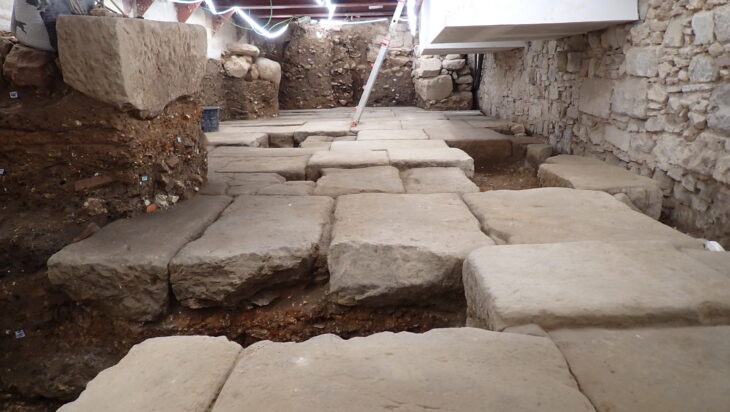
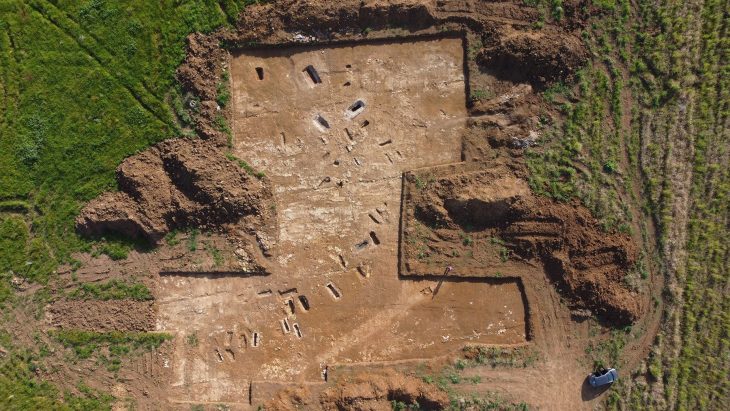
According to a new study, two warriors from the 7th century in Sweden were buried in graves where they were laid on beds made of various feathers.
The Valsgard Cemetery near Uppsala in central Sweden is famous for its 600 and 700 CE ship tombs. It is home to about 90 cemeteries during the Merovingian period (the pre-Viking era).
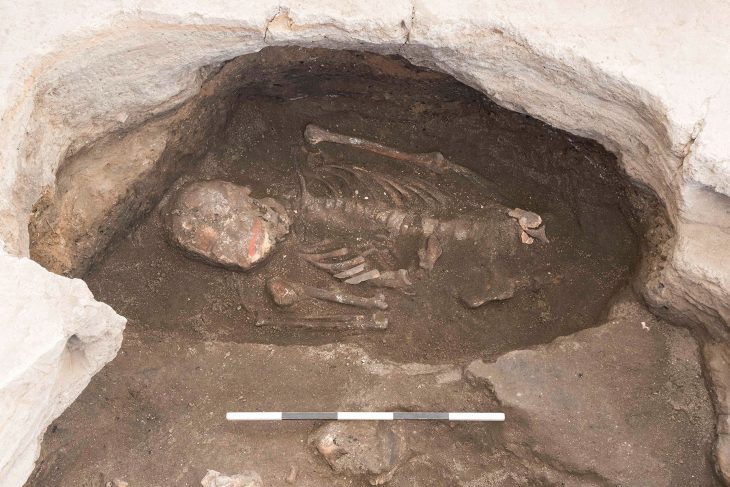
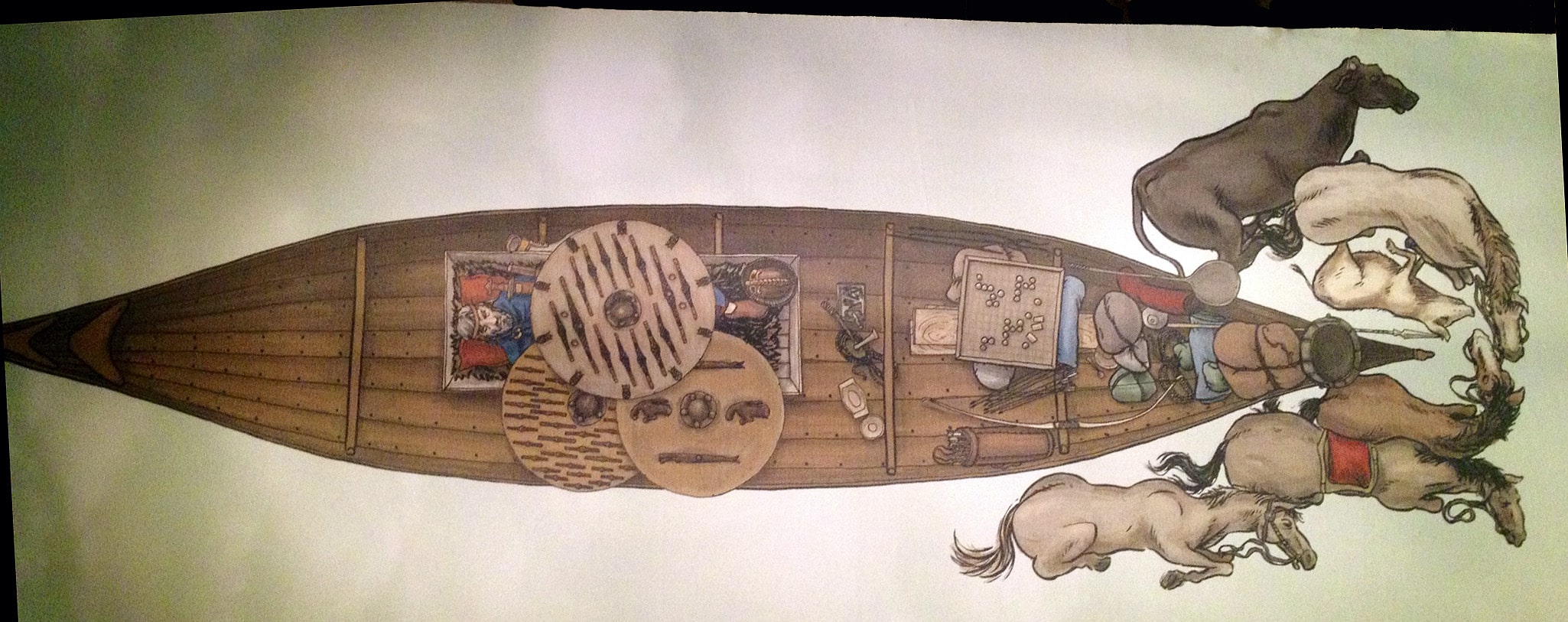
The warriors were also buried in their boats with ornate helmets, shields, and weapons, and even game pieces that scientists said, along with several layers of bedding, would make the journey “to the land of the dead” easier.
Researchers from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology’s NTNU University Museum examined the boat graves of two people thought to belong to high-ranking warriors.
The boats were about 10 meters long and had room for four to five pairs of oars, and were equipped with provisions, cooking, and hunting tools for their final voyage, and animals, including horses, lay close to the ships.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The buried warriors appear to have been equipped to row to the underworld, but also to be able to get ashore with the help of the horses,” Birgitta Berglund, professor emeritus of archaeology at the NTNU University Museum, said in a statement.
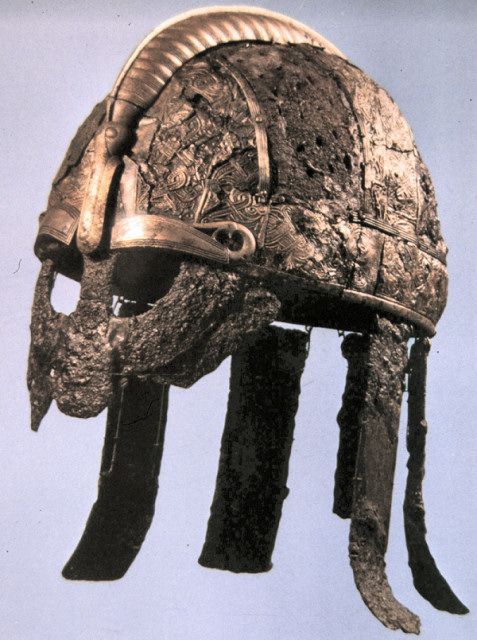

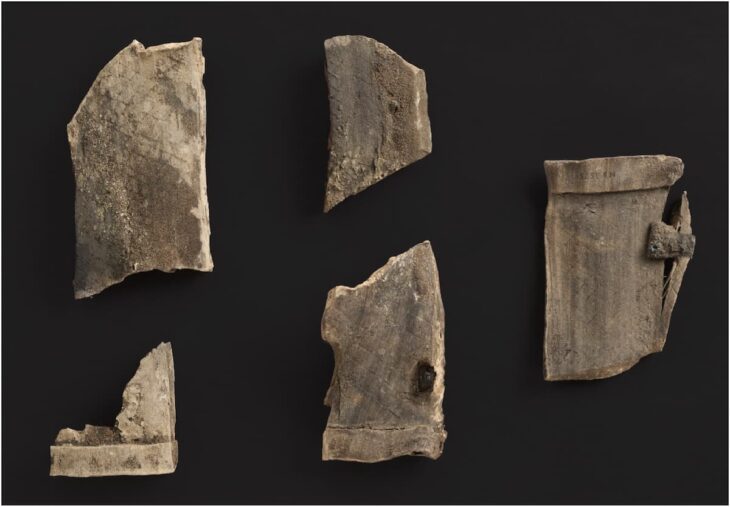
“Beauty sleep was also taken care of in death. Down bedding was found under the two warriors,” Berglund said.
Berglund said that while wealthy Greeks and Romans had used down in their bedding a few hundred years earlier, down bedding was not widely used by rich Europeans until the Middle Ages.
Experts say that the contents of the bedding served to do more than just fill the boat– and that the down bedding, the oldest known from Scandinavia, could indicate that warriors belonged to the top echelons of society.
Microscopic analysis of the bedding showed it contained feathers from geese, ducks, grouse, crows, sparrows, waders, and — and to the researcher’s surprise — eagle owls.
“I’m still surprised at how well the feathers were preserved, despite the fact that they’d been lying in the ground for over 1,000 years,” biologist Jørgen Rosvold, who studied the feather material, said.
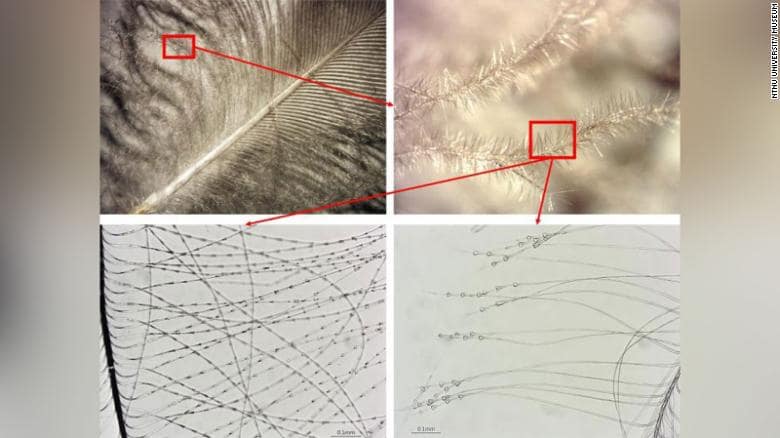

According to Berglund, in Nordic folklore, the type of feathers in the bedding of a dying person was important.
“For example, people believed that using feathers from domestic chickens, owls and other birds of prey, pigeons, crows, and squirrels would prolong the death struggle. In some Scandinavian areas, goose feathers were considered best to enable the soul to be released from the body,” she said.
Experts also found a beheaded Eurasian eagle-owl in one of the graves, and say that because similar measures were taken to stop the more recently buried from returning from the dead, it is conceivable they could have been done earlier.
“It’s conceivable that the owl’s head was cut off to prevent it from coming back. Maybe the owl feather in the bedding also had a similar function?” she said. In some Viking burials, swords were bent before they were buried with a warrior to stop them from being used if the warrior were to wake, researchers noted.
“In Salme in Estonia, boat graves from the same period have recently been found that are similar to those in Valsgärde. Two birds of prey with a severed head were found there,” Berglund said.
The team describes Valsgärde as a Scandinavian answer to Sutton Hoo – the famous English burial site near Woodbridge in Suffolk, which is the subject of the Netflix movie The Dig.
The research was published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports.