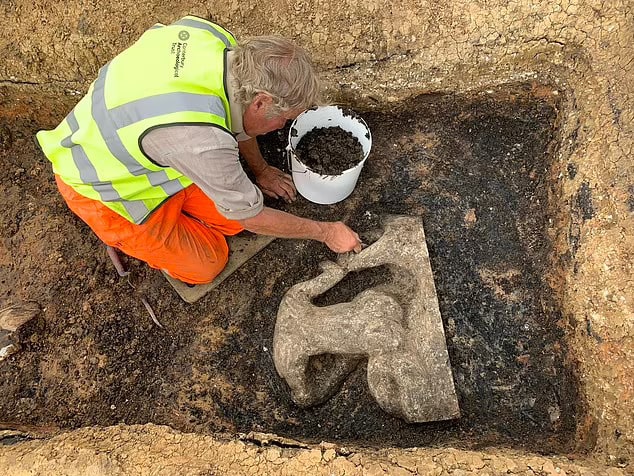
A remarkable discovery has been made in Urchfont, a village located in Wiltshire, England, where a Bronze Age hoard of copper alloy tools has been unearthed, including an exceptionally rare anvil. This collection, dating back to approximately 1650-900 B.C., is believed to have belonged to a skilled metalworker.
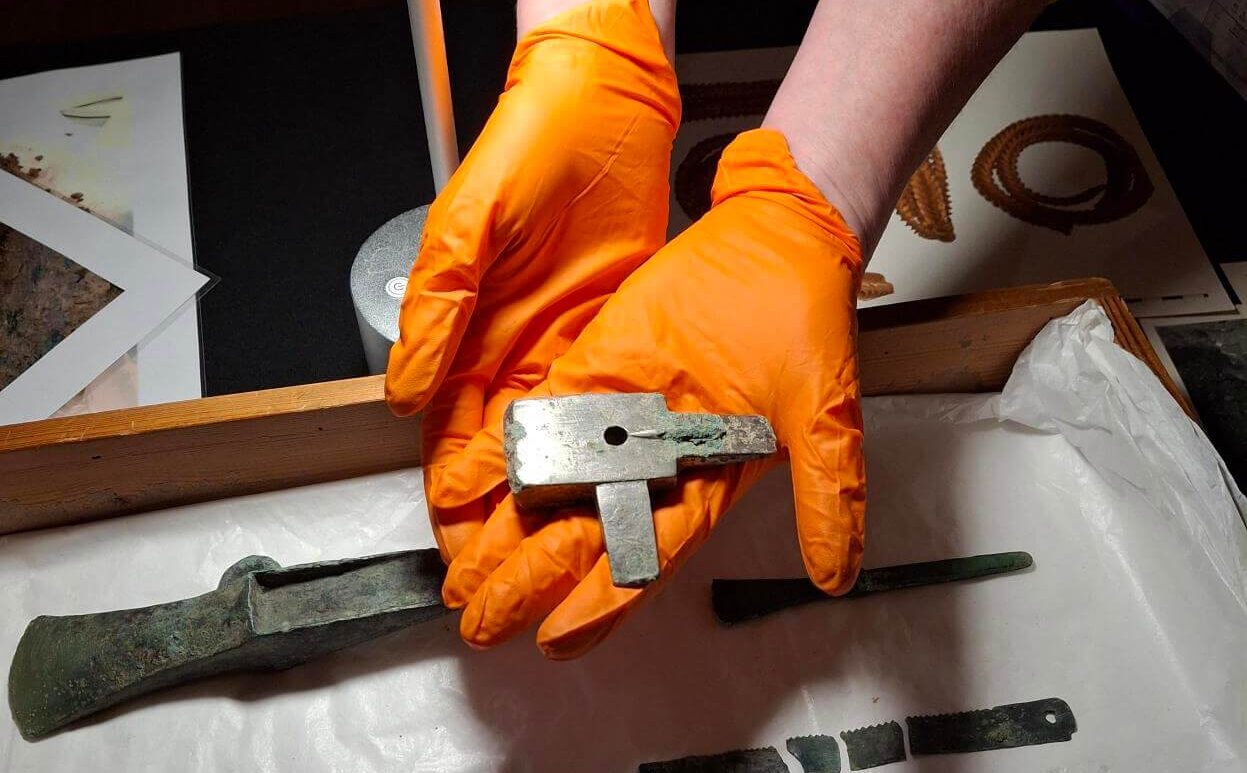
The significance of this find lies not only in the rarity of the artifacts but also in what they reveal about ancient metalworking practices. The presence of the anvil, a crucial tool for shaping and crafting metal, suggests that the owner was engaged in specialized metalwork, possibly as a goldsmith. This contrasts with the more common role of blacksmiths, indicating a focus on fine metalwork and the creation of intricate designs.
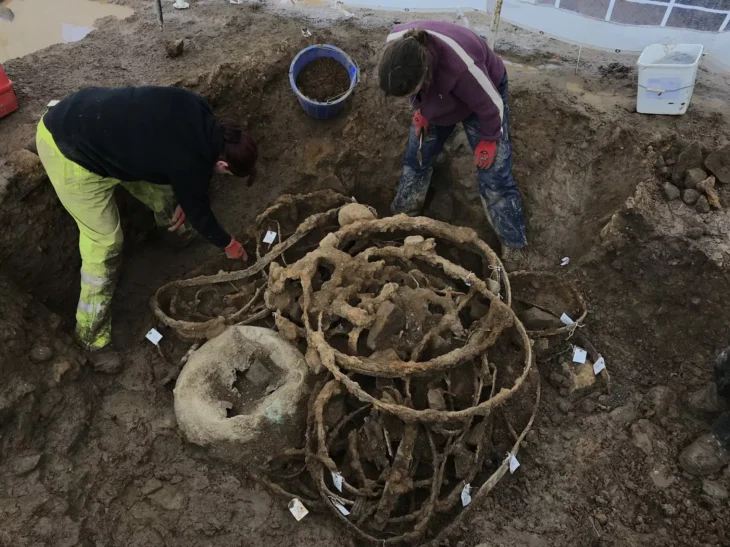
The find began last February when a metal detectorist stumbled upon a tanged chisel. Recognizing the significance of the discovery, he promptly ceased digging and reported the find to the Wiltshire Finds Liaison. Subsequent excavations revealed several additional artifacts, including fragments of copper alloy sheeting and a copper alloy rod.
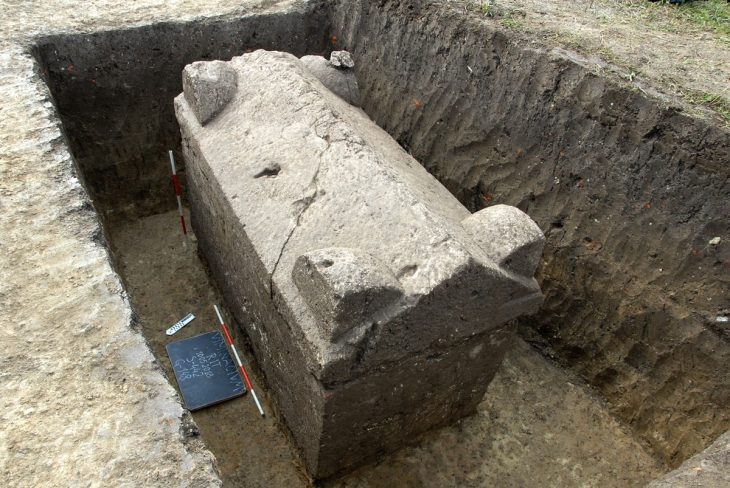
Archaeologists transported the remaining hoard in a single soil block to the British Museum for micro-excavation under controlled laboratory conditions to ensure careful analysis.
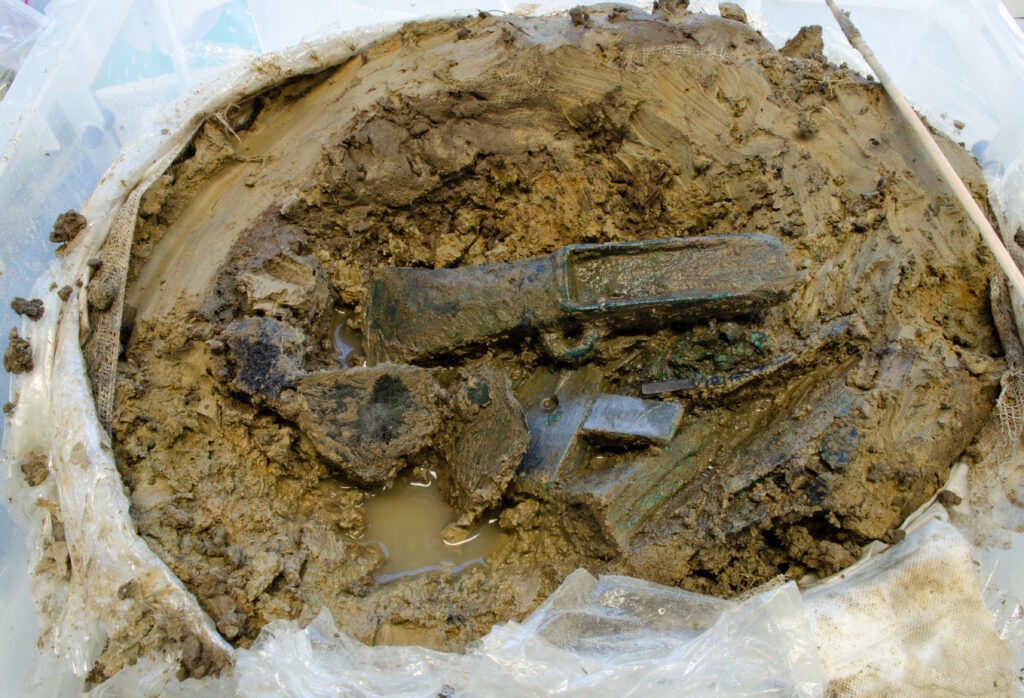

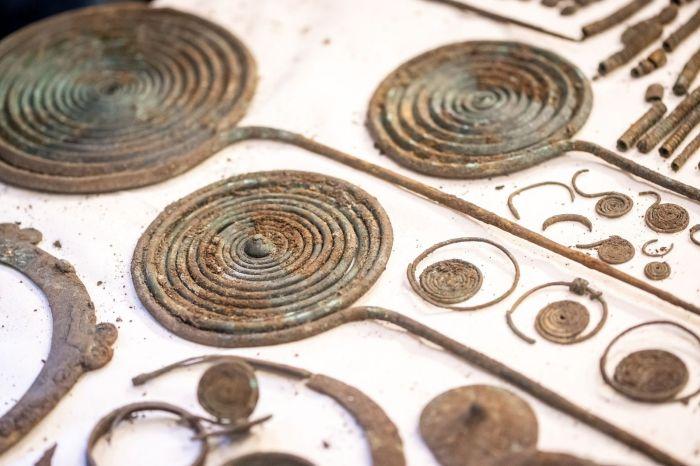
The excavation of the soil block yielded an array of intriguing items: more fragments of copper alloy sheeting, a hacksaw blade, a looped palstave axe, and remnants of at least two decorated copper alloy vessels. Additionally, fragments of sheet metal and a small copper alloy bar, likely part of a chisel handle or another small tool, were discovered. Notably, organic and charred materials were also preserved within the dense soil, providing further insights into the context of the hoard.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Among the most telling artifacts are two pieces of a pouring basin with sprues, indicating that the hoard’s owner was likely a metal craftsman. The presence of the small, silver-colored anvil suggests that this individual specialized in fine metalwork, possibly as a goldsmith rather than a blacksmith.
The Wiltshire Museum has expressed a great interest in acquiring this significant hoard, which not only sheds light on the craftsmanship of the Bronze Age but also enriches our understanding of the region’s historical metalworking practices. This discovery is a testament to the enduring legacy of ancient artisans and their contributions to the development of metallurgy.
Cover Image Credit: Wiltshire Museum