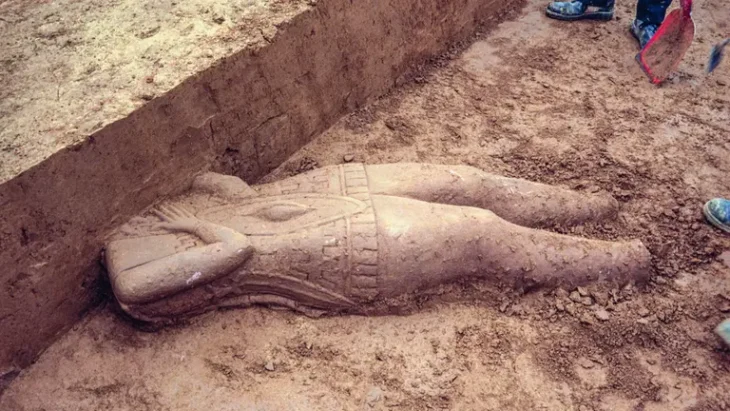
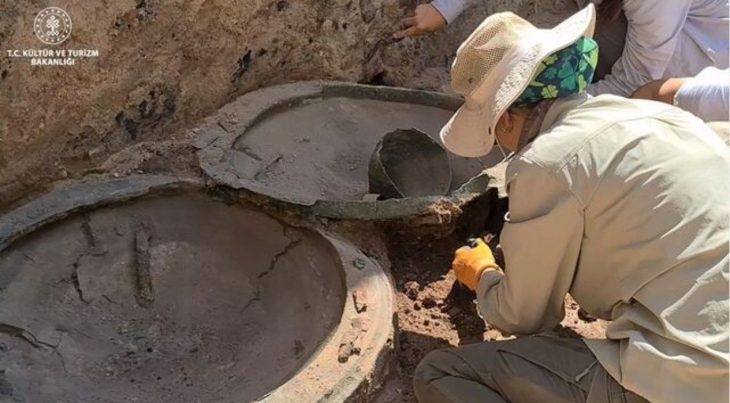
In an archaeological find in the El Caño Archaeological Park, located in the district of Natá, province of Coclé, in Panama, a tomb has been discovered that sheds light on the sophisticated Coclé society of pre-Hispanic times.
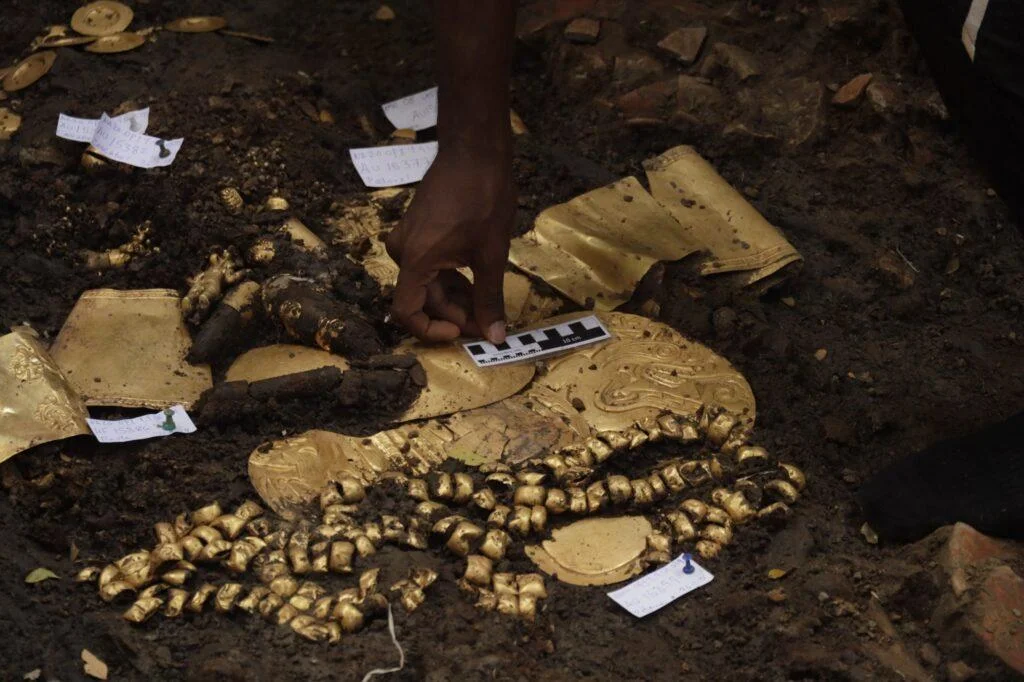
The tomb thought to belong to a Coclé lord and dating back to 750 CE, was found to contain a wealth of funerary offerings, including ceramic and gold artifacts.
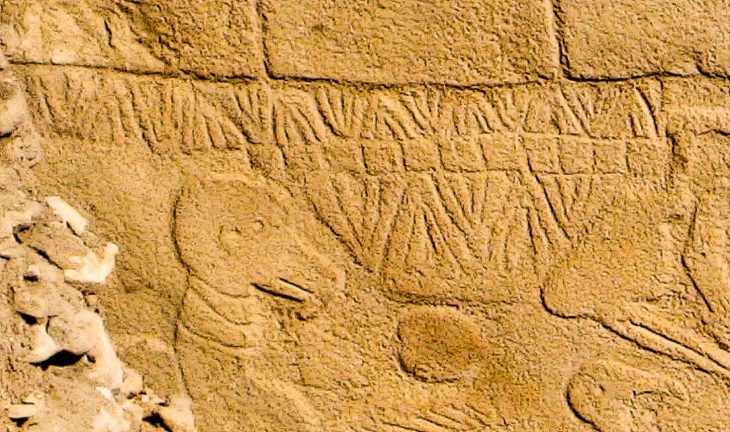
The El Caño Archaeological Park is well-known for its necropolis of tombs and stone monoliths that date back to 700–1000 CE. American explorer Hyatt Verrill first realized the importance of the site in 1925 when he discovered ancient monoliths beside the Rio Grande River.
Linette Montenegro, National Heritage Director of the Ministry of Culture (MiCultura), explained that this discovery is part of the ongoing archeological project in the park.
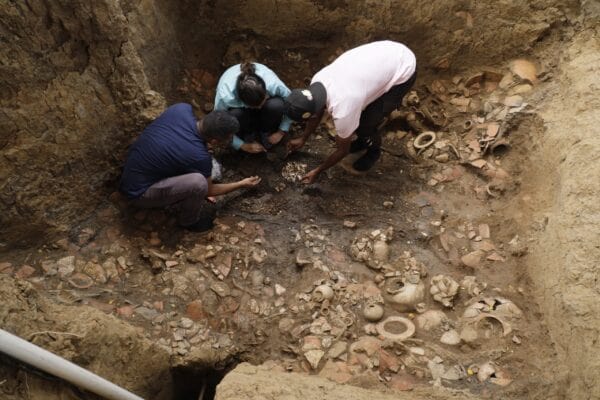

The project, started in 2022 and financed through a cooperation agreement between the Ministry of Culture and the El Caño Foundation, aims to thoroughly explore Tomb No. 9 during the 2021-2024 campaigns.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
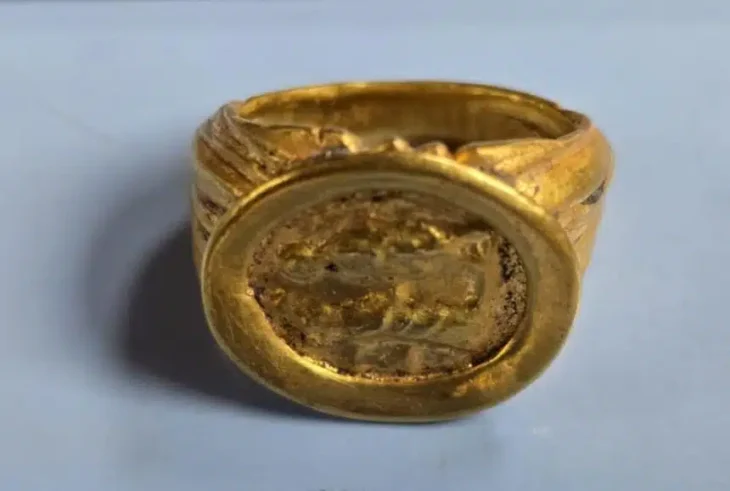
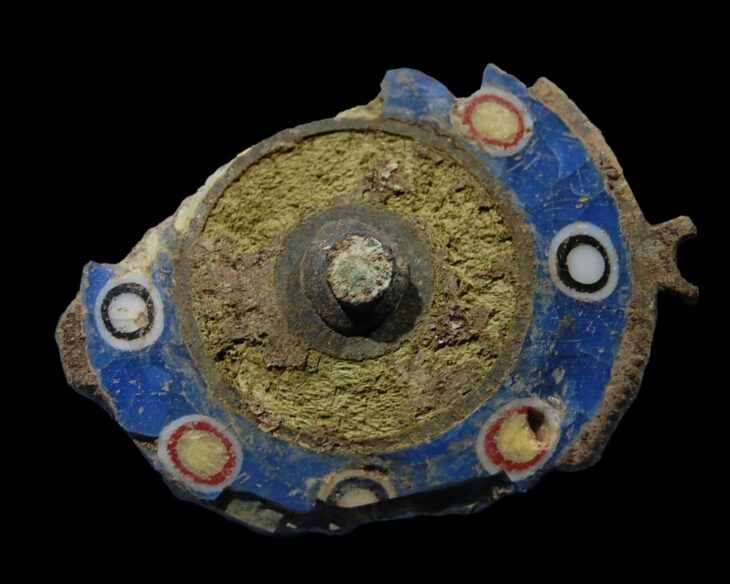
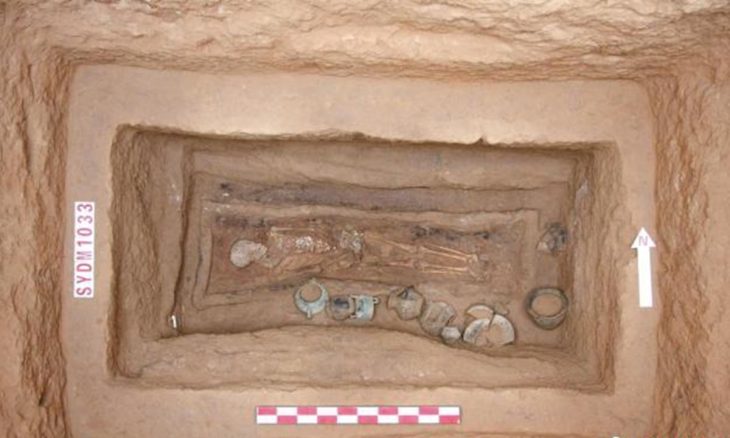
The tomb’s contents, consisting of 5 pectorals, 2 belts of gold beads, 4 bracelets, 2 earrings in the shape of human figures, an earring in the shape of a double crocodile, 1 necklace of circular beads, two bells, bracelets, and a skirt made with dog teeth, and a set of bone flutes, is testimony to the cultural and social wealth of the Coclé society.
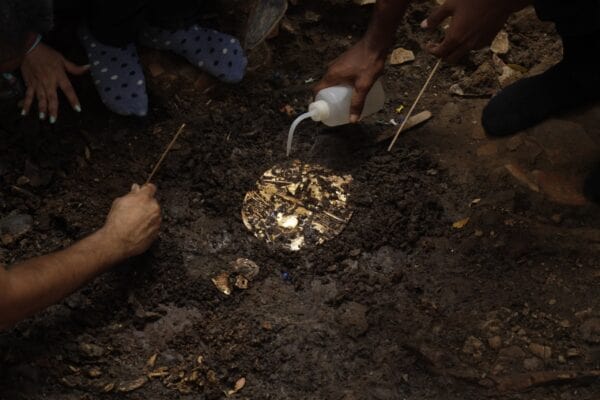

Dr. Julia Mayo, director of the El Caño Foundation and leader of the archaeological project since its inception in 2008, highlighted the importance of this discovery.
The collection, which probably belonged to a high-status adult male, represents a window into life and death in the Rio Grande chiefdom. The tomb, built around 750 A.D., is especially intriguing due to the presence of sacrificial attendants buried alongside the lord, indicating multiple and simultaneous burial practices.
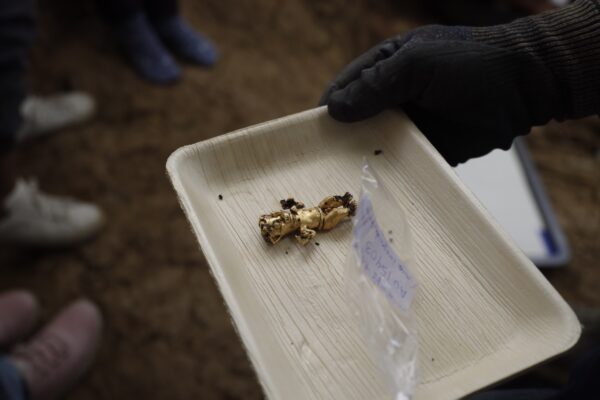

Dr. Mayo noted that the excavation process is ongoing, making it difficult to determine the exact number of individuals buried within the tomb. She said that this type of burial, known for burying a variable number of people in the same tomb, provides valuable information about the beliefs and funerary rituals of the Cocle society.
Dr. Mayo explained that the Coclé lord was buried in a face-down position, a customary practice in this culture, often atop the remains of a woman.
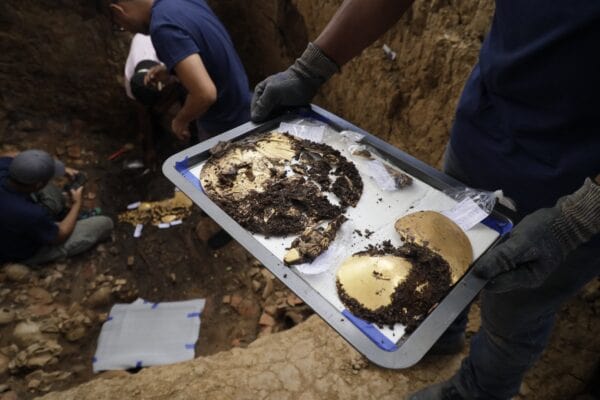

El Caño Archaeological Park, built around 700 A.D. and abandoned around 1000 A.D., has yielded significant archaeological discoveries. In addition to the known monoliths, the site includes a cemetery and a ceremonial area with wooden structures. This discovery stands out for its uniqueness and the insight it provides into Cocle society’s funerary practices.
Cover Photo: Ministry of Culture of Panama