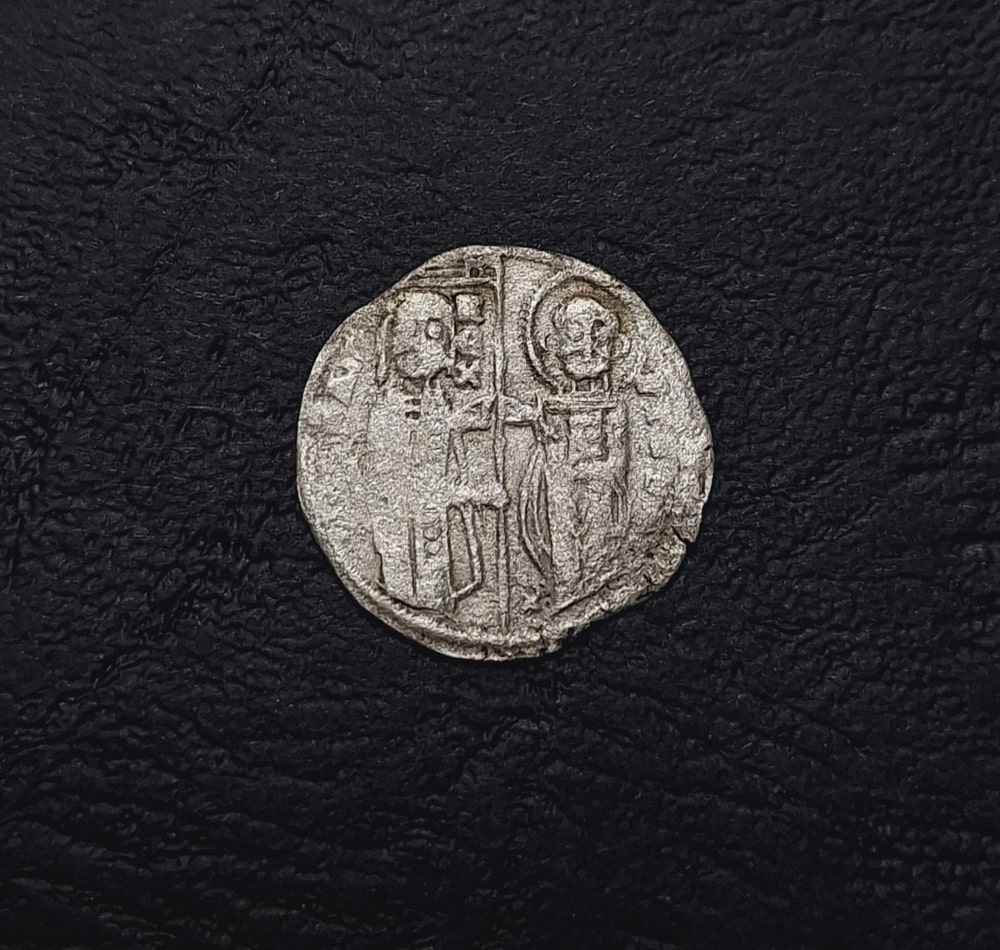
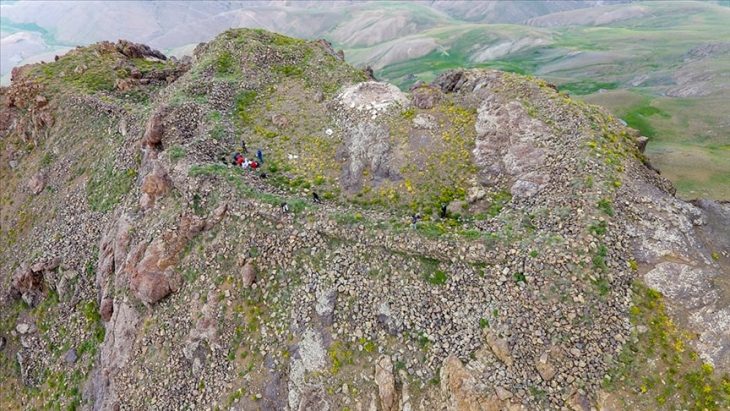
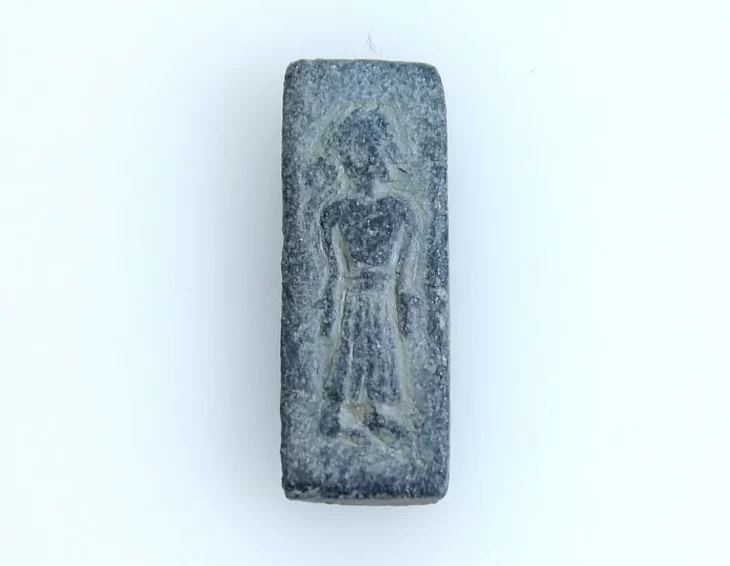
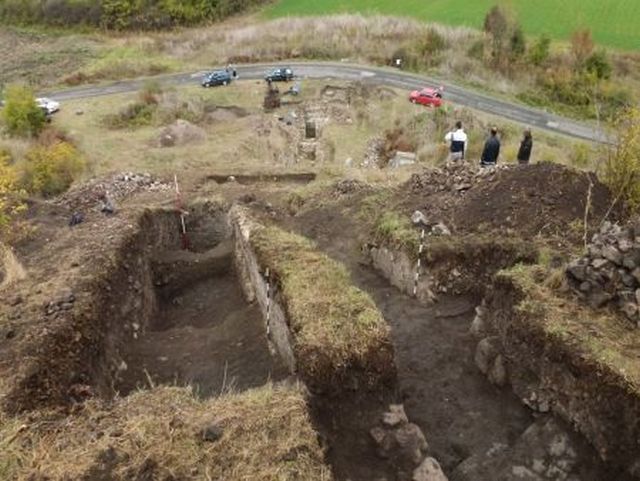
Archaeologists have discovered a silver grosso minted by the Serbian king Stefan Uros II Milutin in the medieval Rusocastro fortress, which changed hands many times between the Byzantine and Bulgarian Empires in the Middle Ages, and whose ruins are situated in today’s Burgas District in Southeast Bulgaria.
The discovery is significant because it broadens the picture of previously unknown coin circulation in the city.
Rusokastro Rock at the north entrance to McFarlane Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica is named after “the settlement and medieval fortress of Rusokastro in Southeastern Bulgaria.
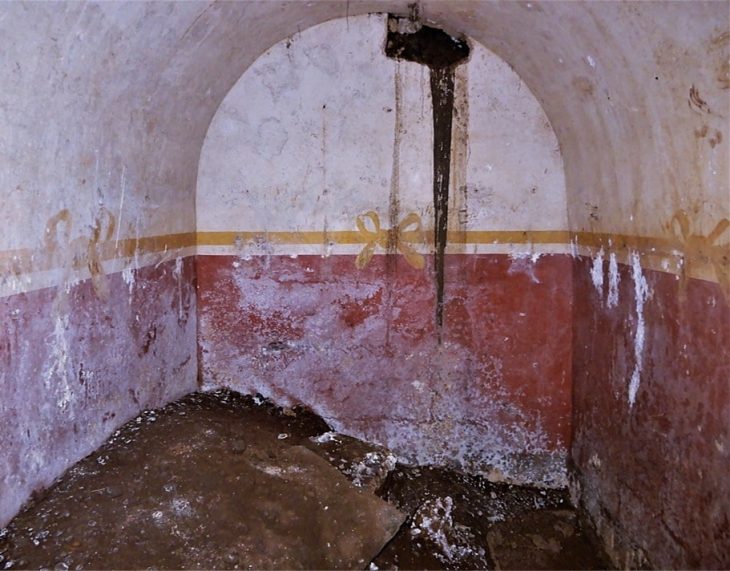
The Rusocastro Fortress is best known for the Battle of Rusocastro in 1332 AD. It was the last big military victory of the medieval Bulgarian Empire before it was conquered by the Ottoman Empire at the end of the 14th century.
King Stefan Uros II Milutin ruled Serbia from 1282 to 1321. Together with his great-grandfather Stefan Nemanja, the founder of the Nemanide dynasty, and his grandson, Emperor Stefan Uroš IV Dušan, King Milutin is considered the most powerful ruler of the Nemanide dynasty. The long and successful military breach of King Milutin, down the Vardar River Valley and deep into the Byzantine territories, represents the beginning of Serbian expansion into southeastern Europe, making it the dominant political power in the Balkan region in the 14th century. During that period, Serbian economic power grew rapidly, mostly because of the development of trading and mining.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

King Stefan Uros, known as the Saint King, and his relics are preserved in the St. Nedelya church in Sofia. One of his five wives was Bulgarian princess Ana Terter, daughter of Tsar Georgi Terter.
The obverse side of the coin depicts Jesus Christ, while the reverse side shows the King together with Saint Stefan, the patron saint of Serbia. The coin is a copy of the Venetian grossi or ‘Matapan’. Due to their weight and the high silver content those were the most stable currency in the Balkans at the end of the 13th and the beginning of the 14th century. However, they bear the image of the Doge, in whose name the coin was minted, as well as St. Marco, the patron saint of Venice.
Previous discoveries of archaeologists at the site are a silver grosso of Isabella of Villehardouin, Princess of Achaea and Morea, coins of Tsar Ivan Alexander and of some Byzantine emperors, an iron fighting knife, and iron tools.
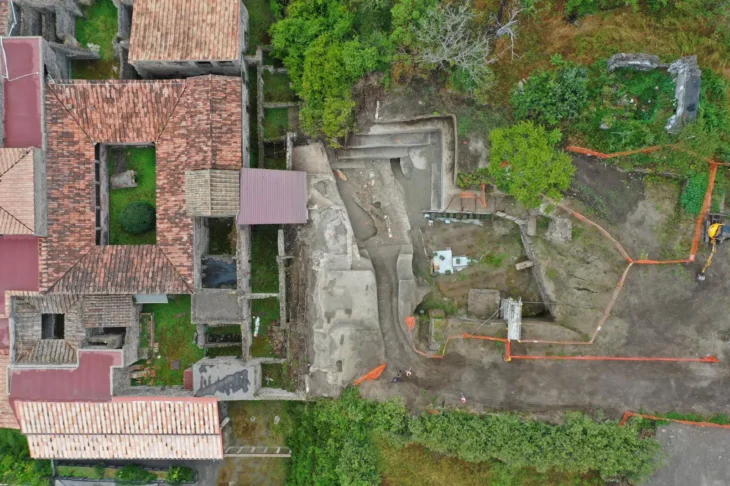
The Burgas Regional History Museum is responsible or the excavations at Rusocastro, which are funded by Kameno Municipality and the Ministry of Culture.
Cover Photo: The silver grosso found at Rusocatro Burgas Regional HIstory Museum