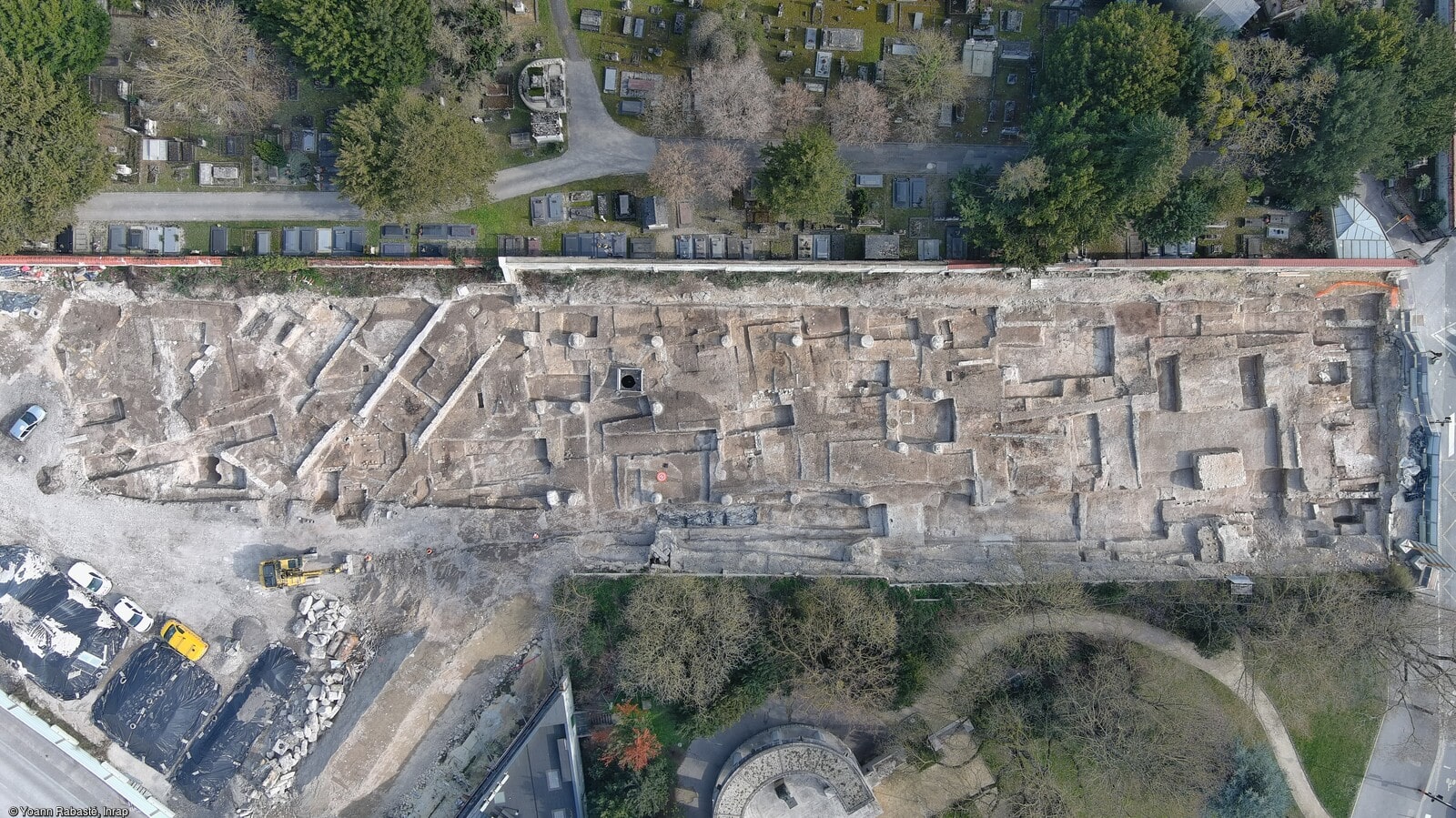
In the city of Reims in northeastern France, archaeologists have discovered an ancient Roman-era monumental complex dating from the 2nd – 3rd century AD.
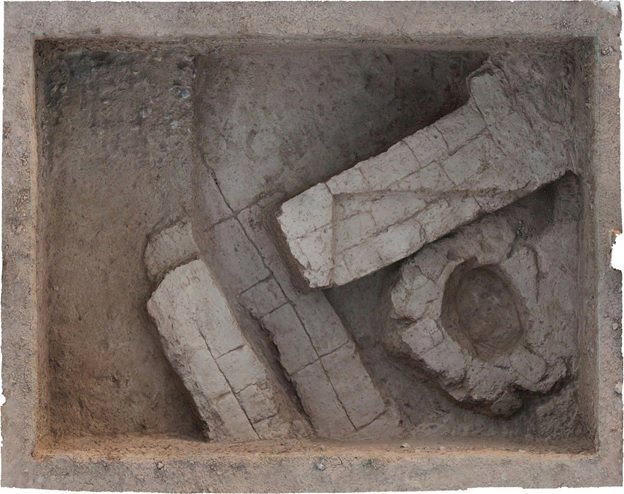
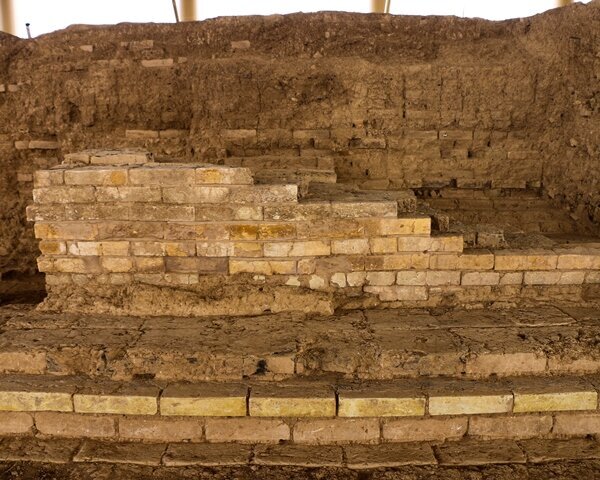
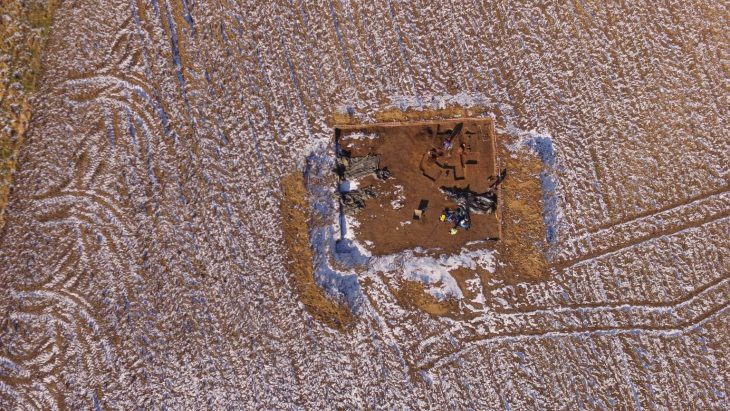
The structure consists of two porticoed galleries 65 ft lengthy forming the arms of a U. Greater than 20 rooms occupy the galleries, from corridors to residing areas with chalk flooring and fireplaces. 9 of the rooms had been a part of the traditional baths. 5 of them had a hypocaust underfloor heating system; lots of the pilae stacks (sq. tile piles) that supported the ground are nonetheless in place and in glorious situation. Within the empty house between the galleries are two rectangular masonry buildings that had been possible a part of backyard. One of many two was a basin or fountain. Two pressurized water pipes had been discovered that stuffed the basin and/or fed the water function.
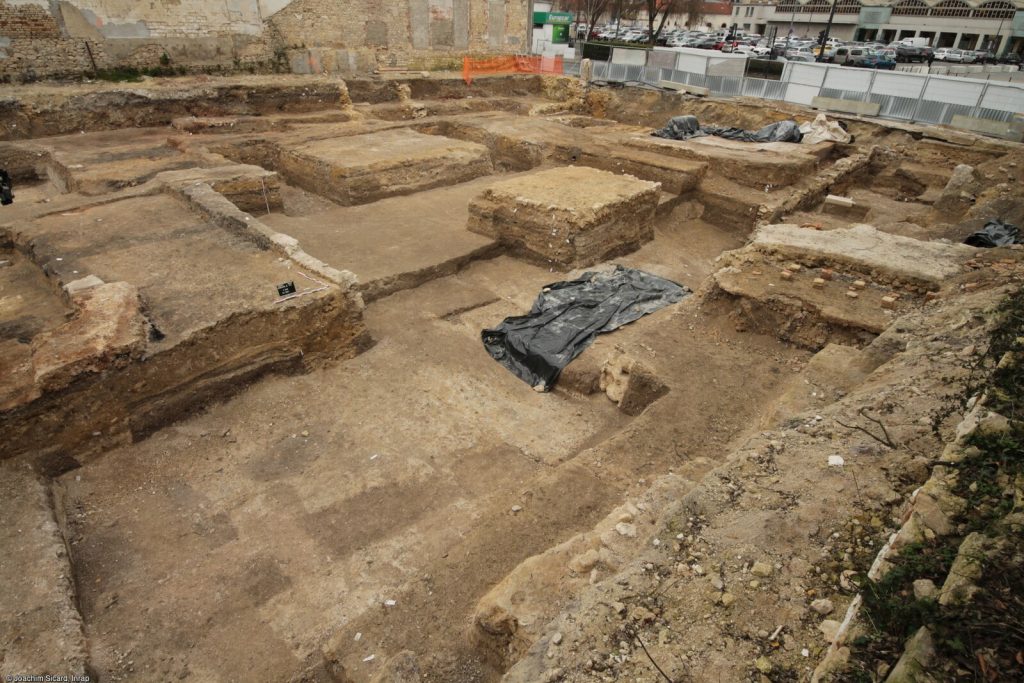

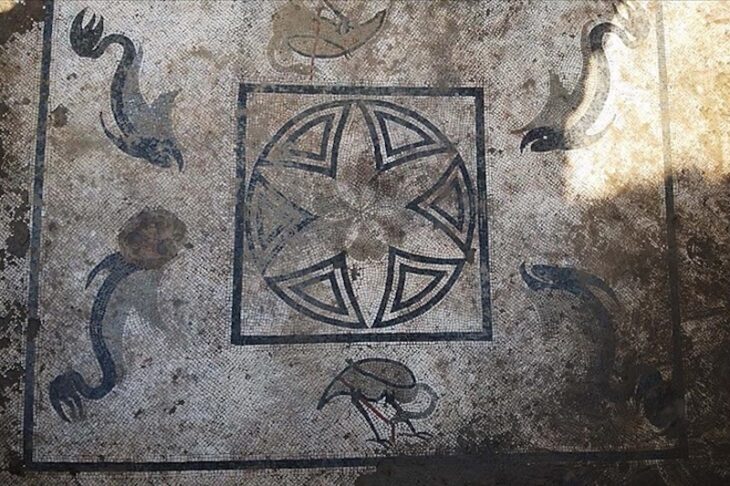
Archaeologists discovered painted plasters adorned with floral motifs. Some of the pigments used, such as a blue similar to “Egyptian blue,” are extremely rare. This discovery typifies a very simple set. The large number of rooms, their organization, the wealth of the decorations, the two large galleries, the hydraulic network, and the archaeological elements discovered (ceramics, architectural blocks, copper alloy tableware, and so on) allow for two interpretations. These relics could be the domus (house) of a wealthy individual or a spa complex, possibly open to the public, given the monumentality.
The Porte de Mars, the largest remaining Roman triumphal arch from the third century A.D., is just 100 meters (328 feet) away from the monumental complex. One of four imposing gates in the city walls, the arch was named after a nearby Temple of Mars.
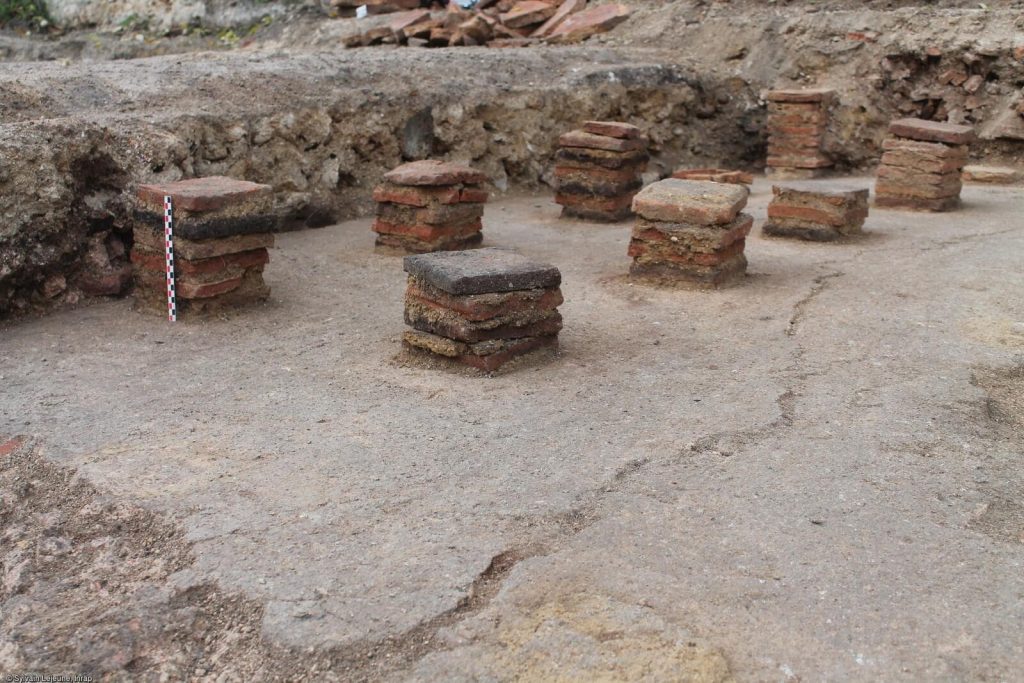

In the third century, this was a very prestigious location, but by the beginning of the fourth, the area had all but been abandoned, and its buildings had been quarried for recycled construction materials. The construction of Reims’ 4th-century walls may have caused the shift. For the next 1400 years, the neighborhood was used for agriculture before becoming a populated area at the end of the 18th century.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Cover Photo: Yoann Rabasté, Inrap