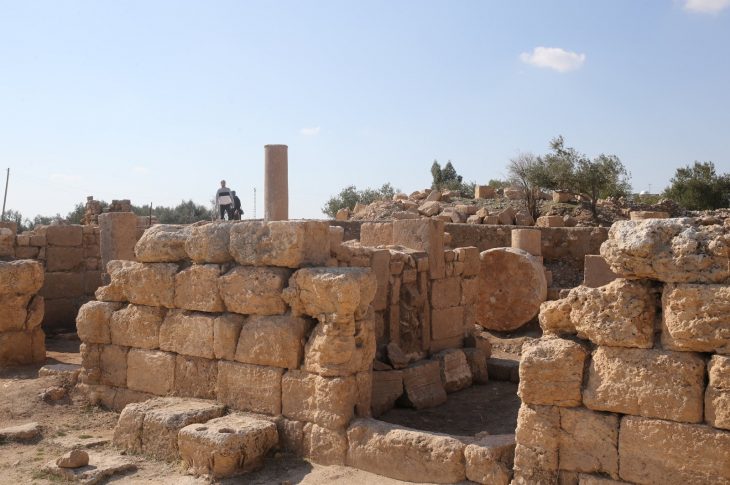
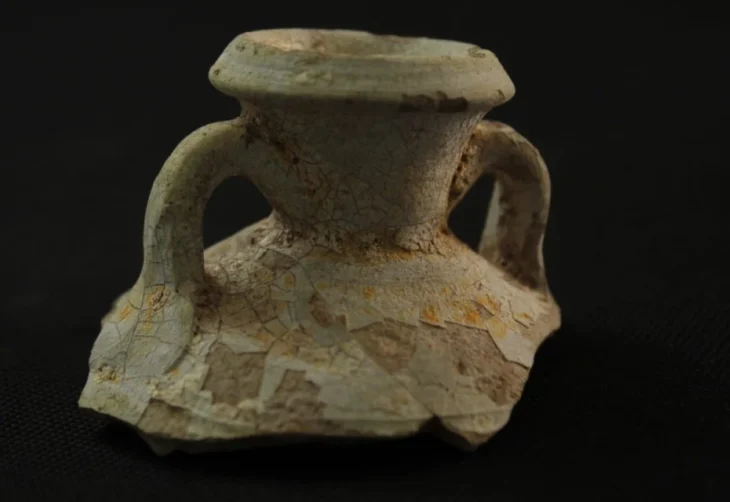
One of the six leading cities of ancient Lycia and the birthplace of Santa Claus (or Sinterklaas in Dutch), the ancient city of Myra and its port, Andriake, yielded very remarkable findings: millefiori (“A Thousand Flowers”) glass plaques.
The Ancient City of Myra is approximately 1.5 km from the town center of Demre, located on the Kaş-Finike road, in Antalya. Strabon writes that Myra is one of the 6 major cities, each with 3 voting rights in the Lycian League. The city was a rich and crowded metropolis, thanks to its port Andriake, which was an important point on the Mediterranean trade routes, and the fertile lands around it. It was the principal mint of the region and also led a sympolitea formed with Tyberissos and Teimiusa in the Late Hellenistic period. Myra preserved its metropolis status until the Byzantine period.
It was the most important political center of Lycia since the beginning of Christianity. St. Paul visited Myra and Patara in the 1st century BCE during his missionary journey. However, the city owes its real fame to St. Nicholas, who was born in Patara but founded his church in Myra in the 4th century CE to spread Christianity.
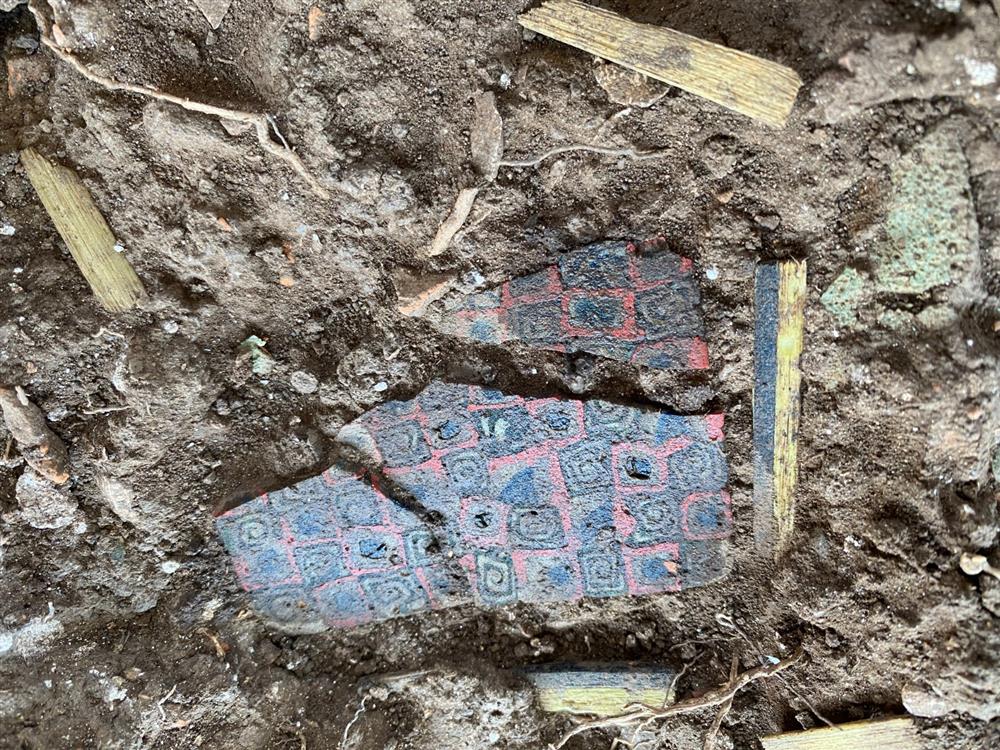
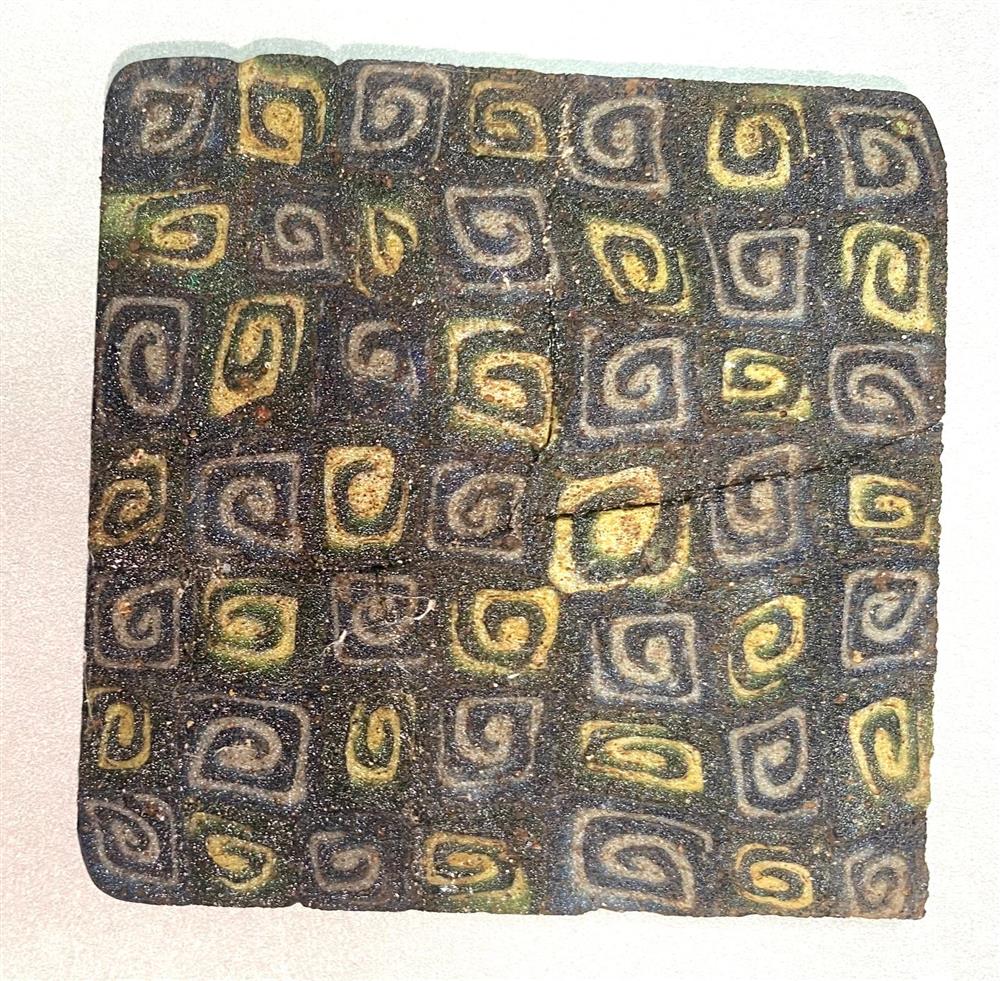
Excavations at Andriake recently uncovered a large number of decorative glass plaques created using the millefiori technique, a complex glassmaking process that involves fusing multiple glass rods of different colors to create intricate patterns that often resemble flowers or geometric shapes.
Considered by experts to be one of the most significant archaeological discoveries of the year in Turkey, millefiori have been found in other parts of the world, but this is the first time they have been found in such abundance and variety in the country.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The discovery was made in the agora area of Andriake, specifically in the customs zone of the port. In the space identified as “Structure 42”, archaeologists found hundreds of pieces of millefiori plaques.
It appears from this discovery that the elite community in Andriake in the fifth century AD possessed highly sophisticated ornamental arts, which were not only visually stunning but also symbolic of authority and rank.
In addition to being ornamental, the millefiori plaques found at Andriake are evidence of the sophistication and luxury of interior design during that era.
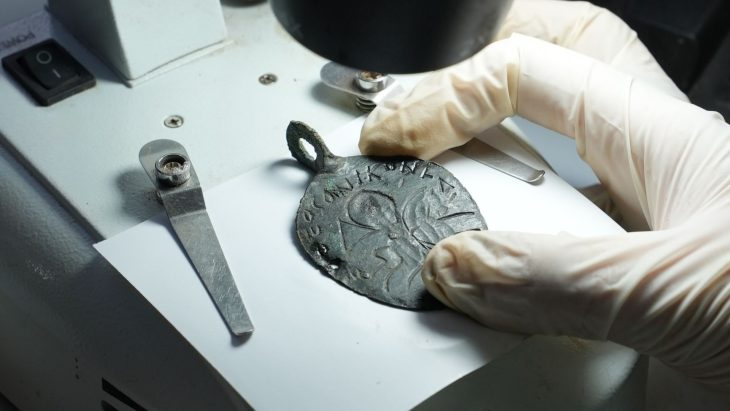
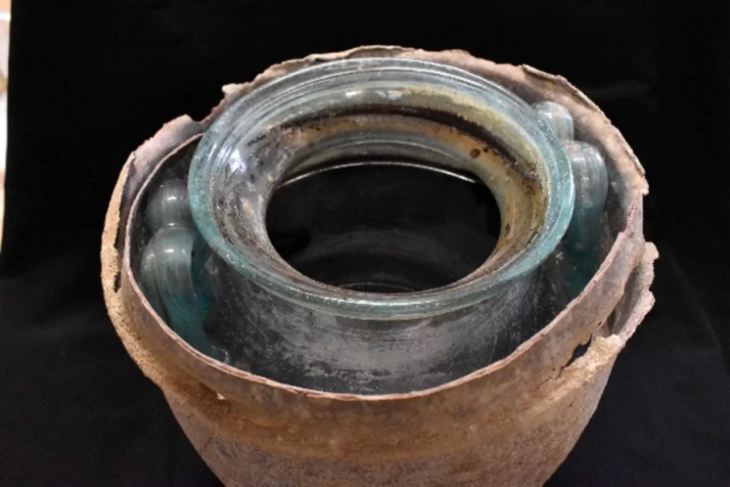
In addition to the millefiori glass plaques, other decorative elements were discovered in the same context. Among the findings are small glass rosettes with square and round forms, along with glass frames that go with the plaques, all of which point to a well-thought-out decorative scheme.
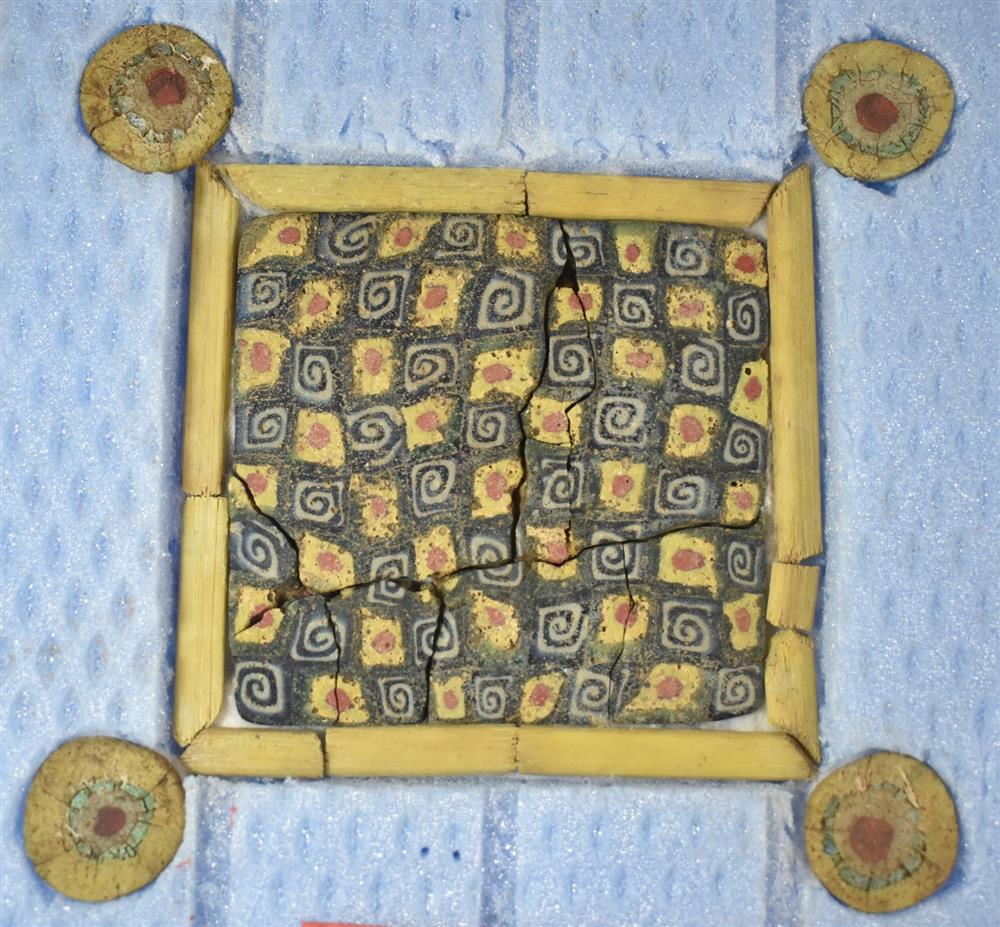

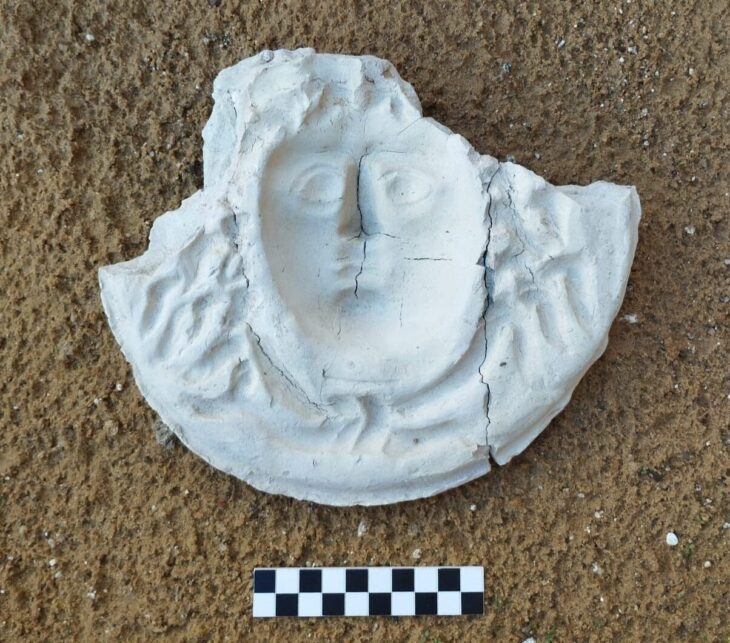
The discovery at Andriake, the harbor settlement of the ancient city of Myra, shows the presence of a very special and rich interior decoration at Andriake, with examples of bird figures in inlaid technique among the similarly sized plates that were found to have been used in wall decoration, and figures of saints, birds, and camels in opus sectile technique, which is also a unique discovery for Türkiye.
Located at the junction of the Granarium and Agora in Andriake, at the head corner of western Agora Street, in the most important place of the harbor, the building is thought to be an administrative building with its precious decorations and plan features.
Ministry of Culture and Tourism of the Republic of Türkiye
Cover Image: Ministry of Culture and Tourism of the Republic of Türkiye