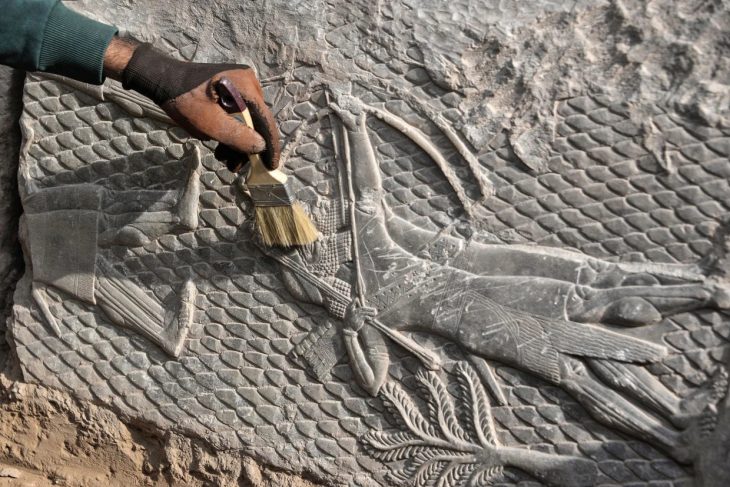
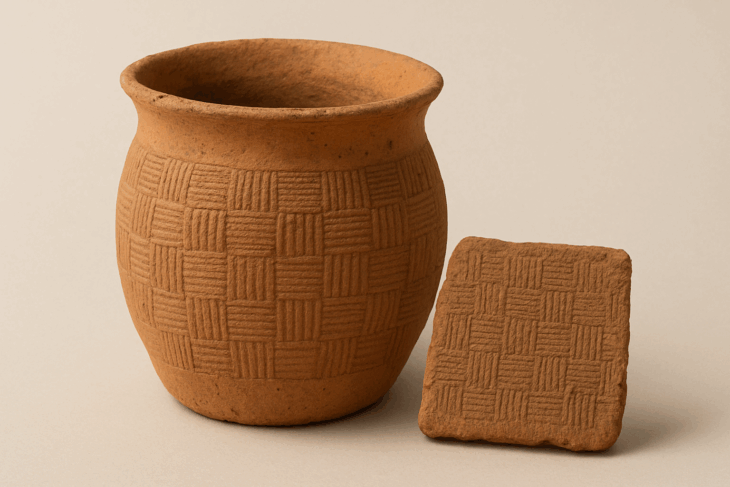
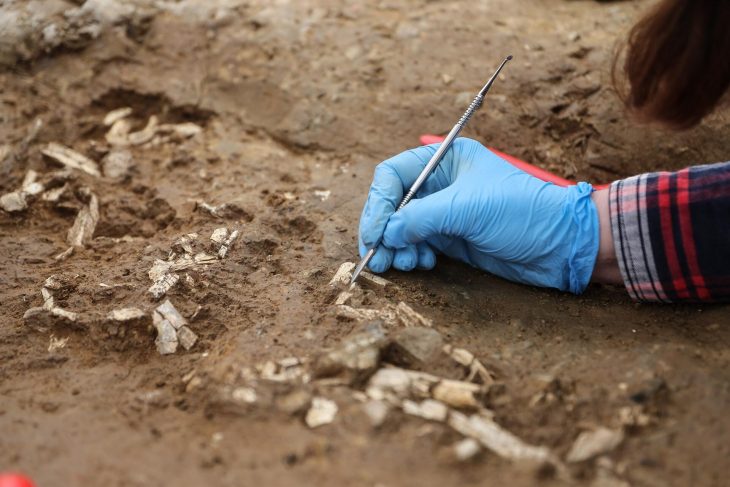
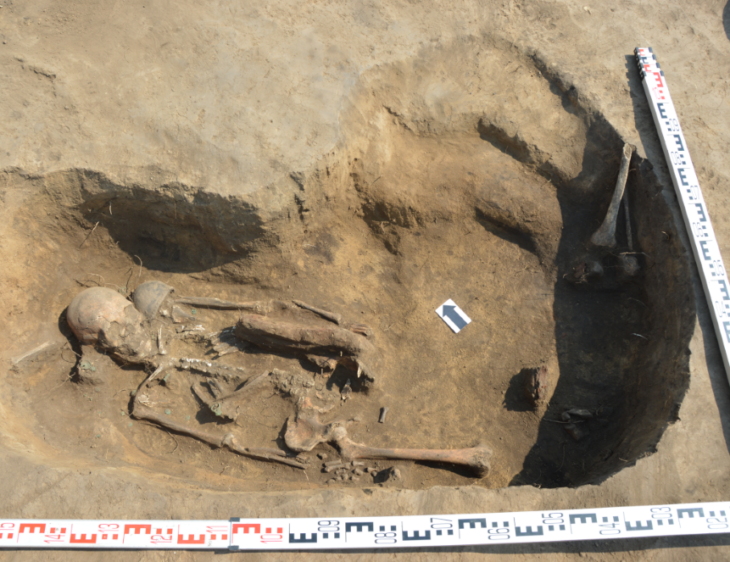
Archaeologists have uncovered the long-lost remains of one of the most important medieval Jewish centers in southern Germany.
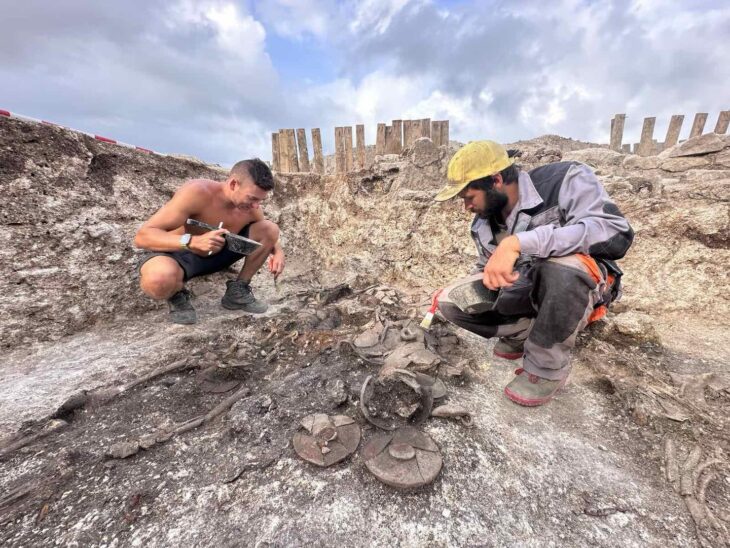
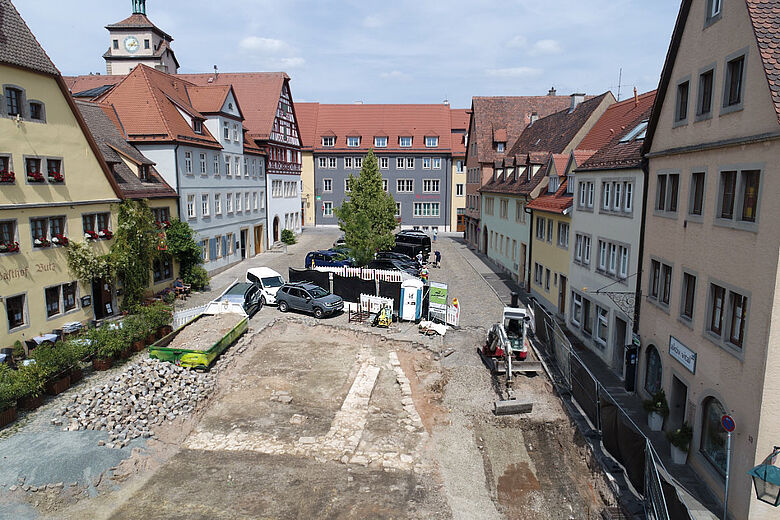
Excavations at Rothenburg’s Kapellenplatz revealed the foundations of the city’s first synagogue, built around 1180, offering a rare glimpse into a once-thriving hub of Jewish scholarship and culture that shaped Central Europe during the Middle Ages.
A Forgotten Landmark Comes to Light
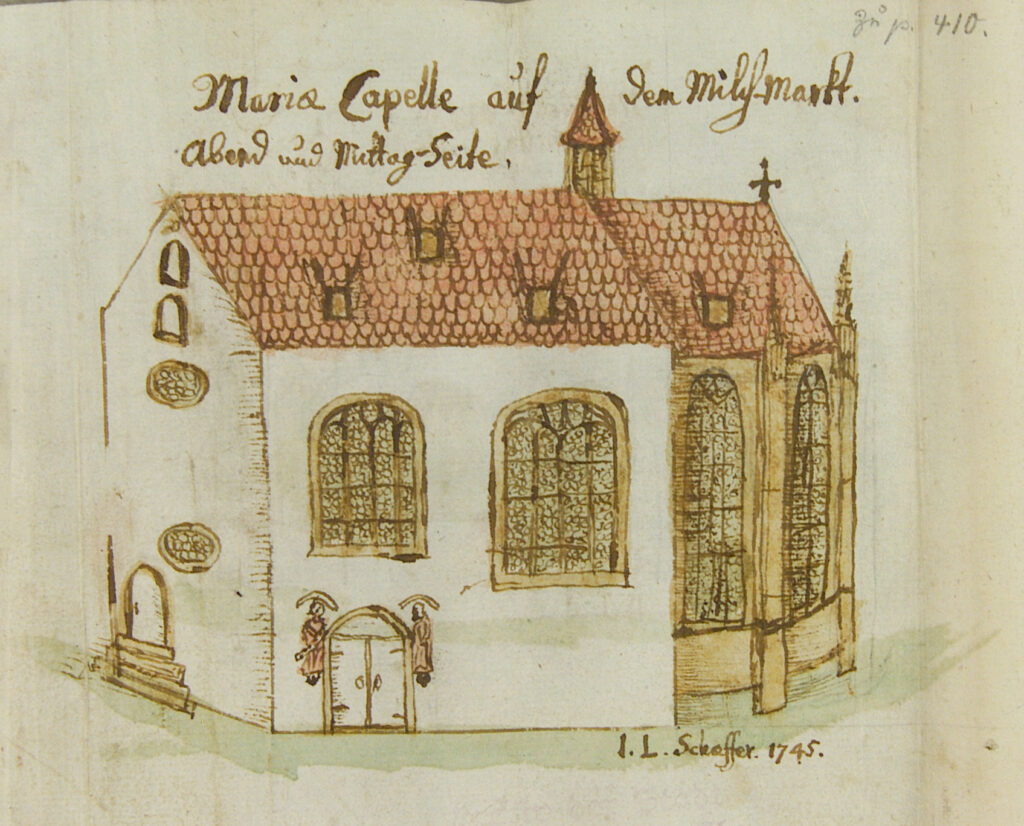
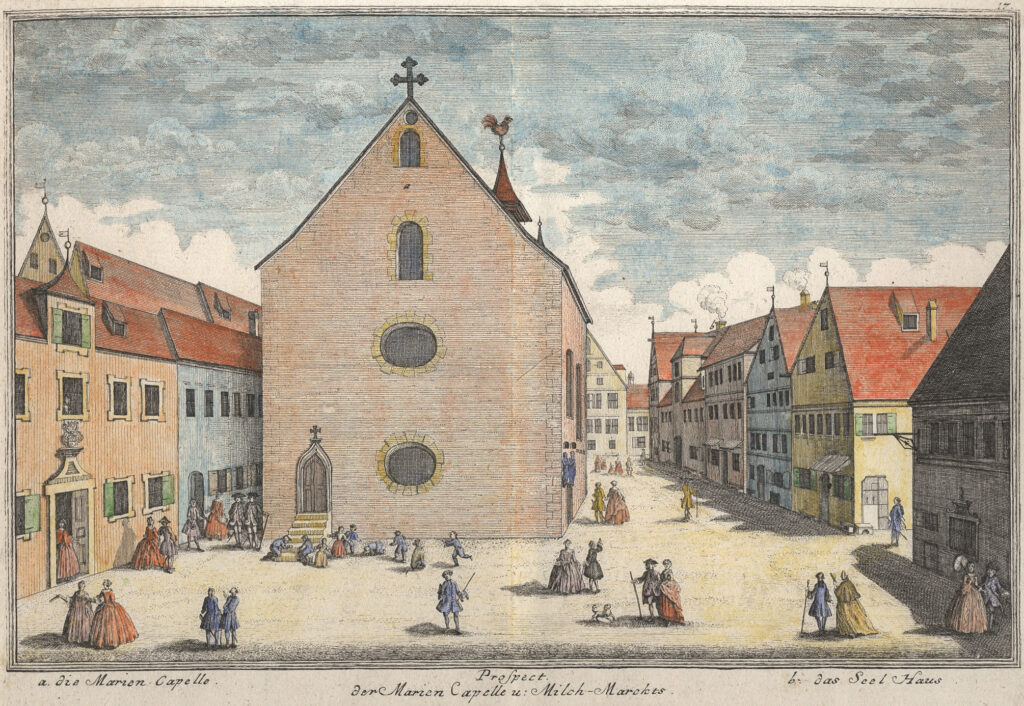
For centuries, the exact location of Rothenburg’s first synagogue had remained a mystery. Historians knew of the building from 18th-century drawings, but no physical evidence had survived above ground. Now, during redevelopment work at Kapellenplatz, archaeologists exposed massive limestone foundations that align precisely with those historic depictions.
According to the Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Monuments (BLfD), which oversaw the excavation, the discovery leaves little doubt: these are the remains of Rothenburg’s original synagogue, a freestanding Romanesque hall that once dominated the cityscape.
Prof. Mathias Pfeil, General Conservator at the BLfD, emphasized the significance of the find:
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The synagogue was long thought to stand elsewhere in the city. Its rediscovery highlights the invaluable role of archaeological heritage protection. Only through such investigations can we continue to piece together the complex history of European Jewry.”

A Center of Jewish Learning – and Tragedy
In the late 12th and early 13th centuries, Rothenburg was home to one of the most influential Jewish communities in southern Germany. Scholars and rabbis from the city left their mark on Jewish law and education far beyond the region. The synagogue stood at the heart of this flourishing life.
Yet the building’s history also reflects persecution and loss. During the devastating pogrom of 1349, at the height of the Black Death, Rothenburg’s Jewish quarter was destroyed. The synagogue, seized by the city, was later sold to a local patrician in 1404 and converted into the Marienkapelle (Chapel of St. Mary) in 1406/07. While much of the core structure survived, Gothic elements such as an apse were added.
The chapel remained in use until 1805, when it was demolished during secularization, erasing the last visible traces of the medieval synagogue.
Layers of History Beneath the City
The rediscovery has sparked renewed interest in Rothenburg’s layered Jewish past. Mayor Dr. Markus Naser underlined the importance of the find for the city’s historical identity:
“These massive foundations vividly demonstrate Rothenburg’s role as one of the great Jewish centers of medieval southern Germany. But they also remind us of the darker chapters of our history. Preserving and researching this heritage is essential to our collective memory.”
While the newly uncovered remains provide strong evidence of the synagogue’s form and location, many questions remain unanswered. Scholars are still debating the building’s precise construction date and early architectural history. It is also unclear whether the complex once included a separate women’s synagogue, which may have been removed during its conversion to a chapel.

Preservation for Future Generations
To protect the site, excavations were limited to the areas required for the Kapellenplatz redevelopment project. The remaining portions of the structure will stay preserved beneath the new pavement. In a symbolic gesture, the surface design of the square will mirror the footprint of the medieval synagogue, ensuring that its presence remains visible to residents and visitors alike.
The discovery adds a vital chapter to the history of Jewish life in Franconia and southern Germany. Although Rothenburg’s Jewish community never regained its medieval prominence after 1349, a new congregation did emerge in the following centuries. By the 15th century, Jewish life shifted northward to the Judengasse, where the city later built a more modest synagogue on what is today Schrannenplatz.
A Monument of Shared Heritage
Experts stress that the Rothenburg synagogue is not only a local landmark but also part of a broader European story. The building’s rediscovery sheds light on the architectural, religious, and cultural contributions of Jewish communities before their destruction or displacement in the wake of plague, persecution, and political change.
For the BLfD and the city of Rothenburg, the find underscores the enduring importance of protecting buried monuments. “Every excavation brings to light more than just stones,” said Pfeil. “It helps restore voices and lives that shaped Europe’s shared history.”

Looking Ahead
Plans are underway to integrate the synagogue’s story into Rothenburg’s cultural tourism and educational initiatives. With its medieval Old Town already drawing visitors from around the globe, the city hopes the rediscovered synagogue will become a focal point for dialogue about Jewish heritage, coexistence, and remembrance.
As archaeologists continue to analyze the finds, one thing is certain: the “lost” synagogue of Rothenburg has once again become part of the city’s living history – a reminder of both the richness and fragility of Europe’s Jewish past.
Bayerisches Landesamt für Denkmalpflege (BLfD)
Cover Image Credit: Bayerisches Landesamt für Denkmalpflege – KT Kohler & Tomo Archaeology