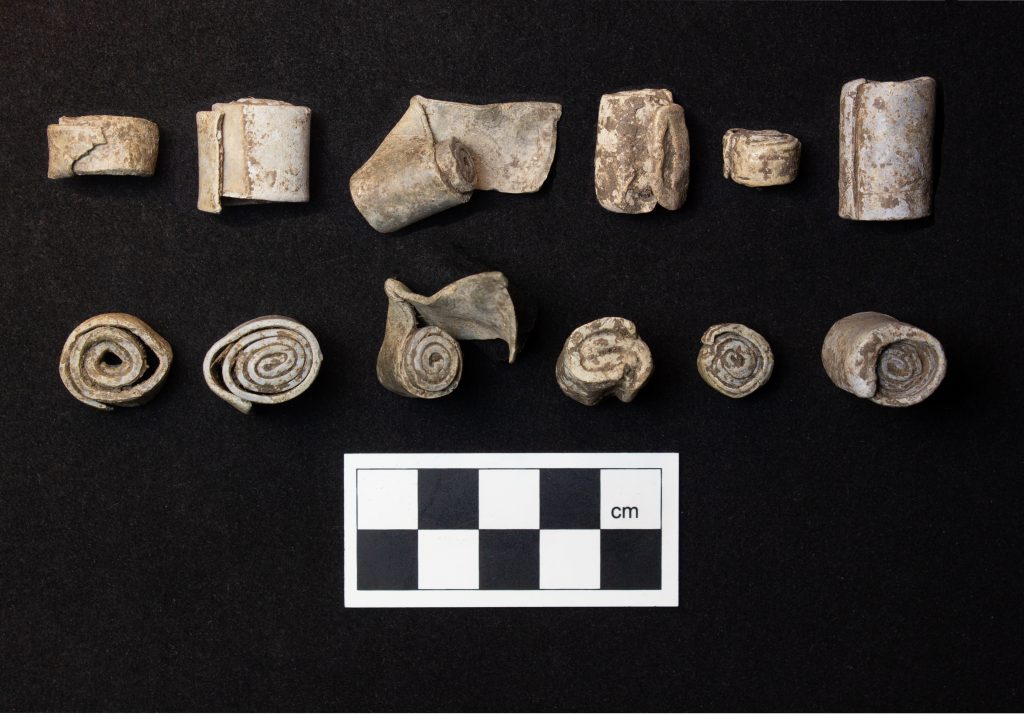
One of the site’s most fascinating discoveries is a group of lead scrolls that are tightly wound and resemble Roman “curse tablets.” Curse tablets, written by someone begging the gods to hex an enemy, were frequently rolled, folded, or punctured with a nail. These scrolls, though blank at the moment, hint at a possible ritual or pilgrimage site within the estate, as do the small votive axes.
Campbell Gregg, the development company’s managing director, hopes the ongoing research will help locals better understand the region’s history.
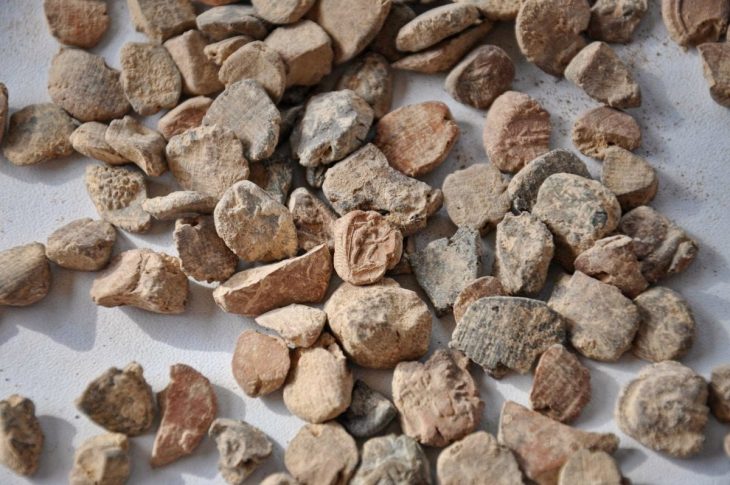
Cover Photo: Miniature axes that may have been used in Roman rituals Red River Archaeology Group