Archaeologists from the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) have discovered a nose ornament made of human bone in the ancient Mayan city of Palenque in Mexico.
The discovery was uncovered during excavations at House C, part of a palace complex built by Pakal the Great, the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) said in a statement.
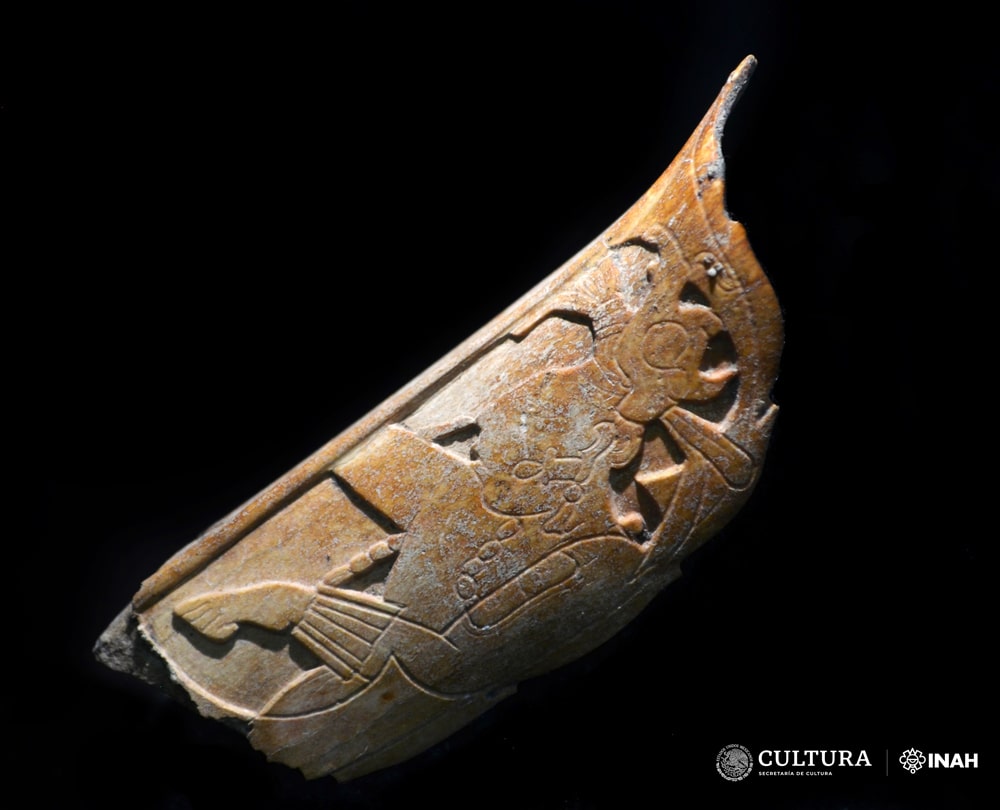
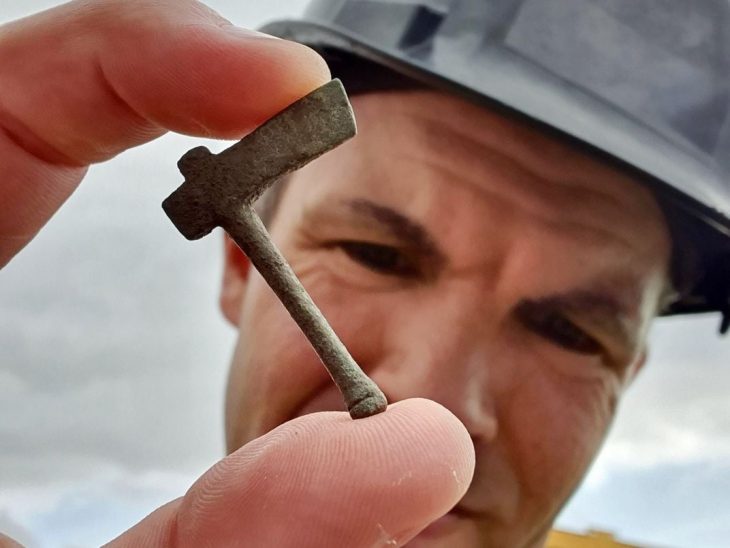
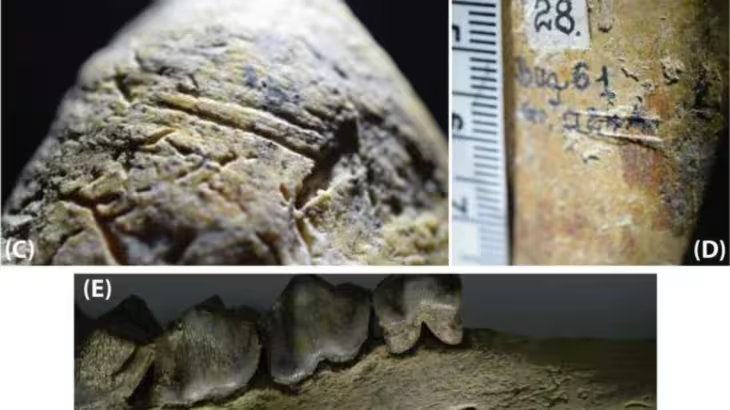
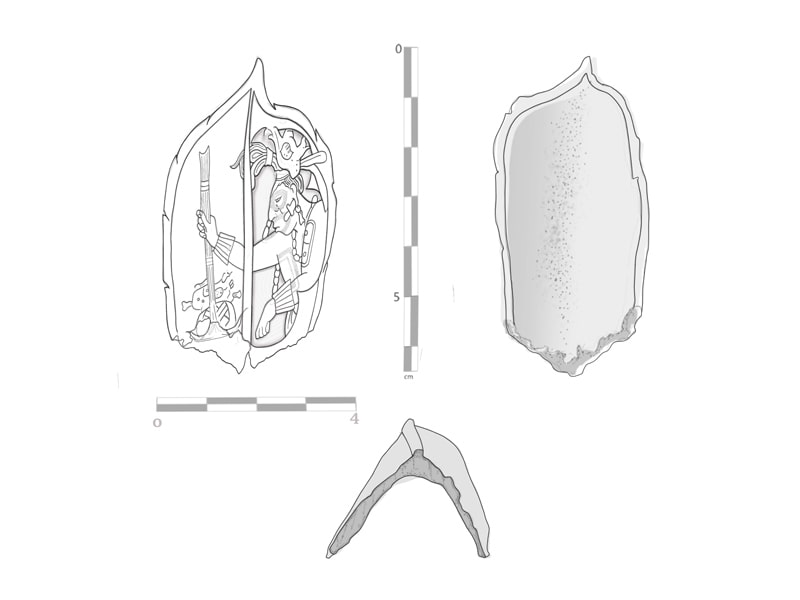
The nose ornament was made with part of a human distal tibia and is engraved with a scene that expresses communication with the gods and ancestors.
For the first time in the history of explorations in the Archaeological Zone of Palenque, in Chiapas, a nose ornament with an eloquent carved scene was located, an attire made of human bone worn by rulers and priests of this ancient city, during ceremonies in which they embodied K’awiil, the Mayan god of maize and fertility.
The Maya often depicted Kʼawiil holding the promise of “Innumerable Generations” who was part of the Maya rulers ritual inauguration and accession to the throne.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The nose ornament that researchers found formed part of a ritual deposit that has been dated to the Late Classic period (600 and 850 A.D.) of Mesoamerican history.
The ancient ornament was found in a stucco floor, where the researchers discovered a pit filled with clay soil and the remains of charcoal. The team also discovered animal remains, obsidian blades, pieces of a bone awl, and a human bone nose ring while sorting the filling’s contents.
According to a press announcement by INAH: “The earth matrix was very dark with a high amount of charcoal and intermingled with seeds, fish bones, turtles, small mammals, obsidian blades, some large pieces of charcoal and, among them, a bone nasal ornament.”
Artifact is of notable aesthetic merit due to its composition; as well as the firmness, precision, and combination of its carving lines, executed in just 6.4 centimeters long by 5.2 wide, and a thickness of 5 centimeters at the bottom, which decreases towards the top.
The nose ring is made with part of a human distal tibia which forms the bony structure of the ankle joint and features a precisely carved scene. In one section of the artifact, the profile of a man can be seen wearing headgear shaped like the head of a bird. In another section, a representation of a human skull without a lower jaw is visible. On the left arm it shows the Mayan glyph ak’ab’, “darkness” or “night”.
According to Arnoldo González Cruz, the director of the Palenque Archaeological Project (PAP), “one of the characteristic features of the divinity is the shape of the extremely elongated head and profile that ended in a point. Therefore, researchers believe the nasal ornament was worn by rulers and priests of the ancient city during ceremonies in which they embodied K’awiil, the Maya god of corn and fertility.”
Cover Photo: Carlos Varela Scherrer