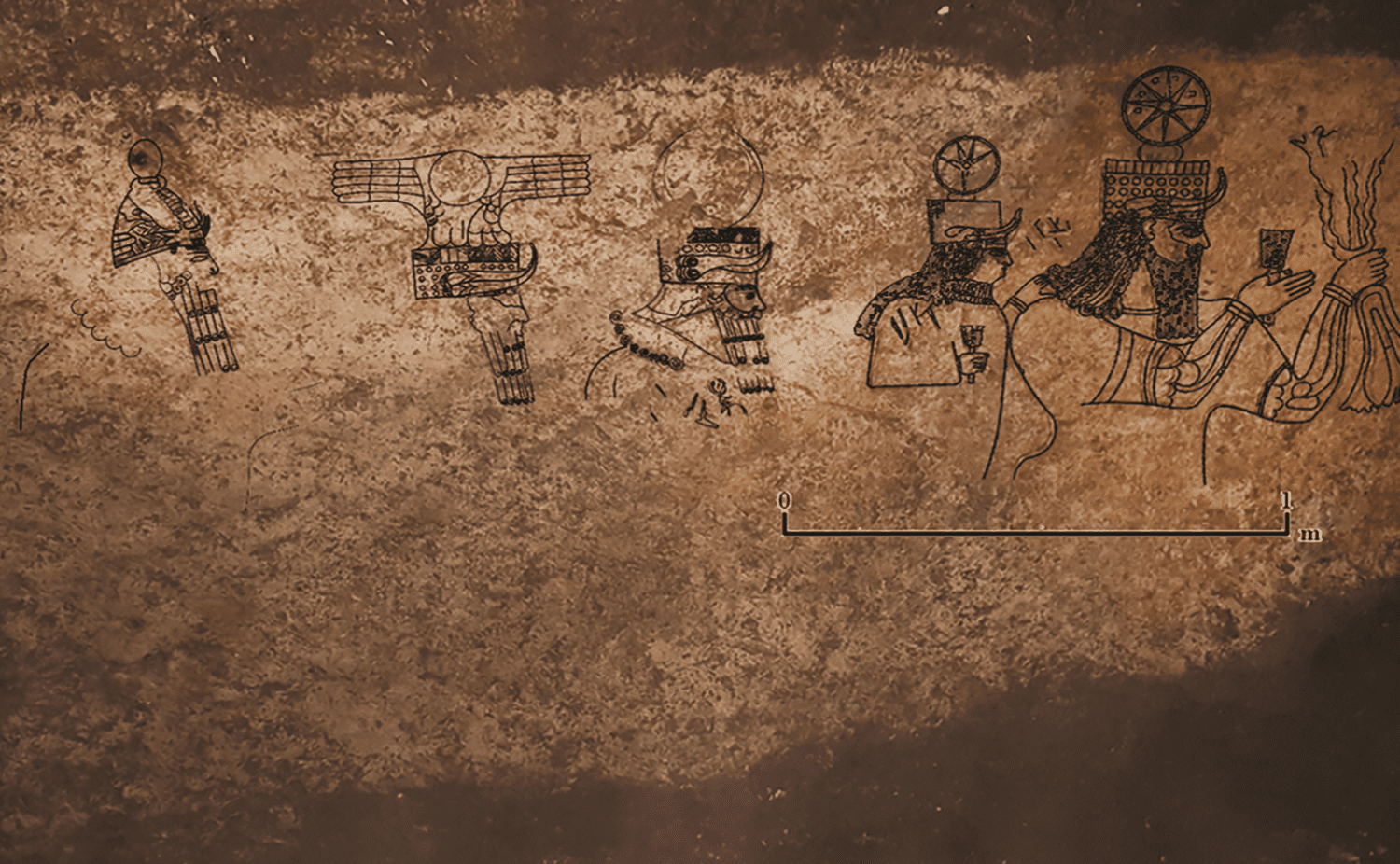An underground Iron Age complex has been found in Turkey that may have been used by a fertility cult during the first millennium B.C.
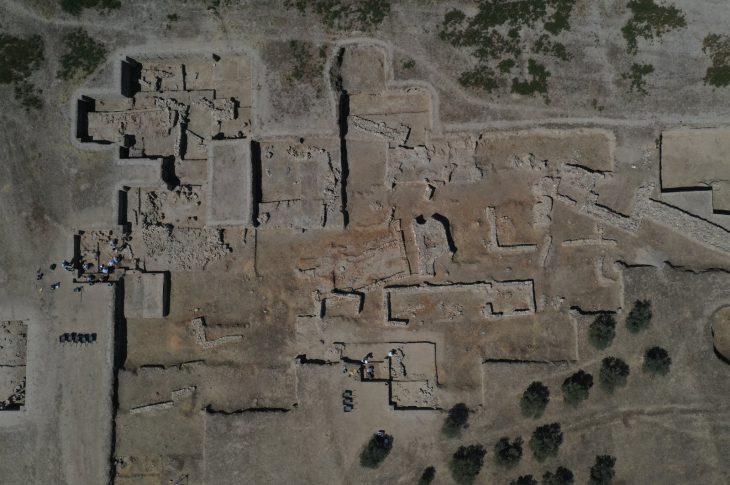
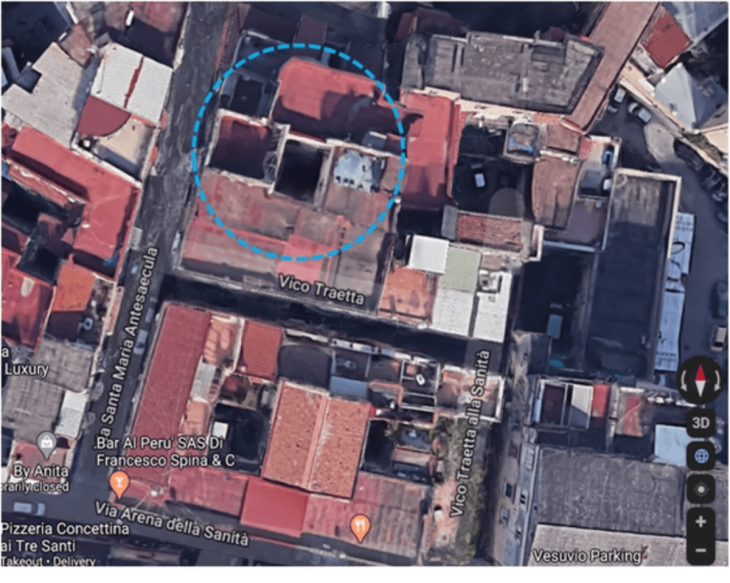
The underground complex was found in the Başbük village of Urfa province in southeastern Turkey.
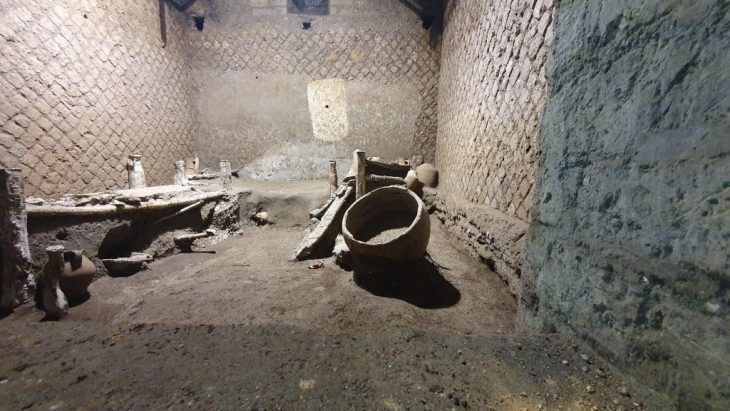
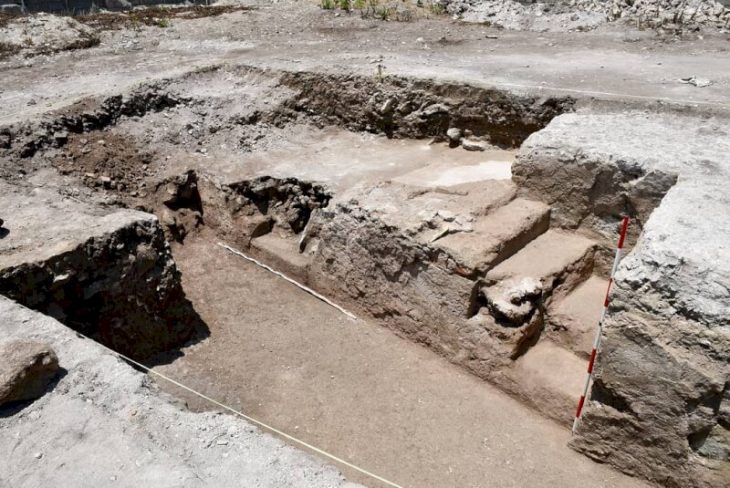
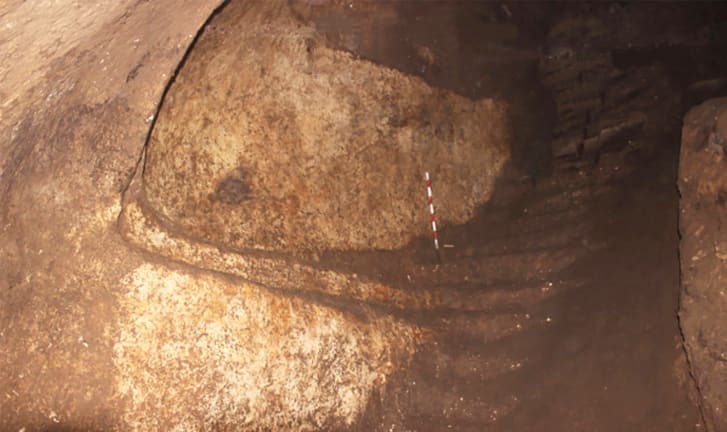
Authorities became aware of the complex whilst the site was being looted. This led to a rescue excavation that revealed a 30-meter tunnel system carved into the bedrock beneath a two-story house.
When the looters were caught by authorities, a team of archaeologists did an abbreviated rescue excavation to study the significance of the underground complex and the art on the rock panel in the fall of 2018 before erosion could further damage the site. What the researchers found has been shared in a study published Tuesday by the journal Antiquity.
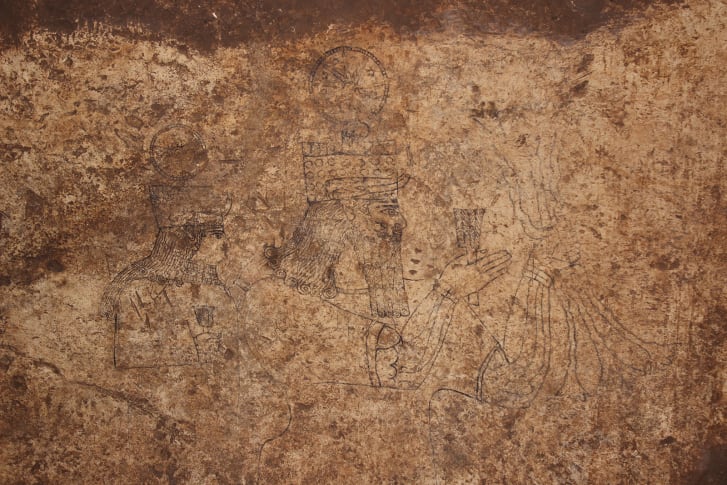

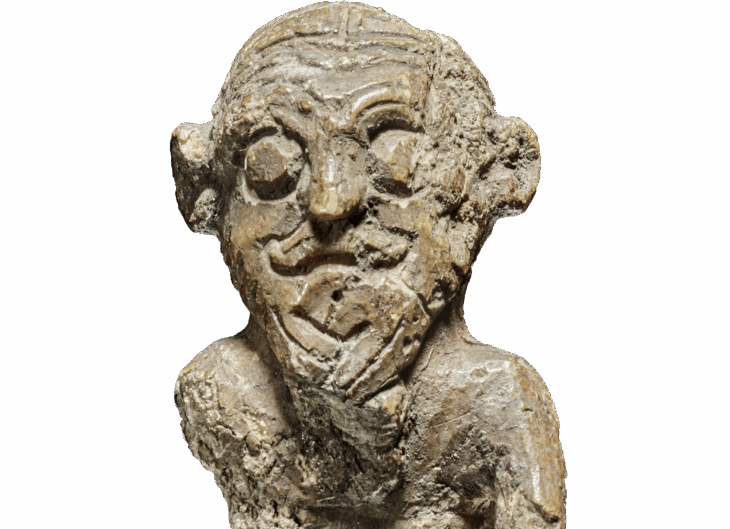
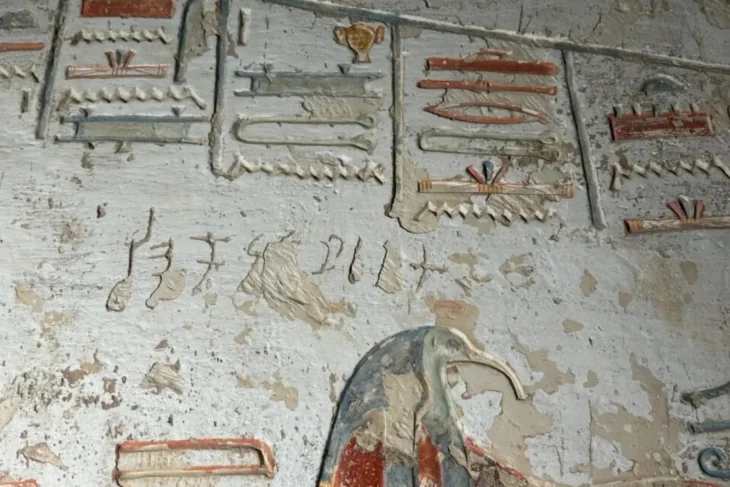
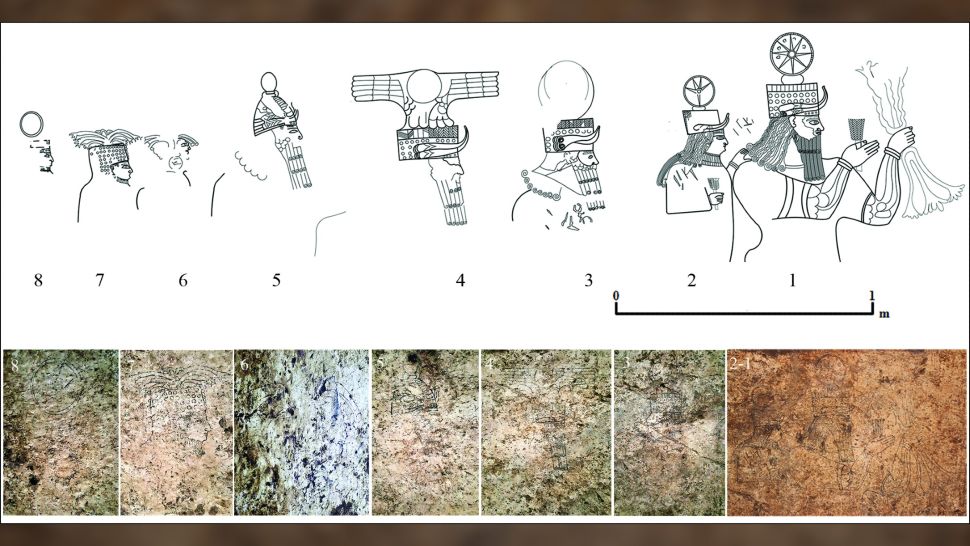
In the complex, archaeologists have found rare rock art drawings on walls, which show a procession of deities depicted in an Assyrian style. Like Hadad – god of storm and rain, Sîn – god of moon and Atargatis – goddess of fertility, protection, and well-being…
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“When the Assyrian Empire exercised political power in south-eastern Anatolia, Assyrian governors expressed their power through art in Assyrian courtly style,” said Selim Ferruh Adalı, one of the authors of the study and associate professor, ancient history, Social Sciences University of Ankara.
“The wall panel contains a depiction of divine procession with previously unknown elements, with Aramaic writing to describe some of the deities while combining Neo-Assyrian, Aramaean and Syro-Anatolian divine iconography,” Adalı added.

An example of this style was carved monumental rock reliefs, but the study authors wrote that Neo-Assyrian examples have been rare.
The artwork was created in the 9th century BC during the Neo-Assyrian Empire, which began in Mesopotamia and expanded to become the largest superpower at the time. This expansion included Anatolia, a large peninsula in Western Asia that includes much of modern-day Turkey, between 600 and 900 BC.
“The inclusion of Syro-Anatolian religious themes illustrate an adaptation of Neo-Assyrian elements in ways that one did not expect from earlier finds,” said Associate Professor Selim Ferruh Adali, “They reflect an earlier phase of Assyrian presence in the region when local elements were more emphasized.”

The artwork shows eight deities, all unfinished. The largest is 3.6 feet (1.1 meters) in height. The local deities in the artwork include the moon god Sîn, the storm god Hadad and the goddess Atargatis. Behind them, the researchers could identify a sun god and other divinities. The depictions combine symbols of Syro-Anatolian religious significance with elements of Assyrian representation, Adali said.
The archaeologists were also able to identify an inscription that could refer to the name ‘Mukīn-abūa’. He was a Neo-Assyrian official during the reign of Adad-nirari III (811–783 BC). He may have been given control of the region and the researchers speculate he could have been using the complex to integrate with and win over locals.

However, the fact that the site is incomplete shows that it was not a success. Something affecting the builders’ efforts, such as an uprising, might have resulted in its abandonment. The authors hope that further research will offer insight into the ancient empire’s culture and politics.
The site was closed after the 2018 excavations because it is unstable and could collapse. It is now under the legal protection of Turkey’s Ministry of Culture and Tourism. “As this was a rescue excavation, we could not fully study the site,” said Dr. Adalı, “Future excavations will eventually take place at Başbük and discover more of the mysterious underground complex.”
When excavations can restart safely, the archaeologists are excited to continue their work and acquire new photographs of the artwork and inscriptions, as well as maybe find more artwork and objects.