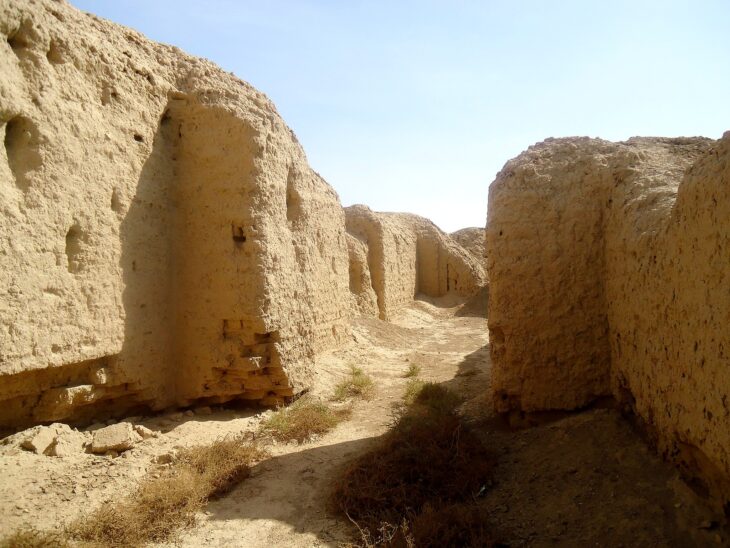
Ancient Susa is one of the oldest cities in the world. The Elamite, Persian, and Parthian empires formerly ruled over the UNESCO-designated city, which is now bordered by the contemporary city of Shush.
Susa is named Shushan in the Book of Esther and other Biblical writings. It is located in the lower Zagros mountain range, some 250 kilometers east of the Tigris river and between the Kharkeh and Dez rivers.
Archaeological evidence suggests that Susa has been continuously inhabited since 4200 BC. Moreover, in Susa, there are traces of a village inhabited around 7000 BC.
Susa’s potters created unrivaled quality pottery in an early period, which they adorned with patterns of birds, mountain goats, and other animals. The city became the capital of Elam in the fourth millennium (the “Uruk Period”) and was able to compete with Sumerian and Akkadian cities in southern Iraq at times.
The city itself expanded eastward to the part of the city that is now called the Royal City. From the written information, we know that there must be a ziggurat. The third part is the artisan area, located further east.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
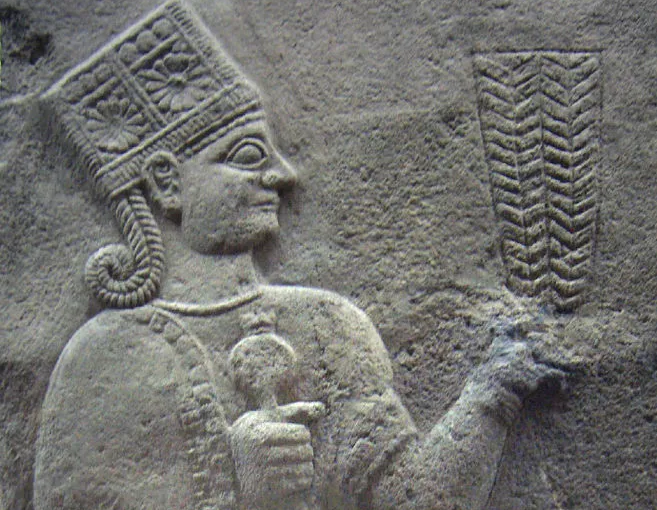
The kings of the Awan dynasty ruled Elam in the last third of the third millennium; they were contemporaries of Sargon of Akkad’s dynasty, which was able to briefly absorb Susa into his kingdom. However, the Awan kings managed to regain their freedom.
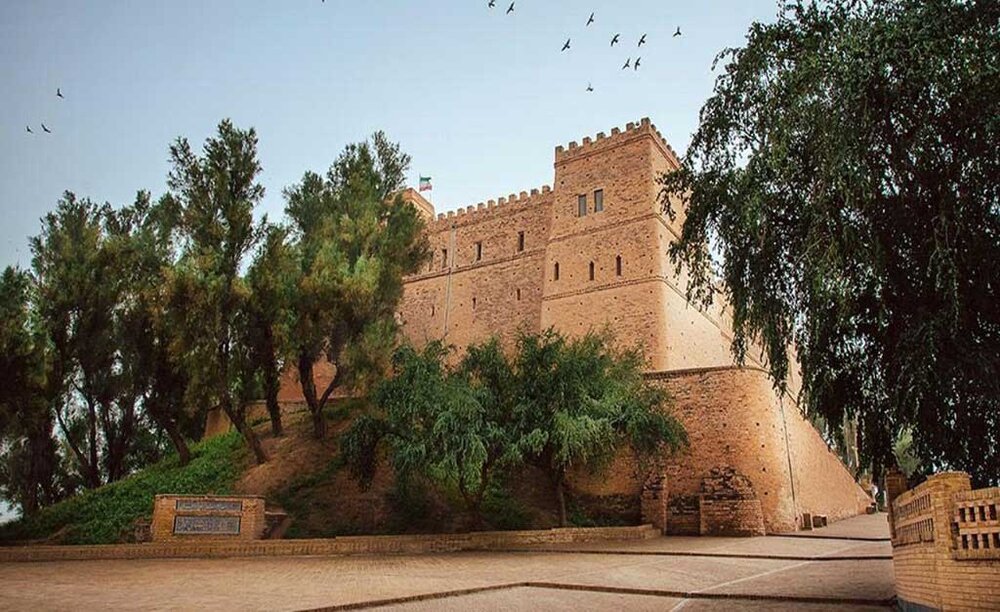

When the Gutians descended from the mountains and wreaked devastation on the alluvial plains of Elam and Mesopotamia, the Awan kingdom fell apart.
Elam became autonomous again after the disintegration of the Old Babylonian Empire, and a new dynasty, most likely from Anšan, took control in Elam. The Kidinuids were eventually supplanted by the Igehalkids and the Šutrukids. Susa flourished the most under these dynasties.
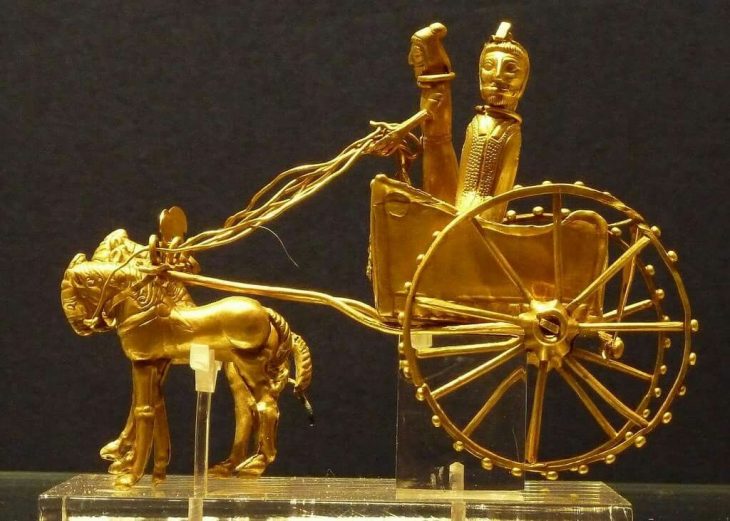
Susa after being conquered by Cyrus the Great, was used as the winter home of Persian rulers. In 538 or 539 BC, Cyrus II, the Great incorporated Susa into the Persian Empire.
King Darius the Great (522-486), one of his successors, constructed one of his palaces at Susa. The palace’s inscription, known as DSf, chronicles Darius’ construction. Susa was without a doubt his favorite palace. Another capital was unknown to Herodotus of Halicarnassus, a Greek scholar who wrote extensively on the Achaemenid empire.
According to said, Alexander of Macedonia captured Susa in 330 BC, plundered the city, and seized approximately 40,000 talents gold and silver from the treasury. Alexander the Great’s preference for Babylon kicked off Shushan’s decline, and soon after, after a rebellion, the city was razed to the ground. It was subsequently rebuilt by Sapor II (309-379 AD) and renamed Iranshahr Shapur, and later helped resist the Arab invasion in 645.
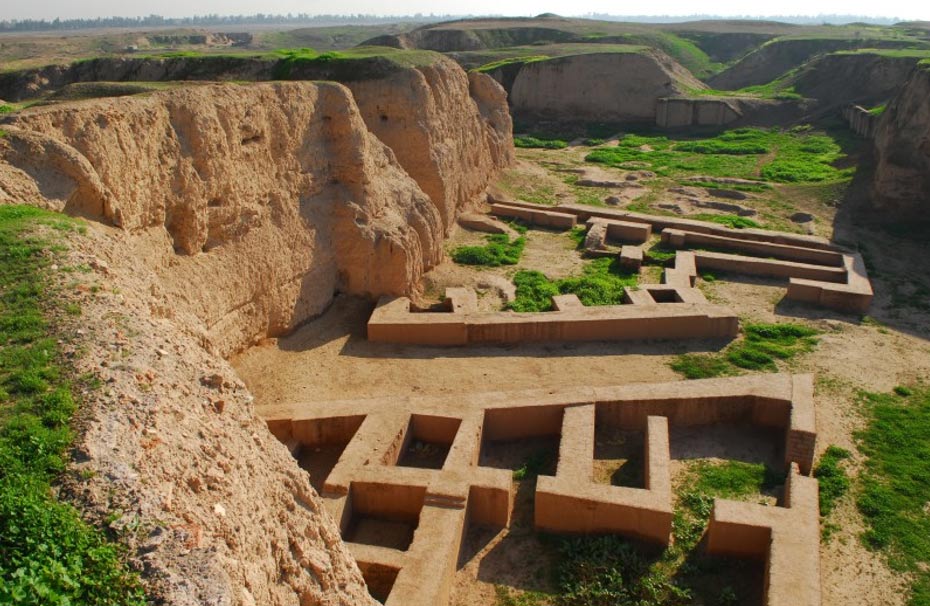

The city became part of the Seleucid empire with the collapse of the Achaemenid Empire and the marriage of Alexander the Great, who was reign at Susa. On Eulaeus, it was now known as Seleucia. Next to Darius’ palace, a Greek-style palace was built. The administrative center, on the other hand, was located in the city’s southern section, where almost all Greek and Parthian inscriptions were unearthed. In the Parthian age, the city minted coins.
During the Sassanid era, the city had a large Christian population. It was ransacked by Sassanian King Shapur II, who transferred the population to Iwan-e Karkheh.
Susa was still one of the important cities until the 13th century AD.

Susa in the Bible
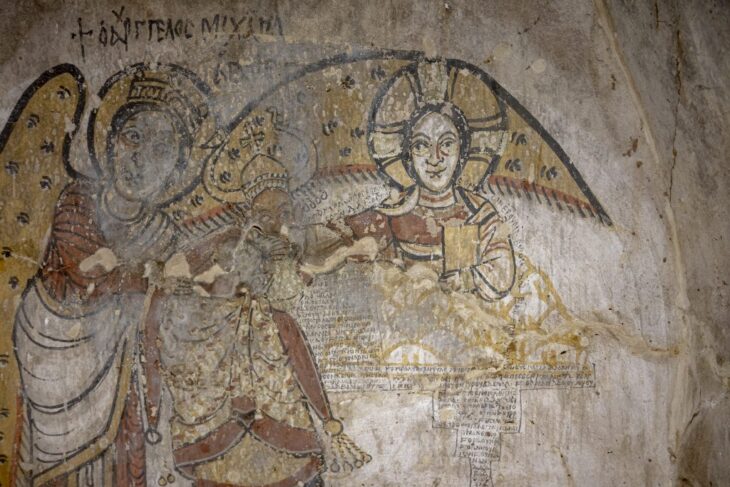
Susa is well known in the Bible from the tale of Esther, in which Haman the Agagite plots to destroy the Jews of Persia. According to the legend, Esther outwitted Haman by convincing her husband, King Ahasuerus of Persia, to thwart Haman’s plot. According to Ancient Origins, the episode is commemorated each year during the Jewish Purim festival, which is characterized by costumed parties and other celebrations.
Susa is also referenced in the books of Nehemiah and Daniel, both of whom resided in the city during the 6th century BC, during the Babylonian captivity, when numerous Jews were taken hostage following Nebuchadnezzar’s assault of Jerusalem. The Shush-Daniel tomb is said to be that of Daniel himself. It is capped by an unusual white cone which some believe was formerly a stone ‘Star of David’.
Susa was also linked to Daniel’s vision of a ram and a goat in Belshazzar’s third year. Shushan, according to Esther, formerly possessed a splendid palace with a huge hall made up of majestic columns and an extremely striking facade. The palace was erected by the Persian kings Darius and Artaxerxes, according to inscriptions unearthed in the remains. Colored glazed brick panels may still be seen in the remains today, while wood from Lebanon, teak from Gandara, and gold from Sardis and Bactria are all mentioned in various sources.
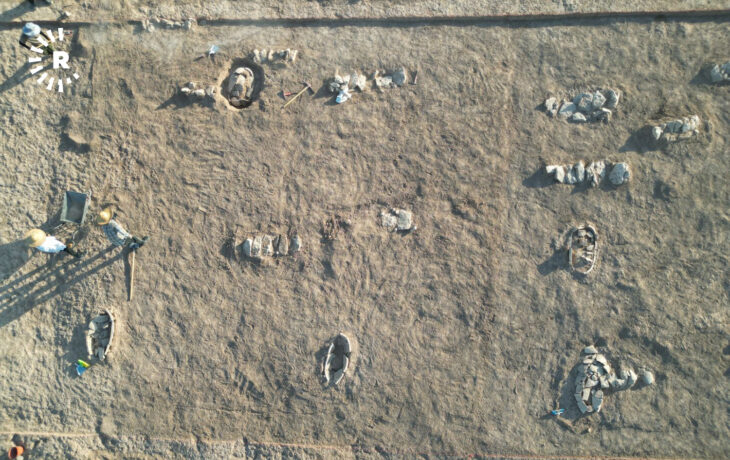
Following some preliminary soundings in 1854, systematic excavation began in 1884. The French archaeologists, led by Jacques de Morgan, erected a Crusader-style fortress to defend themselves. Research has continued into the twentieth century. Unfortunately, remains were partly destroyed during the First Gulf War.
Source
R. Boucharlat, “Suse à l’ époque sassanide”, in: Mesopotamia 22 (1987) 316-322
R. Boucharlat, “Suse et la Susiane à l’ époque achémenide. Données archéologiques”, in: Achaemenid History 4 (1990) 149-175