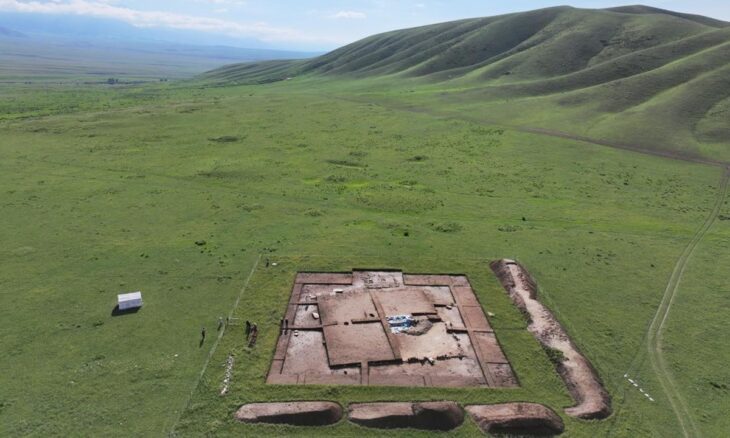
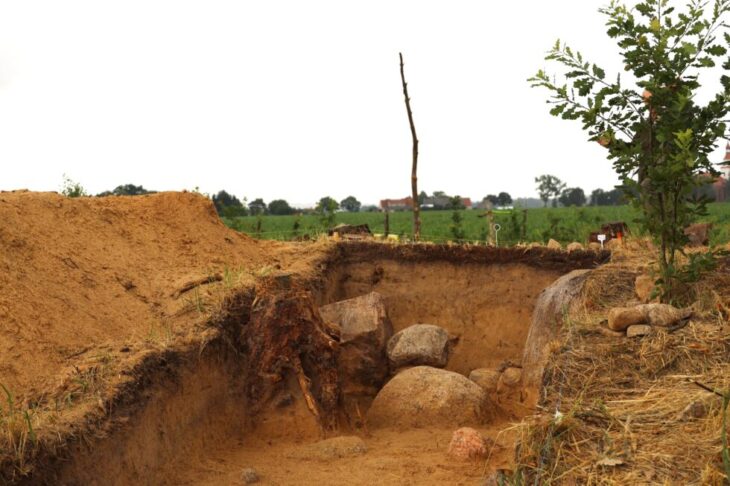
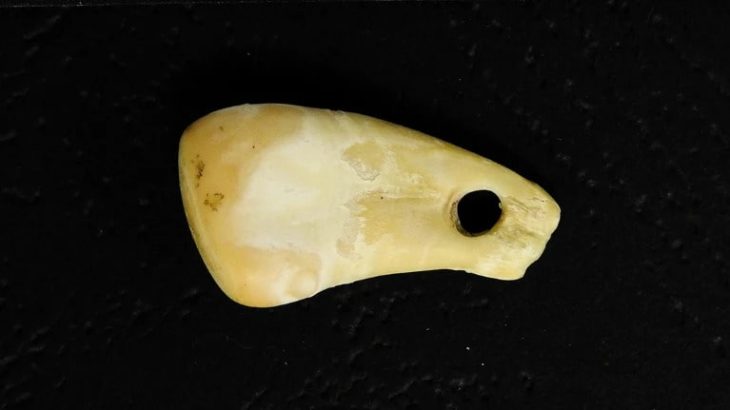
Archaeologists have uncovered a remarkably rich Bronze Age burial of a young woman at the site of Tepe Chalow in northeastern Iran, offering new insights into the long-overlooked Greater Khorasan Civilization (GKC). The grave, dating to the early second millennium BCE, is considered the most lavish ever discovered at the site and among the most significant in the entire GKC cultural zone.
The discovery was made by a team led by Dr. Ali Vahdati, in collaboration with researchers Raffaele Biscone, Roberto Dan, and Marie-Claude Trémouille. Their study, published in the Journal of the British Institute of Persian Studies, documents the burial of a girl under 18 years of age, accompanied by 34 luxury grave goods made from gold, bronze, ivory, chlorite, serpentine, lapis lazuli, and pottery.
A Civilization Reconsidered
Dr. Vahdati explains that what initially drew his attention to Tepe Chalow was the unexpected presence of artifacts typically associated with the Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC). These materials had previously been thought to be confined to regions like Turkmenistan and northern Afghanistan. Their discovery deep within Iranian territory prompted Vahdati and his team to propose a broader cultural framework—the Greater Khorasan Civilization (GKC).
Emerging at the end of the third millennium BCE, the GKC quickly expanded across Central Asia, encompassing parts of modern Iran, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, and Uzbekistan. By the early second millennium BCE, it had established extensive trade networks reaching the Indus Valley (Mohenjo-daro), Mesopotamian cities, and coastal communities along the Persian Gulf. Artifacts found in Iraq, Pakistan, and Gulf littoral sites attest to the GKC’s role in the regional exchange of goods such as chlorite, metals, and semi-precious stones.
Tepe Chalow’s Grave 12: A Glimpse Into the Past
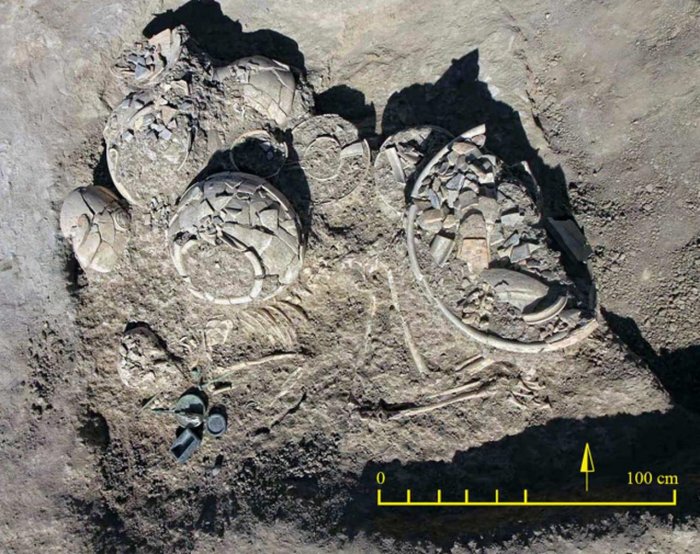
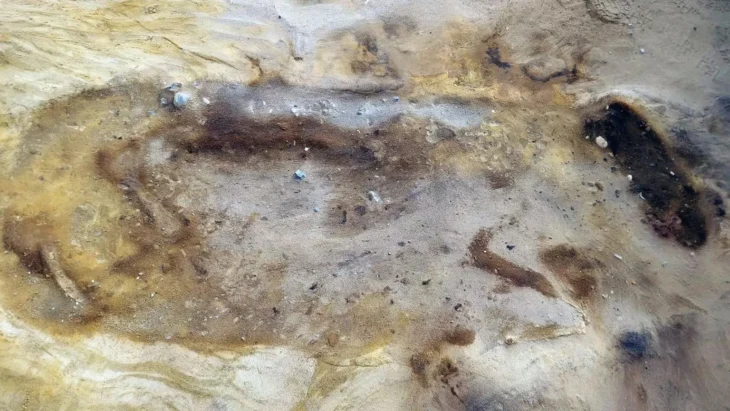
Grave 12 at Tepe Chalow is particularly exceptional for its wealth and symbolic items. The burial followed a characteristic funerary rite observed in the Chalow necropolis: the young woman was laid in a crouched position on her right side, facing southeast. Pottery vessels were arranged above the head, behind the back, and near the feet.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
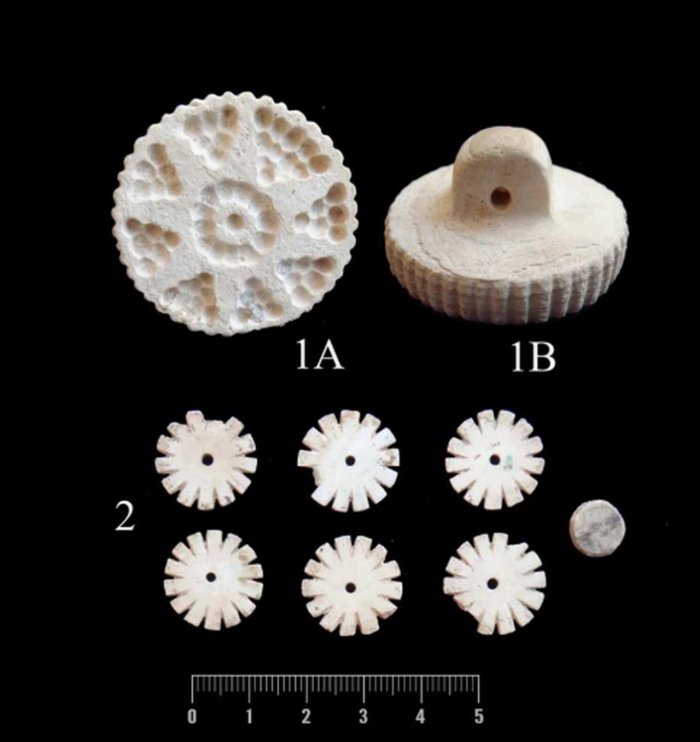
Among the 34 grave goods were: Twelve pottery vessels, including large storage jars
Thirteen metal items, such as gold earrings, a gold ring, four bronze pins (one shaped like a hand holding a rosette), a bronze mirror, and two bracelets
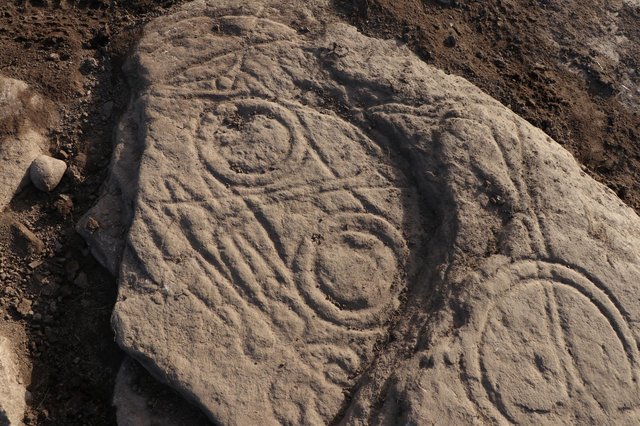
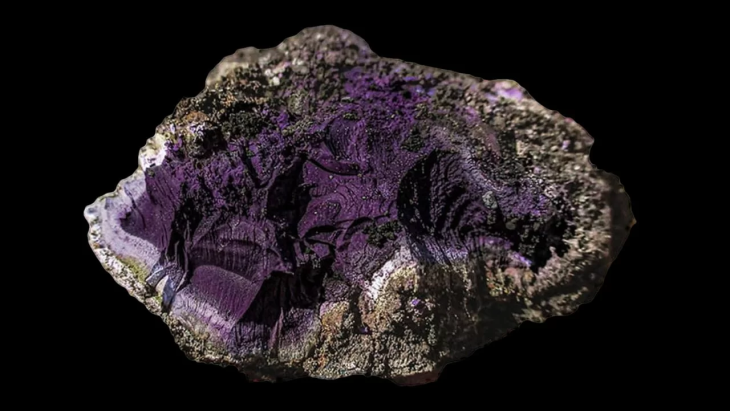
Seven stone objects, including three chlorite cosmetic containers—one of which featured intricate carvings of snakes and scorpions—beads, and a distinctive stamp seal engraved with a pair of human feet enclosed within a circular motif
Two ivory pins, likely used as decorative or ritual hair accessories
The burial’s richness suggests the young woman held a significant social role. According to Dr. Vahdati, the presence of multiple seals implies involvement in trade or administration—functions typically associated with elite individuals in Bronze Age societies.

Women of Status in Bronze Age Iran
Interestingly, female burials at Tepe Chalow tend to be more richly furnished than male ones. This challenges assumptions about gender roles in early complex societies and suggests that women in the GKC may have had prominent societal functions. Grave goods such as mirrors, cosmetic boxes, jewelry, and offerings of food (like sheep bones in cooking vessels) reflect both social standing and spiritual beliefs in an afterlife.
A Window into the Broader Cultural Network
Over four excavation seasons, archaeologists have identified 38 graves at Tepe Chalow, many grouped into family clusters. While erosion exposed some graves just beneath the surface—Grave 12 was only 15 centimeters deep—other layers contain older burials and storage pits, pointing to long-term settlement and cultural continuity.
Tepe Chalow’s strategic location along ancient trade routes connecting the Iranian Plateau with Central Asia further emphasizes its importance. Scholars suggest that this corridor may have served as a precursor to the later Silk Roads.
Future research will include isotopic and DNA analysis to uncover more about the individual’s diet, ancestry, and mobility. Technological studies of the artifacts are also underway to understand production techniques and trade dynamics.
As Dr. Vahdati puts it, “What we are uncovering at Tepe Chalow reshapes our understanding of early civilizations in Central Asia. The Greater Khorasan Civilization is no longer a peripheral player—it was central to Bronze Age connectivity, innovation, and cultural development.”
Vahdati, A. A., Biscione, R., Dan, R., & Trémouille, M. C. (2025). Grave 12 at Chalow: The Burial of a Young Lady of the “Greater Khorasan Civilization.” Iran, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/05786967.2025.2488251
Cover Image Credit: A general view of Grave 12 unearthed at Tepe Chalow and the position of burial goods in the grave. Vahdati et al. 2025