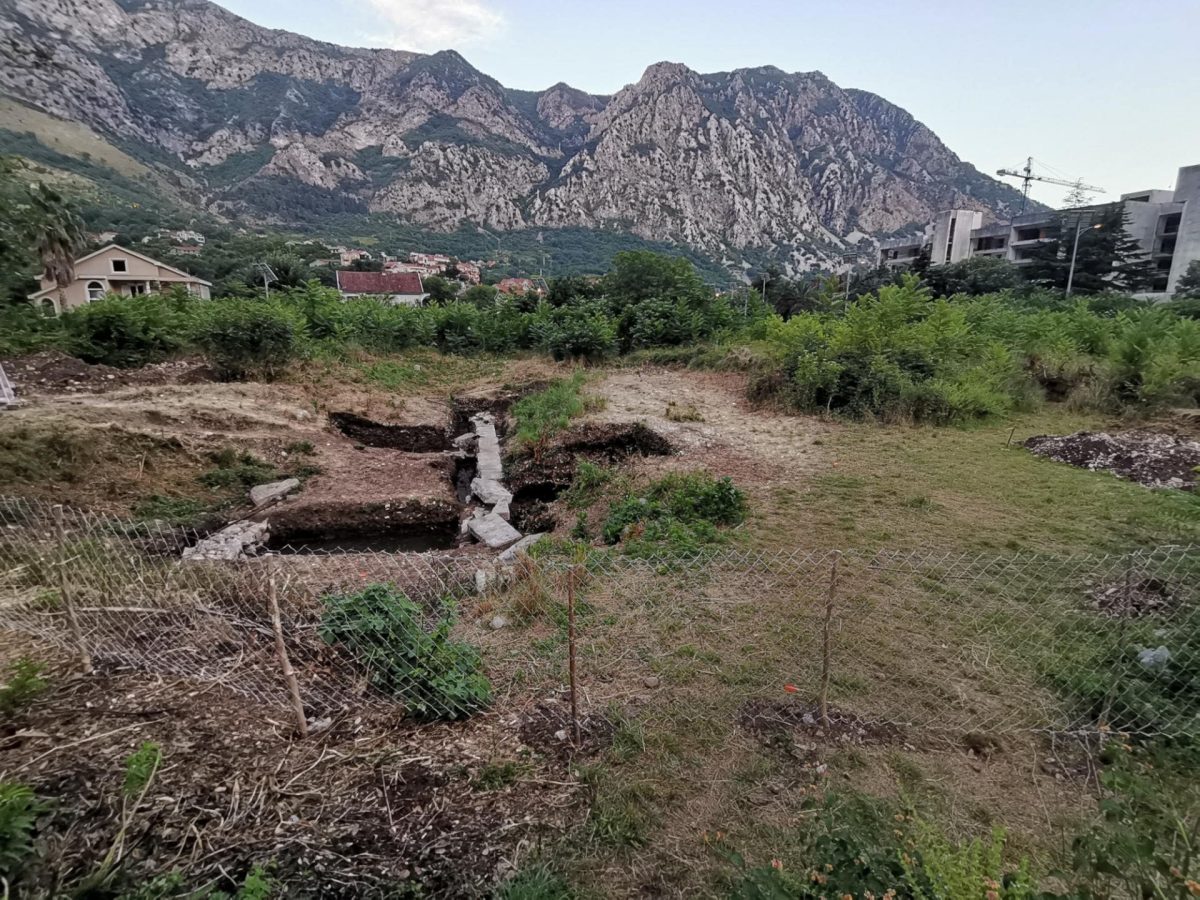
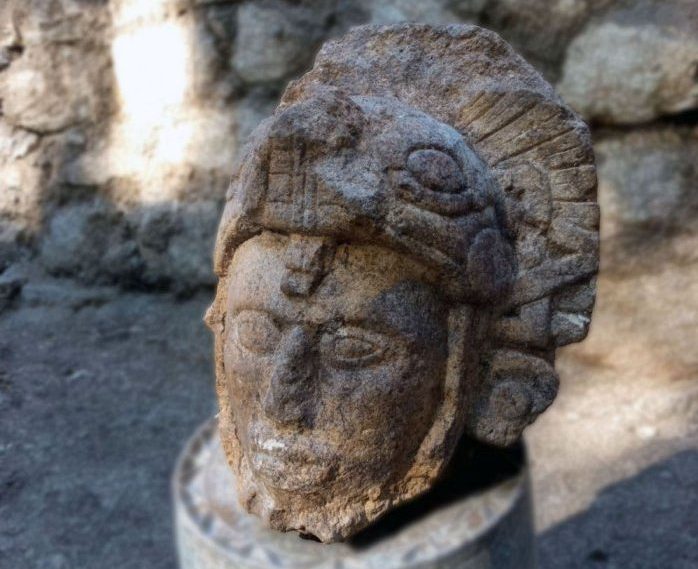
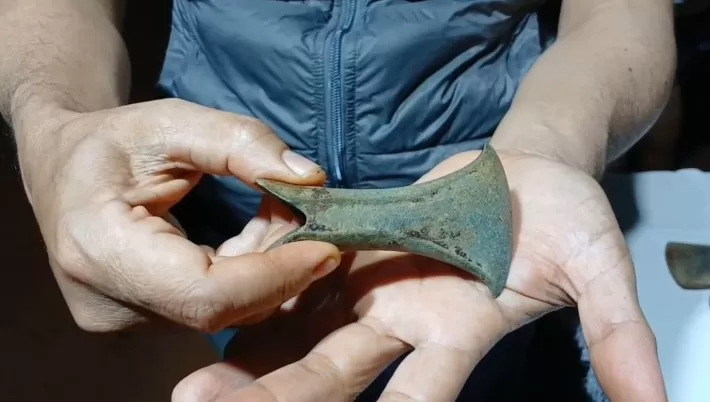
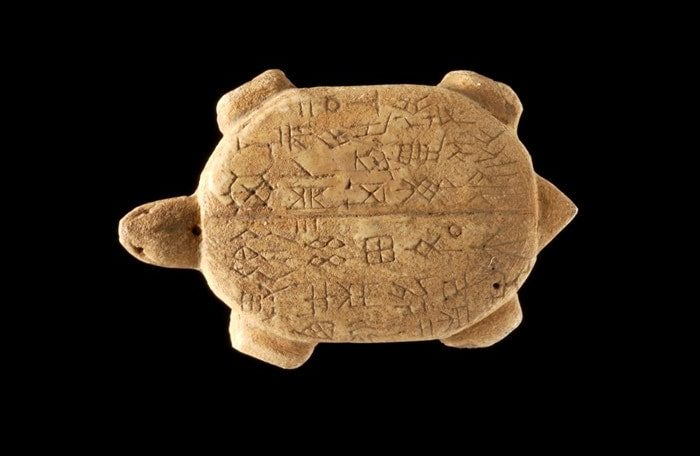
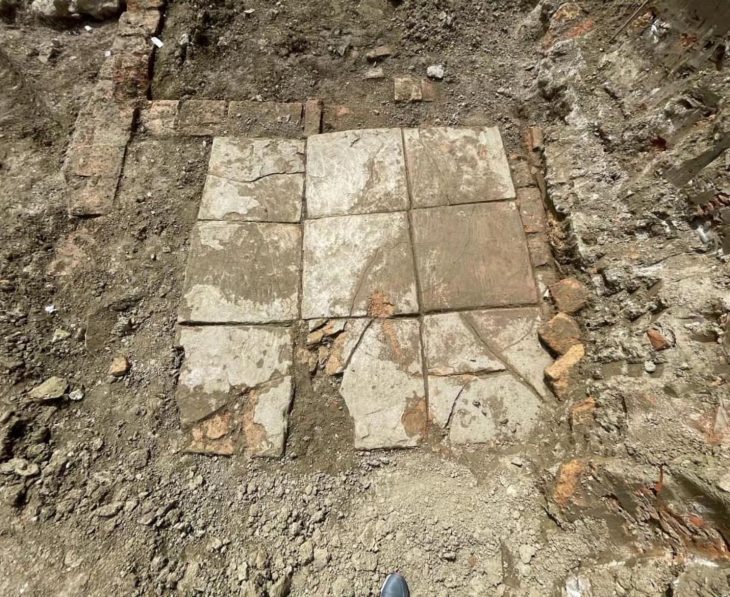
In ancient Rhizon (Risan) in Montenegro, remains of a Roman stylobate (a shared base for multiple columns) were uncovered.
In Risan, the twenty-first campaign of systematic archaeological research, as part of the international scientific research project “Risinium – the capital of Queen Teuta”, was completed these days at the site of Forum, i.e. Carine IX. The research was carried out in the organization of the Center for Conservation and Archeology of Montenegro and the University of Warsaw.
Risan is a very ancient city, which was first mentioned in the IV century BC as an Illyrian settlement under the name of Rhizon. It was the main city in the entire Bay of Kotor, which even bore its name – “Sinus Rhizonicus”. The city was conquered by the Romans, who called it Rhizinium. It flourished during the Roman rule (I-II centuries AD).
As far back as the 4th century B.C., an ancient manuscript called Pseudo-Scylax mentions Rhizon (modern-day Risan) when describing a merchant route around the Mediterranean Sea.
This year’s campaign was carried out at the Forum site, with a total area of approximately 75 m², in an old trench that was excavated in the 1960s and 1980s of the XX century.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
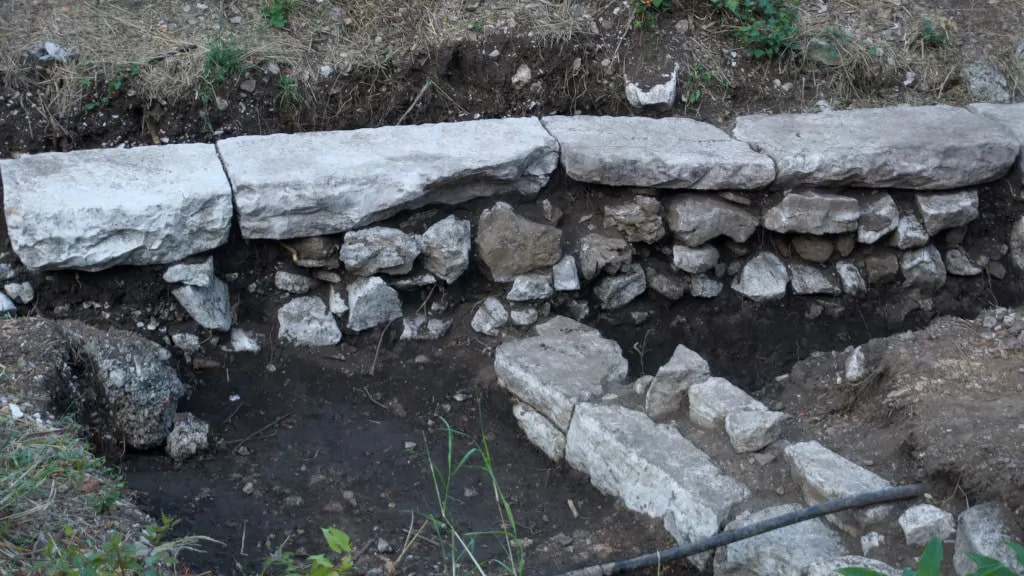

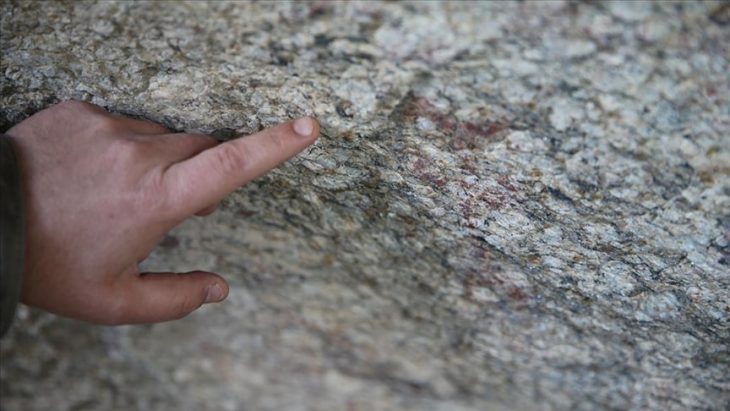
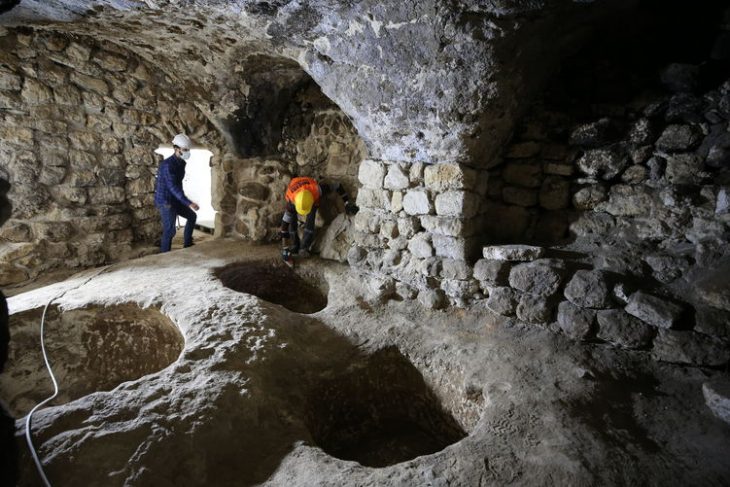
The mentioned trench was expanded, resulting in a total of six trenches being opened. Within them, five walls were discovered, ranging from one Hellenistic wall to three Roman walls, including a recent one. The most significant finding consists of remains of a stylobate from the Roman period, which supported the colonnade of a representative structure.
So far, archaeologists have discovered remains of the stylobate measuring 24 meters in length and 5 meters in width, along with the shafts of mighty columns with a diameter exceeding 50 cm.
“The front part of the stylobate, on which the portico is located, was carefully machined, which proves that it opened onto a large space, probably a forum” – noted Prof. Piotr Dyczek.
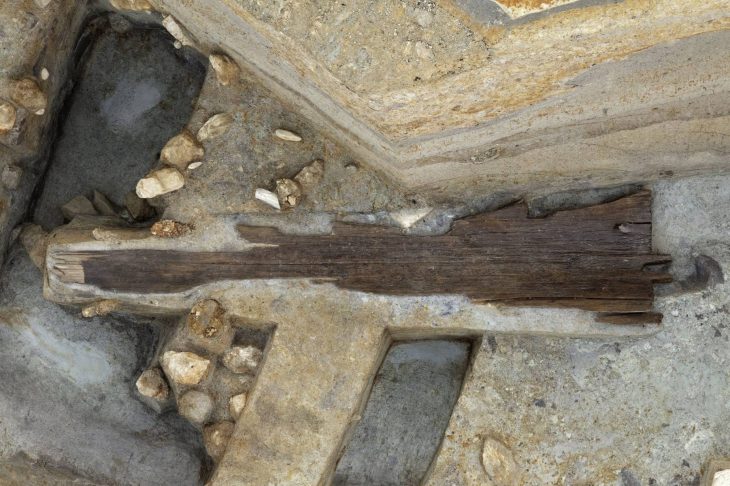
Below the level of the portico, walls from the Hellenistic period (2nd century BCE) have been discovered. The dating of this structure was made possible by the analysis of the adjacent, thick surface made of fragments of amphorae and their corks. This arrangement of walls demonstrates that there were representative buildings in this location.
In the subsequent excavation seasons, scientists will analyze whether these are elements of a Hellenistic agora construction.
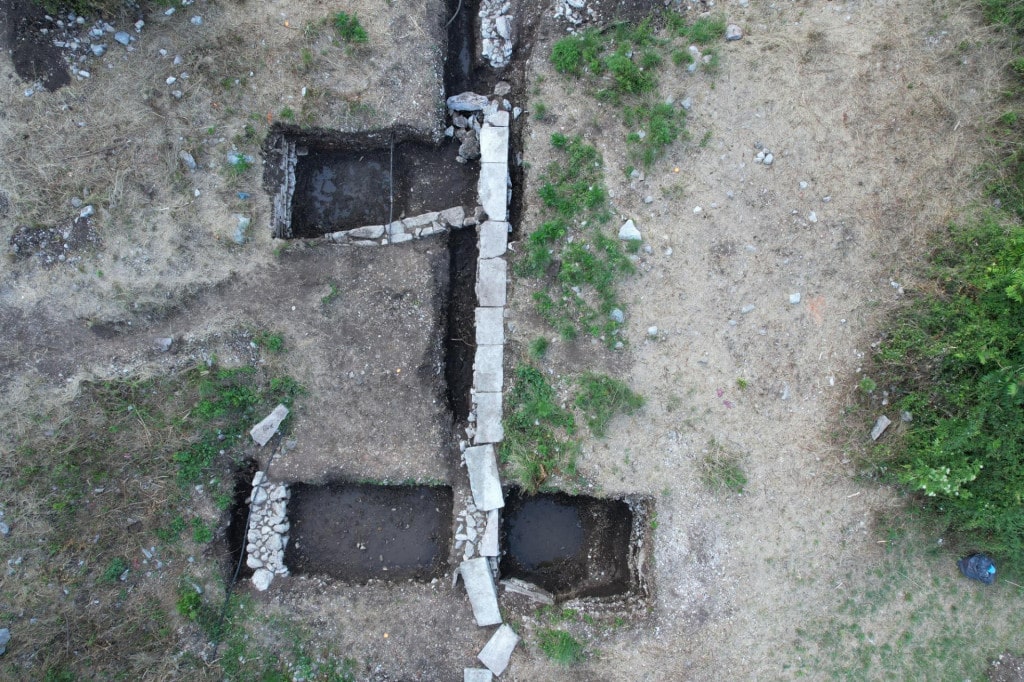

Dr. Dejan Gazivoda stated that during the excavations, numerous fragments of lidded amphorae, fragments of luxury vessel parts, and a large number of coins, among other ceramic pieces, were found.
Gazivoda emphasized that in the past twenty years, both immovable and movable findings have indicated the great significance of ancient Rhizinium (Risan). These findings include two Illyrian palaces, various parts of the city, a Roman-period hypocaust, a treasury containing over 4,500 coins from the time of King Balajos, and other extraordinary discoveries.
“Carine and Gradina sites provide evidence that Rhizinium was the largest urban Illyrian settlement and, at one point, even the capital and the only polis in Montenegro,” stated Dr. Dejan Gazivoda.
The research is funded by the University of Warsaw.