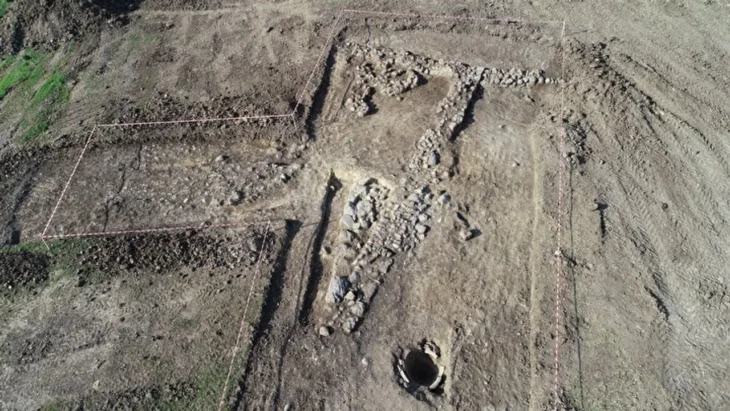
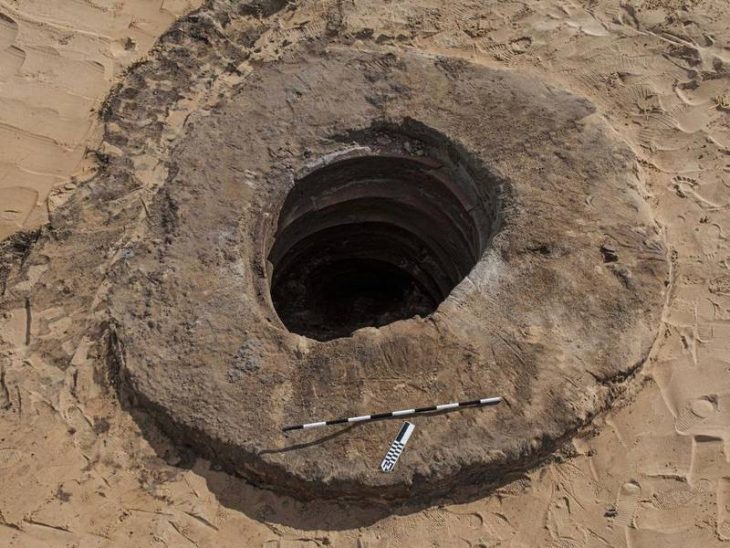
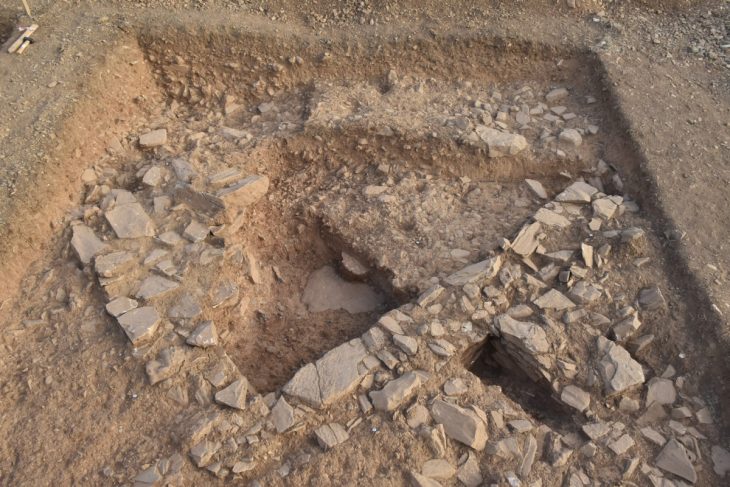
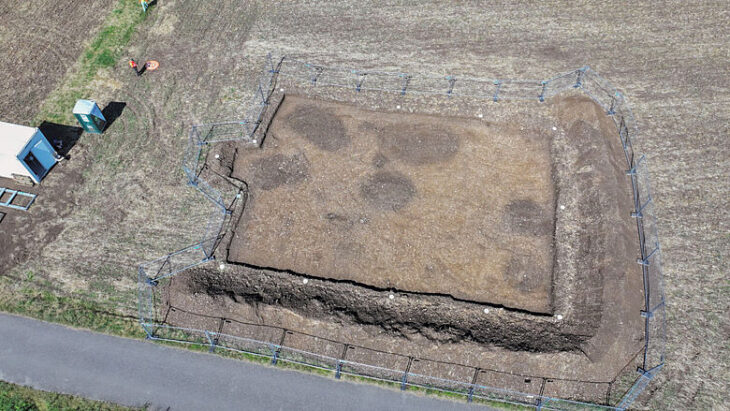
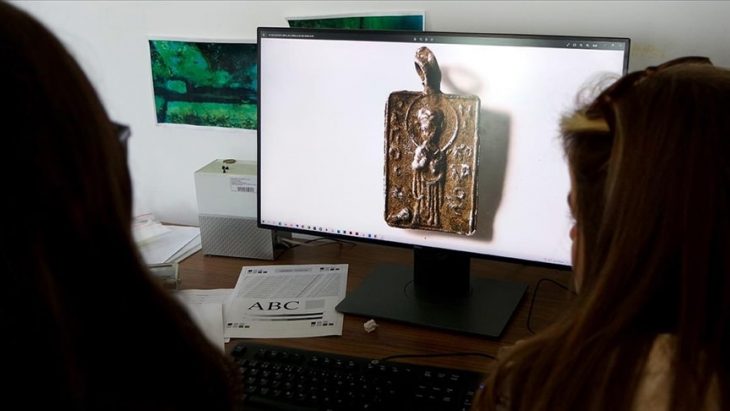
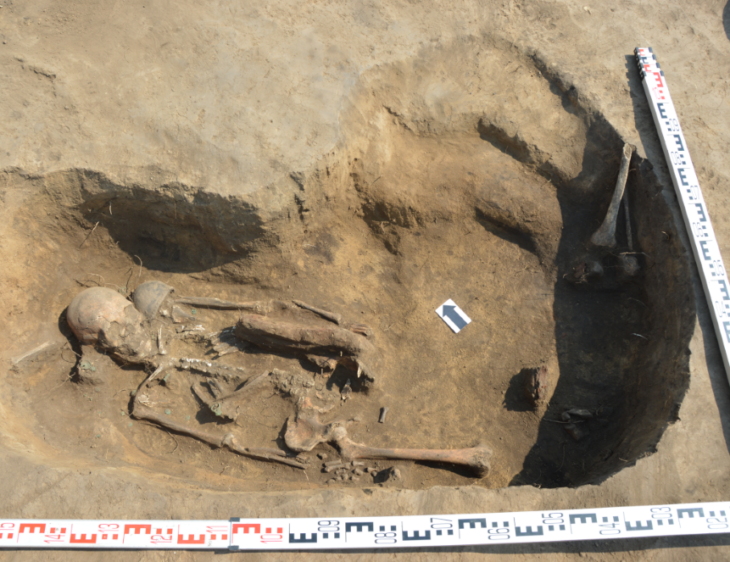
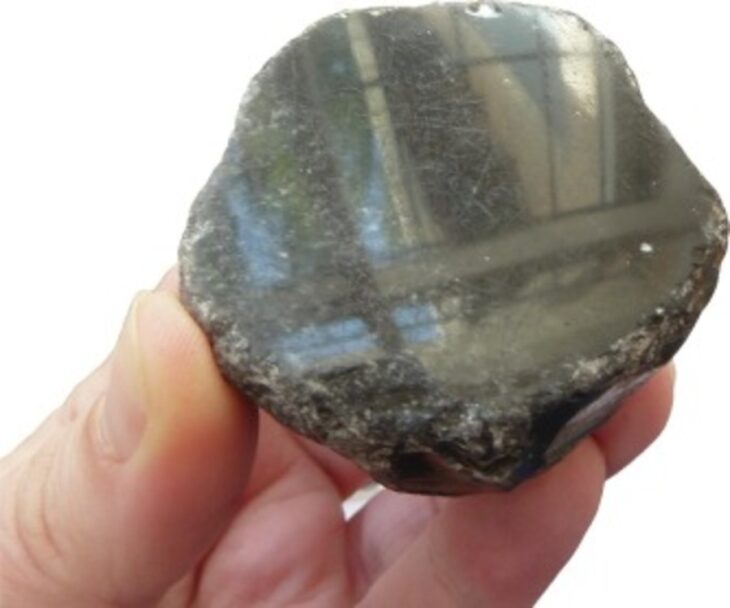
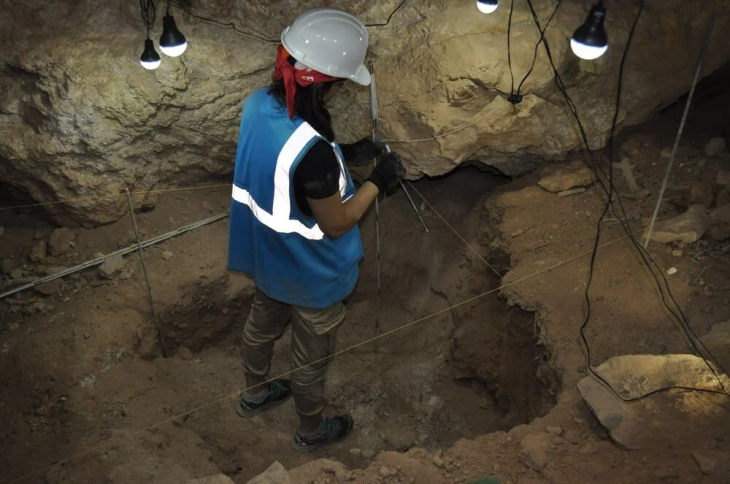
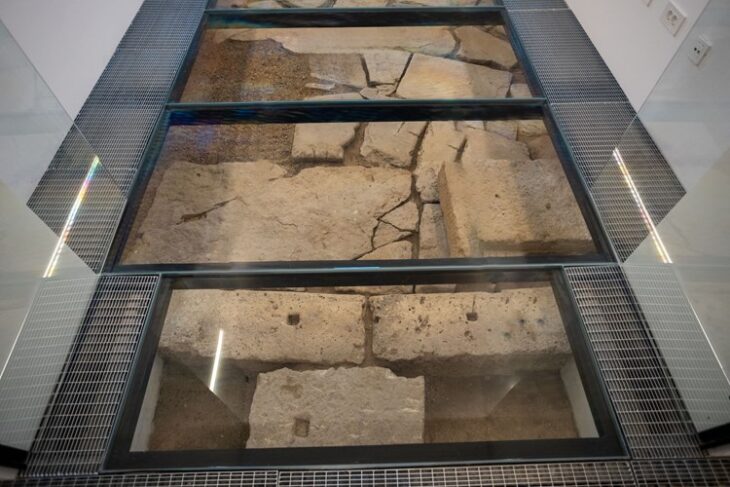
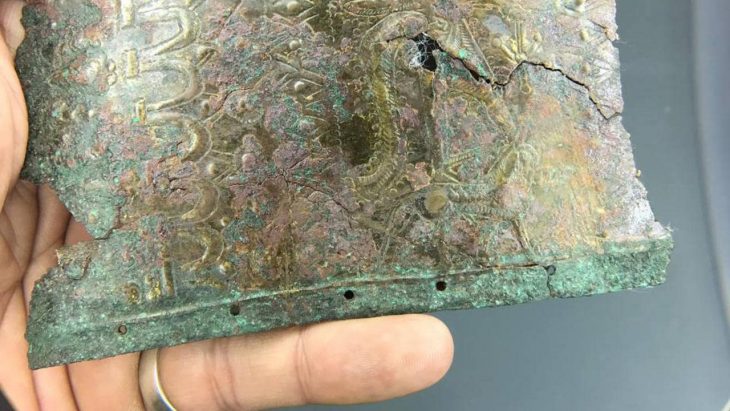
The remains of a 12-year-old boy wearing a bronze warrior belt were found at Pontecagnano, an outpost of the pre-Roman Central Italian Etruscan civilization in southern Campania.
Lead archaeologist Gina Tomay told ANSA about the finds.
“It’s a find of great significance,” said Tomay of the boy, who lived in the IV century BC and was discovered with two ceramic cups at his feet, one for food in the afterlife and the other for the wine that would ensure him a place at the banqueting ceremony called symposium.
Tomay said the boy was the 10,000th find at Pontecagnano, over 60 years of success and good practices “due to study, research and systematic excavations”.
The Etruscan colony there reached its peak between the VIII and VII century BC, she said, in an area “particularly well-favored by nature and also close to the sea”.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In the Pontecagnano area, remains of the Villanovan Culture (9th-8th century BC), the ancestor of the Etruscans, were found. Archaeological studies in the area provide evidence of early settlements.
Objects from all over the Mediterranean, from Greece to Egypt, from the Far East to Sicily and Sardinia, have been discovered in Pontecagnano.
The Etruscan Center was probably called Amina and dates back to the 6th century B.C. At the height of his power, he ruled over all the land from Salerno to the Silaurus River (Sele). It was known for the Argive Juno temple supposedly built by Jason. Here, in 268 BC, the Romans built a new city, Picentia, which housed the nucleus of the Piceni deportees.
Several kilometers of farmland and the Sele River separates the settlement from the two-story Greek city of Paestum in the west, and not far to the south is Pompeii, whose origins, according to recent research by archaeologists Massimo Osanna, also lie in Etruscan in the 7th century BC.
The Etruscan child and 10,000th find in Pontecagnano, according to Osanna, the former Pompeii head who is now the director-general of Italy’s public museums, “is also an interesting and valuable case study.”
The discoveries may attract more tourists to the site, which has been lauded in archeological literature but has been overlooked by main tourism routes, unlike neighboring Paestum.