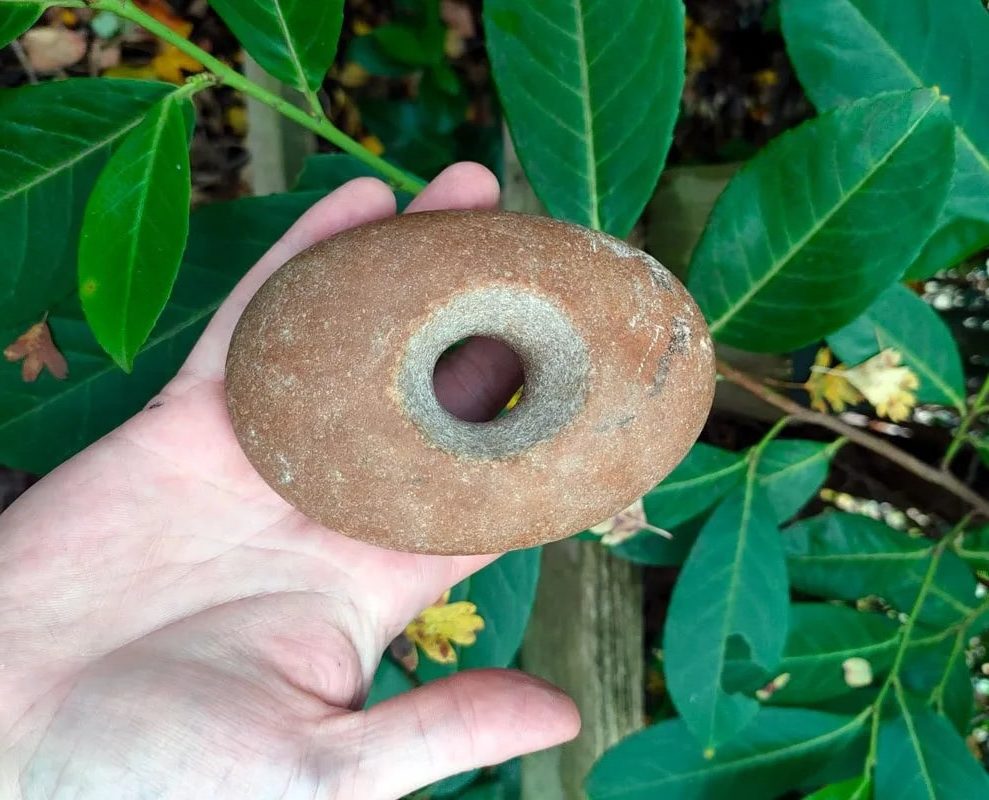
Archaeologists discovered an attractive Mesolithic stone mace head while excavation of a site near Buckingham. The work was done by Cotswold Archaeology as part of the work for the HS2 project.
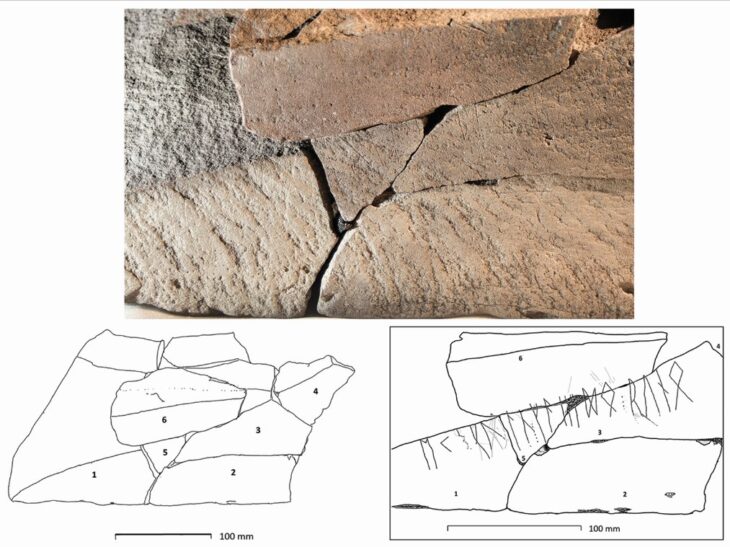
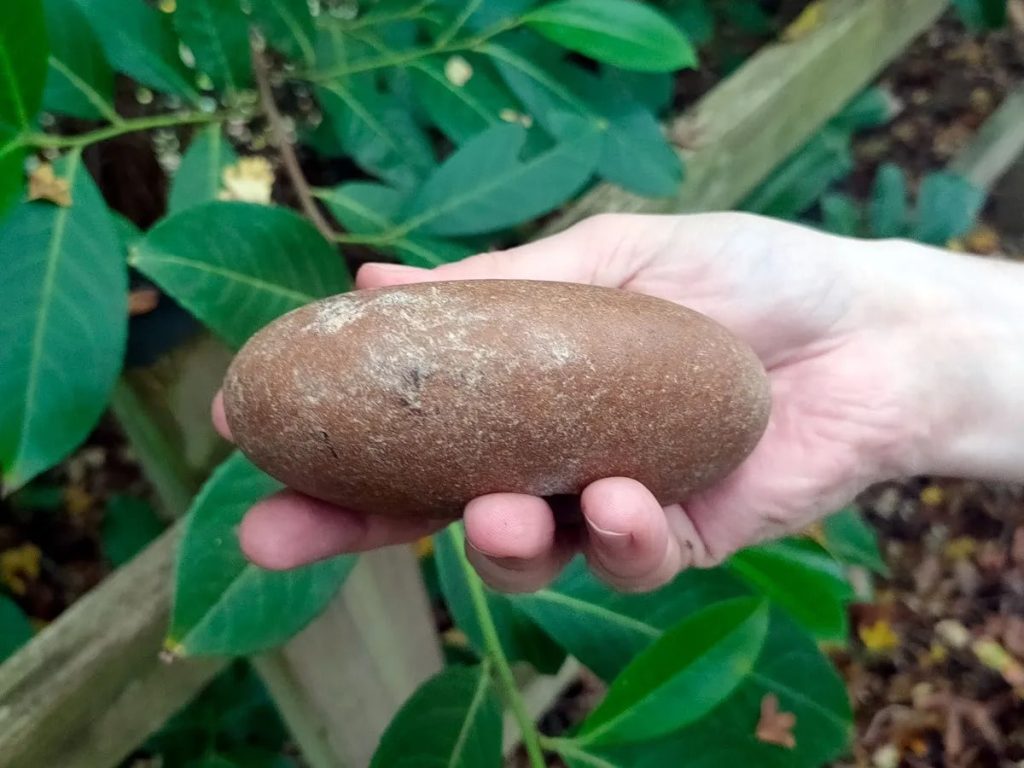
The quartzite pebble mace head discovered at the site is roughly oval in plan (105mm x 74mm x 40mm) with a central hourglass perforation (approximately 35mm-20mm in diameter). Both ends of the mace head exhibit light impact damage, suggestive of use as a percussive tool.
The object was hafted, as evidenced by minor wear at the narrow point of the central perforation. Small chip marks around the circumference of the central perforation suggest that it was made using a technique known as pecking, rather than having been drilled.
Unlike later Neolithic mace heads, which are worked to take a specific shape, these Mesolithic objects take the shape of the raw material. Similar pebble mace heads have been found in Britain, including Eton Rowing Lake in Berkshire and Oakhanger in Hampshire, and they are thought to date from the Mesolithic period.

Mesolithic hunter-gatherer activity is thought to have been concentrated in resource-rich areas such as woodland and along watercourses, with recorded sites mostly located on dryer, rising ground. The site was in such a location, on a tributary of the River Great Ouse.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
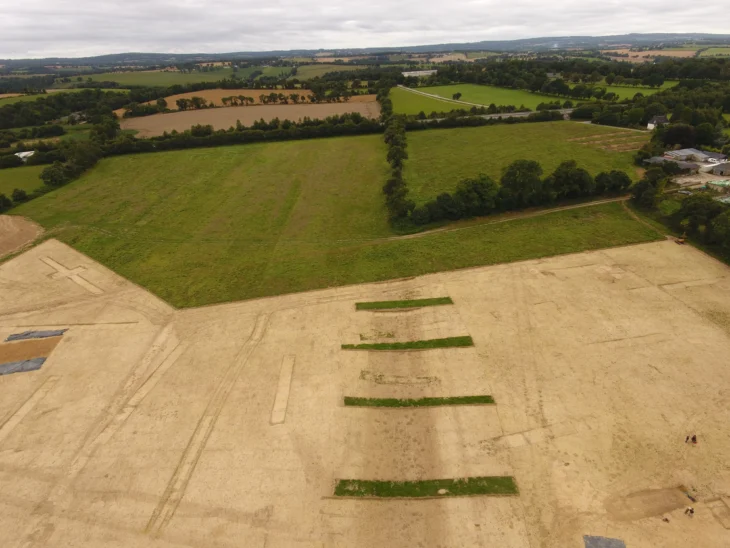
The mace head was found in a post-medieval quarry fill that had cut off a curving ditch. With the mace head coming from a truncated internal deposit, it’s possible that this ditch was once part of a prehistoric ring ditch.
Using aerial photography, two more ring ditches, possibly representing Bronze Age round barrows, have been identified nearby, and two more ring ditches, as well as Bronze Age cremation burials, are known from the surrounding area.