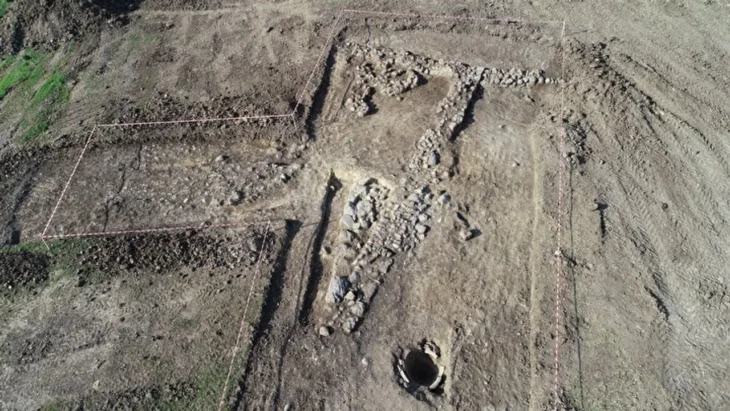
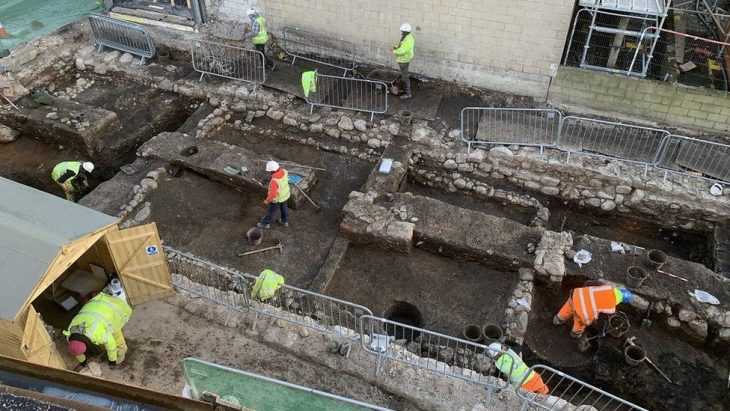
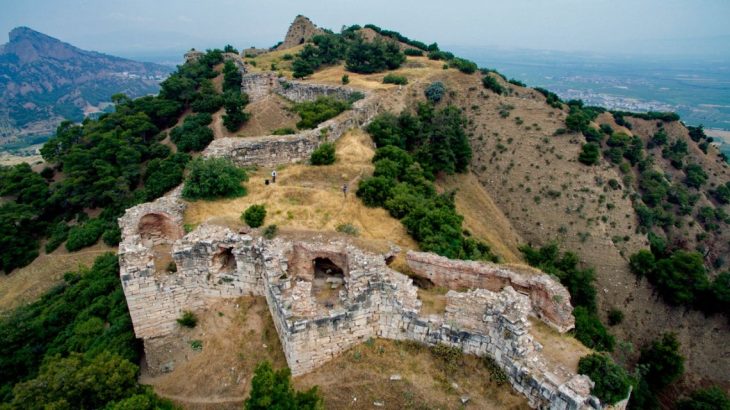
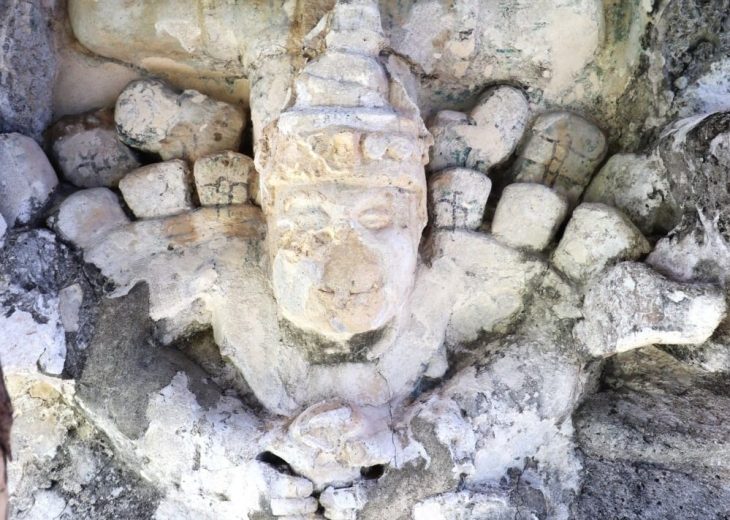
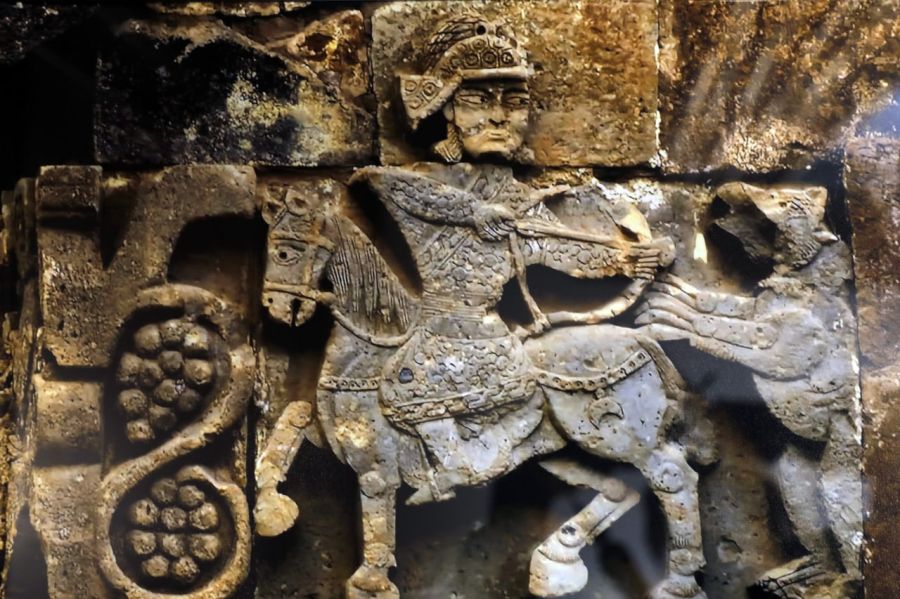
The archeology study team, consisting of Turkish and Mongolian scientists, found important findings in the study carried out to find the summer palace and city ruins thought to have been built by the Mongol Ilkhanid State ruler Hulagu Khan in the Çaldıran district of Van in the 1260s.
Hulagu Khan was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Western Asia. He is also the grandson of Genghis Khan, who is famous for not losing any war he entered. Hulagu Khan is the founder of the Ilkhanid state.
Under the chairmanship of İzmir Katip Çelebi University (İKÇÜ) Turkish-Islamic Archeology Department Head Professor Ersel Çağlıtütuncigil, Mongolian State University Faculty Member of History Department and Director of İKÇÜ-MUIS Turcology Research Institute Dr. Ankbayar Danuu and a team of Turkish and Mongolian historians, archaeologists, Sinologists, and Turcologists, they found new findings about the ruins of the summer palace of Hulagu Khan, which is mentioned in ancient Persian and Armenian historical sources, between 1261 and 1265.
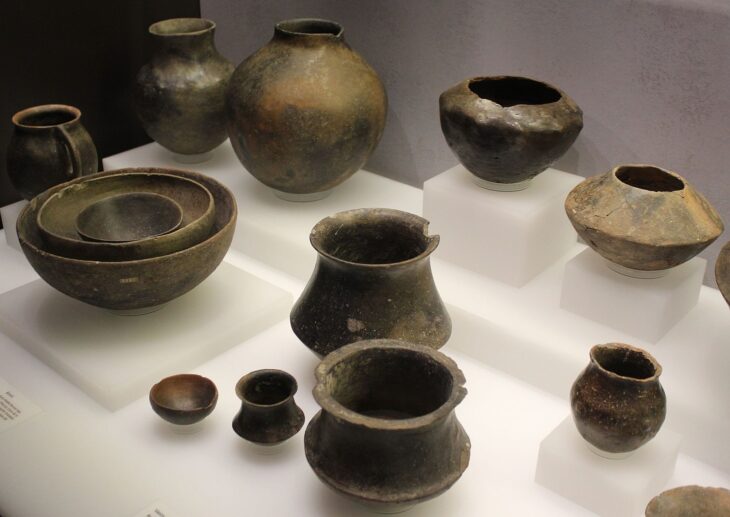
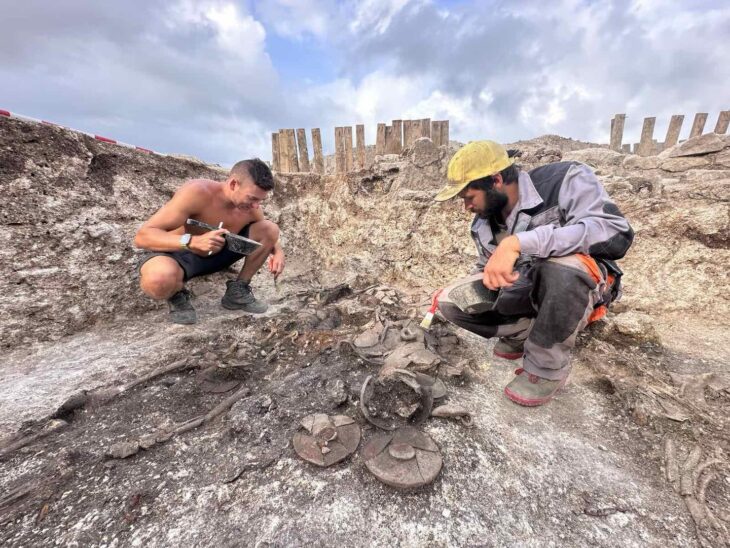
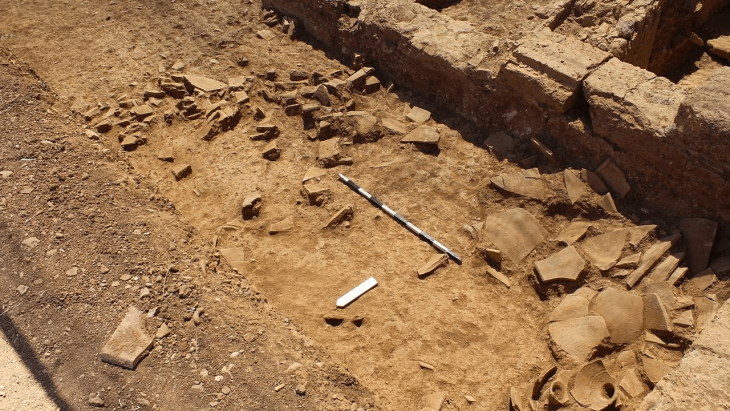
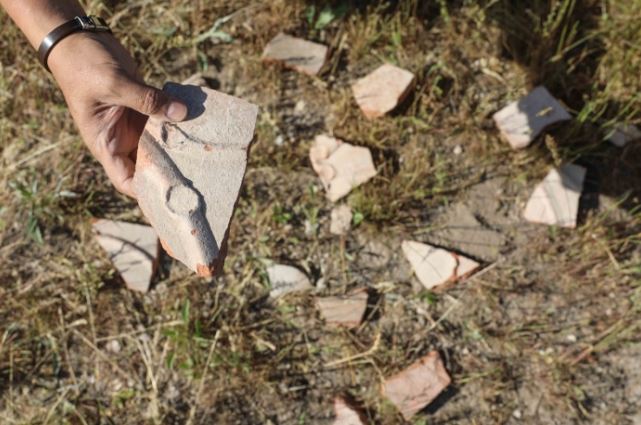
The team first examined the artifacts found in the Van Museum, which were found to be used in the palace, which is thought to have been built by the Ilkhanid ruler Hulagu Khan. Concentrating their work in the region where the artifacts are thought to be found, the team uncovered the remains of a caravanserai and a ceramic kiln, which they think may belong to the Ilkhanate period.

Professor Ersel Çağlıtütuncigil, Head of the Department of Turkish-Islamic Archeology at Izmir Katip Çelebi University, said, “ With the knowledge and experience of the team from Mongolia, we noticed that some of the artifacts were roof tiles belonging to the Mongolian Ilkhanate State during the examinations we made in the museum. We conducted research based on where these tiles came from in the museum. In fact, we are trying to reach a whole by combining some clues like the detective. We believe that we have reached an important conclusion with the data we have obtained,” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Stating that they saw many examples of roof tiles scattered over the area and found a caravanserai, Ersel Çağlıtütuncigil said, “There are some building remains here, probably showing that there was a city. For now, research shows that the settlement spread to the east of the caravanserai. As a matter of fact, we encountered intense ceramic finds in that region. It is possible to see similar roof tiles, which are among the ceramics we found, in the inventory of the Van Museum. More importantly, we see exact examples of these roof tiles in Mongolia (Karakorum).”

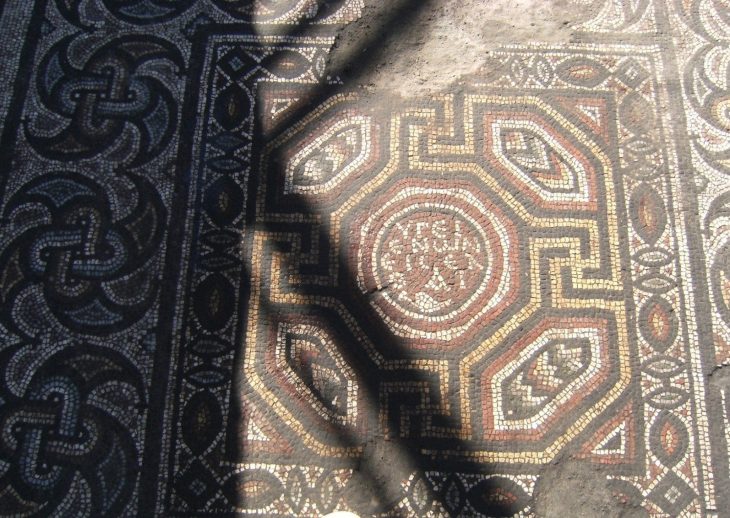
It is mentioned that Hulagu Khan had a church built for his wife in the region
“As far as we know, this type of roof tiles does not exist in Anatolia. Therefore, these data show us that there is a direct Ilkhanid structure in Anatolia. Also, we think that there should be a Buddhist temple here. An artifact in the museum inventory also supports this view. The Mongols were also building a Buddhist temple along with the palace. Sources say that Hülagü Khan had a church built for his wife, Dokuz Hatun.”
“Probably that church is around here too. He must also have built a mosque for Muslims living in the region. Beyond the caravanserai, there is a kiln where the ceramics were fired and many building remains that we have not yet made sense of.”
Çağlıtütuncigil stated that they evaluated the summer palace built by Hülagü Khan to be in the same region.

Director of Turcology Research Institute Dr. Danuu Ankbayar said, “To date, the ruins of palaces of three Mongol Khans, including the palace of Kublai Khan in Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region, the summer palace of Ambaghai Khan in Iran and Sarai city of the Golden Horde, were found. This time, we discovered the fourth palace. It is believed that it was a palace city with an area of at least 1200×1200 meters. Archeological research excavations are planned to be carried out in cooperation with Turkish scientists,” adding that it is necessary to prepare for the excavations within the legal framework, and he asked the Chairman to support this at the decision-making level.
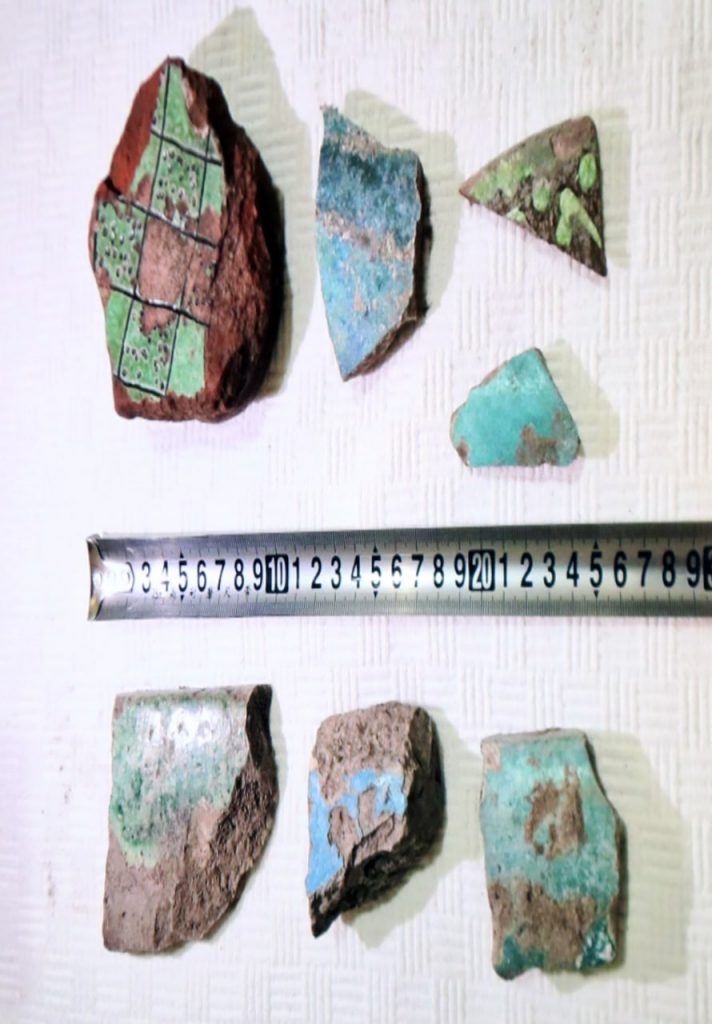
The researchers said that the model of the city of Kharkhorum was probably used in terms of building design and architectural arrangement. The construction of a Buddhist temple and the involvement of Buddhist sculptors and artisans in the decoration of the palace increase the possibility that the palace is Mongolian in nature. The preliminary observation of the research team revealed the remains of blue and green pottery of the Ilkhanate period, as well as the remains of wall-patterned pottery.