A recently uncovered archaeological site in the Rhodope Mountains of southern Bulgaria is now entering the scientific spotlight. In a statement shared directly with us by researcher Georgi Georgiev, one of the site’s discoverers, the carved rock near the village of Skobelevo is believed to represent a prehistoric star map—possibly one of the earliest known attempts to depict the night sky in stone. The find promises to redefine our understanding of ancient astronomy and the spiritual life of early civilizations in the Balkans.
This unique find not only adds a significant piece to the puzzle of human history but also opens new avenues in the field of archaeoastronomy.
An Accidental Discovery with Historic Significance
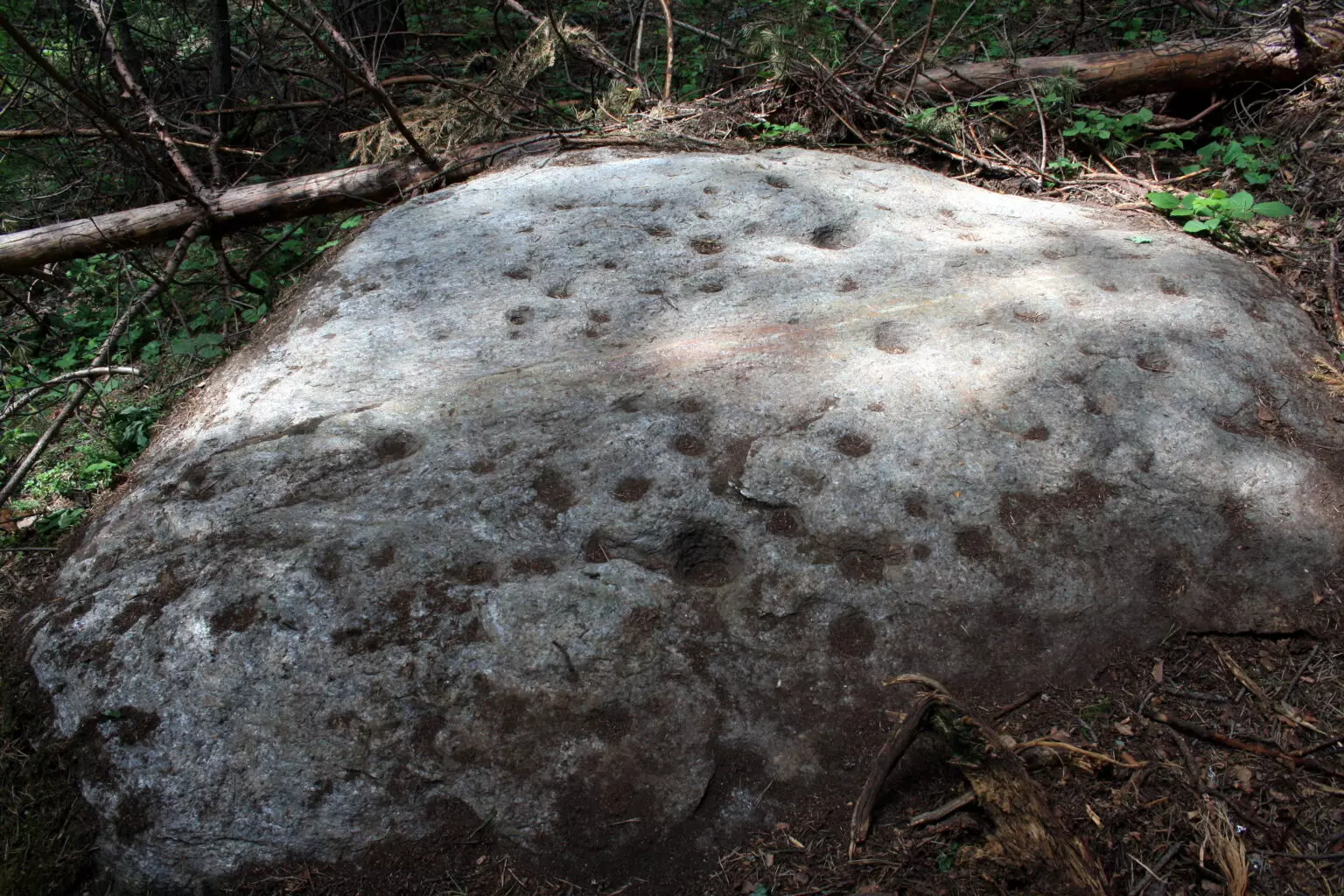
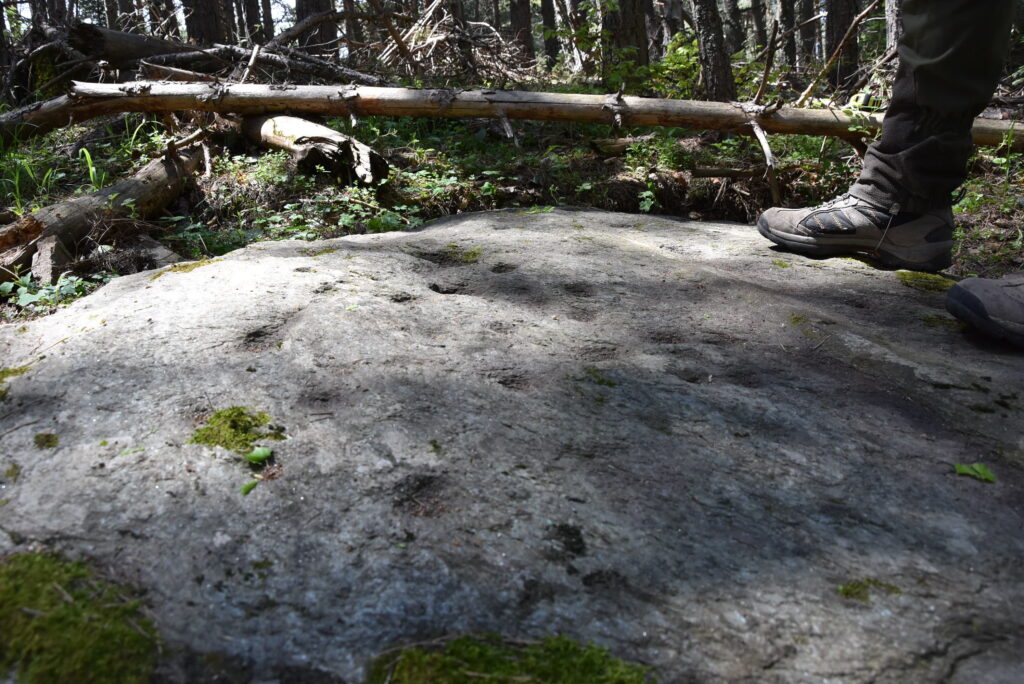
The star-studded rock was discovered on May 20, 2013, by researchers Georgi Georgiev and Ivelina Georgieva during a field expedition near an ancient Thracian necropolis. Measuring approximately 2×3 meters, the rock lies deep in the forest, oriented along an east-west axis and embedded with a natural marble vein. This luminous vein is thought to symbolize the Milky Way, further supporting its interpretation as a celestial map.
The stone’s surface features 56 meticulously carved conical holes of various diameters—24 in the northern half and 32 in the southern—representing stars of different magnitudes. Several constellations are clearly outlined, including Ursa Major (the Great Bear) and Leo, with additional alignments suggesting Cassiopeia, Cygnus, Lyra, and the Pleiades star cluster.
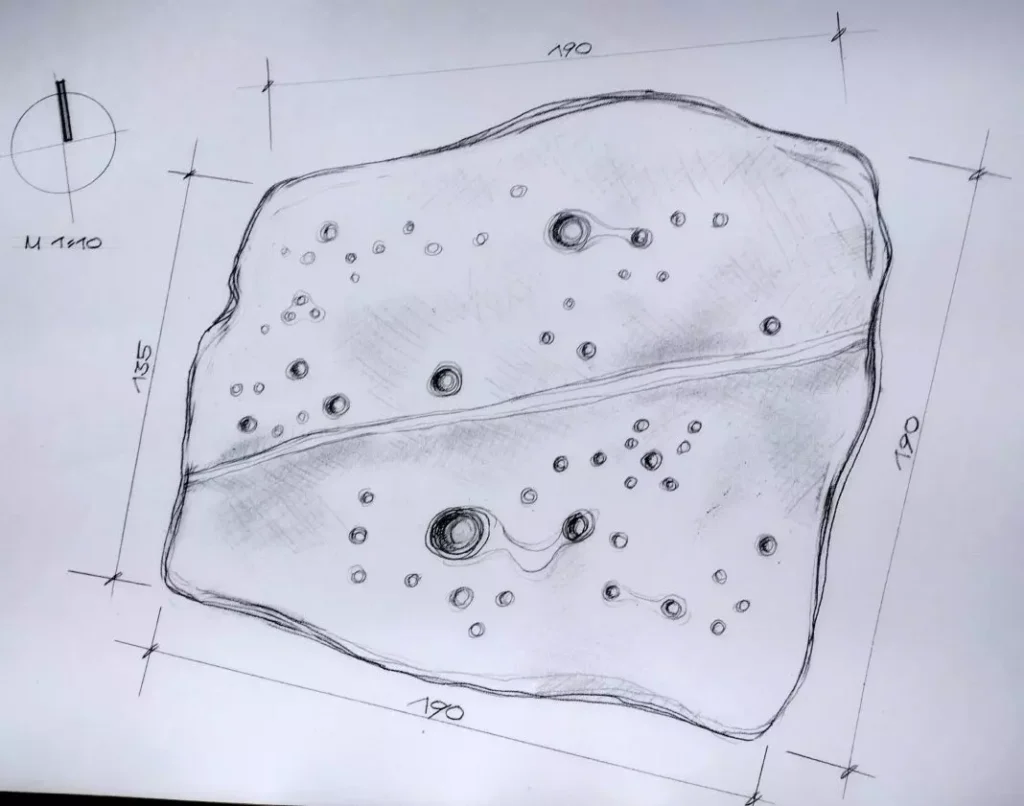
Estimated Dating: When Was the Star Map Created?
While the Skobelevo star map has yet to undergo definitive scientific dating, researchers suggest it likely originates from the Late Neolithic to Early Iron Age, approximately 2000 to 500 BCE. This estimate is based on the proximity of the site to Thracian necropolises and mound tombs, as well as its alignment with similar prehistoric sanctuaries in the Balkans.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Although no ceramics or organic materials were found at the immediate site—making radiocarbon or stratigraphic dating currently unfeasible—the archaeological context and the map’s symbolic and functional characteristics point to a period when ancient peoples were actively observing and recording celestial phenomena for ritual and agricultural purposes. Until further studies are conducted, this date range remains the most probable based on comparative archaeological analysis.
Recreating the Northern Sky in Stone
Experts believe that these carvings were not random but reflected the diurnal and annual movements of celestial bodies, particularly those in the Northern Hemisphere. The presence of constellations in accurate configuration and scale suggests a sophisticated understanding of astronomy. One theory posits that the rock served as a primitive star clock, helping ancient observers track time and seasons through the position of circumpolar stars.
Moreover, the rock’s mica-rich surface creates a shimmering effect under sunlight, mimicking the night sky—a striking artistic and symbolic choice that enhances its astronomical purpose.

Cultural and Ritual Importance
Surrounding archaeological evidence—including nearby necropolises, tombs, and sanctuary remnants—suggests that the site may have been part of a larger cultic complex. It could have served dual functions: as a spiritual sanctuary for rituals and a navigational tool for early travelers or sailors.
Notably, the site includes a second stone with a cylindrical indentation aligned eastward, possibly forming a deliberate pair with the main map-bearing rock.
Preserving a Petrographic Monument
Despite its potential as a cultural monument of national and scientific significance, the site remains largely unprotected. Georgiev and Georgieva advocate for its official recognition and inclusion in Bulgaria’s national archaeological registry. Their work aligns with modern efforts to preserve and promote intangible heritage and archaeoastronomical knowledge.
Non-invasive studies—such as heliacal sunrise observations, traceology, geological sampling, and GPS mapping—have already been conducted, further validating the rock’s anthropogenic and astronomical significance.

Linking Past and Present
Interestingly, similar representations of star configurations have been found on ancient coins and jewelry from the 1st and 2nd centuries AD. Symbols like the crescent moon and star, common in Roman iconography, may echo humanity’s long-standing fascination with the cosmos. This continuity highlights how ancient knowledge systems have influenced artistic and cultural expressions through time.
Conclusion
The Skobelevo star map offers a rare glimpse into the cosmological understanding of prehistoric societies in the Balkans. As one of the few known examples of a stone-carved celestial map, it holds profound implications for the study of early astronomy, mythology, and cultural development. With appropriate protection and scholarly attention, this ancient artifact could soon become a key destination for cultural tourism and a milestone in Europe’s archaeoastronomical heritage.
Cover Image Credit: A prehistoric star map carved in stone near Skobelevo village is believed to be one of the oldest known depictions of the night sky. Photos courtesy of Georgi Georgiev.