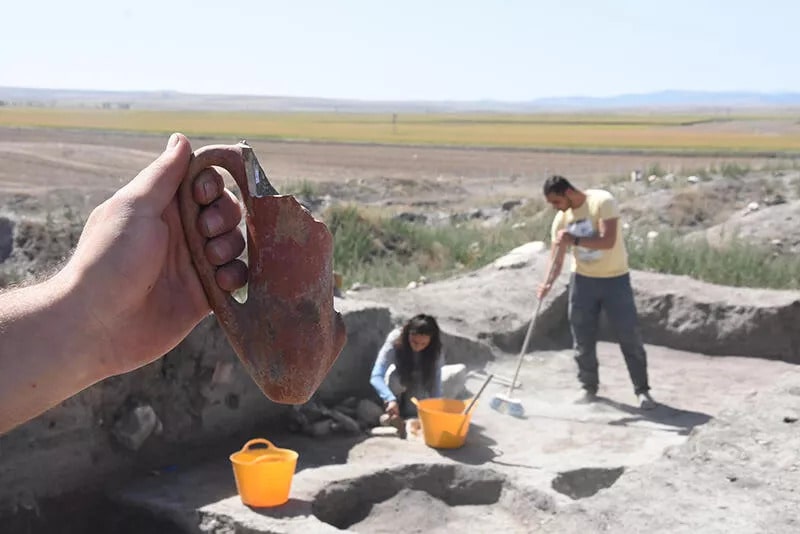
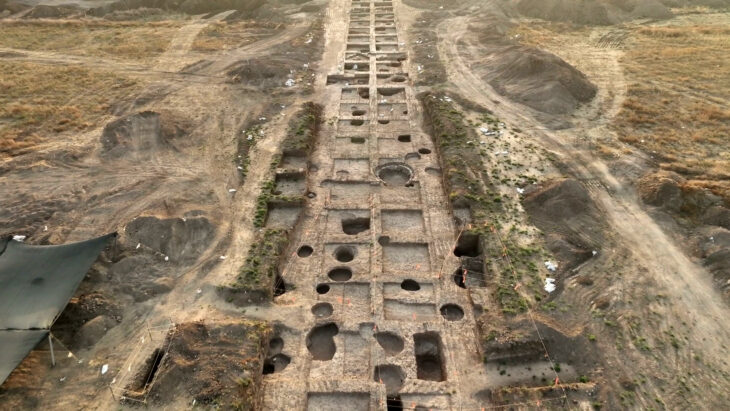
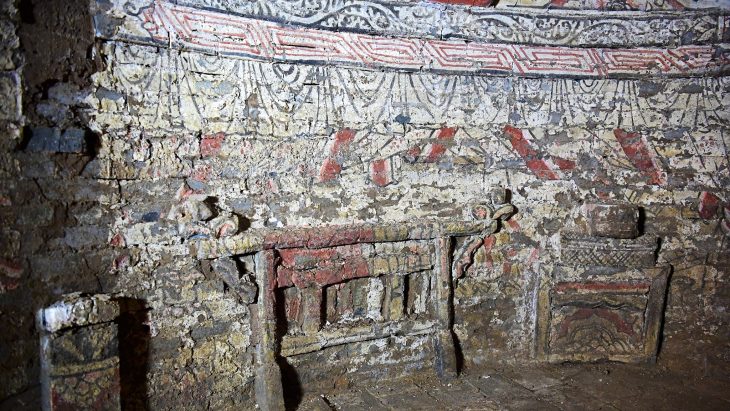
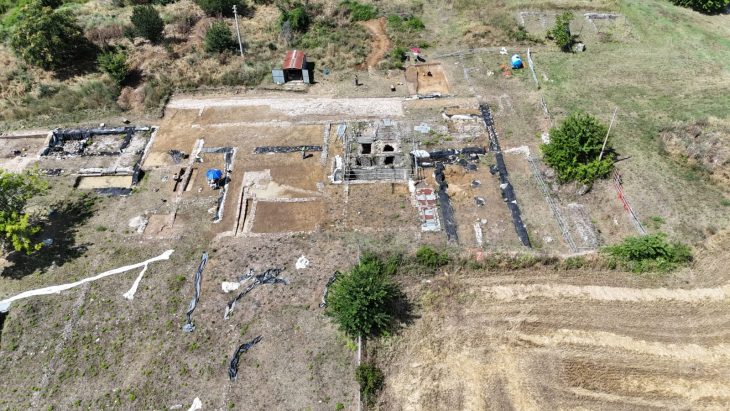
In the excavations of the Early Bronze Age Küllüoba Höyük (Kulluoba Mound) in Eskişehir, where the first urbanization structure of 5000 years ago in Anatolia was unearthed, vessels belonging to 4,500 years ago, which were found to contain painkillers medicine, were found.
Head of the excavation, Associate Professor Murat Türkteki, said that in the analysis of the double-handled beverage container, they found data showing that it was used in the preparation and drinking of various painkillers.
Kulluoba excavations started in 1996. To date, objects revealing the cultural characteristics of the Early Bronze Age, as well as animal bones and settlements have been found in the excavation area. During the excavations, tomb areas of stone cist and pottery dating back to 3 thousand BC were identified. At the same time, evidence of urbanization in Anatolia 5,000 years ago was unearthed.
In the excavations carried out this year, a team of 30 faculty members and students from Hacettepe University Anthropology Department, Batman, and Konya Selçuk University are taking part under the leadership of Bilecik Şeyh Edebali University (BŞEU).

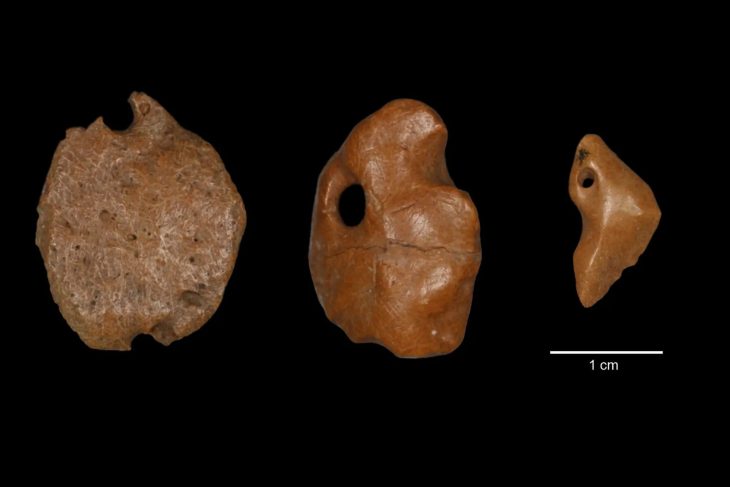
The vessels that were uncovered in archaeological excavations were examined in detail. Remains of drugs thought to have been used as a pain reliever 4500 years ago were found in one of the vessels.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
BŞEÜ Archeology Department Faculty Member and Head of Küllüoba Mound Excavation Associate Professor Murat Türkteki said that in addition to the cemetery studies, studies were carried out in order to understand the international relations and interregional relations of the settlement 4,500 years ago.
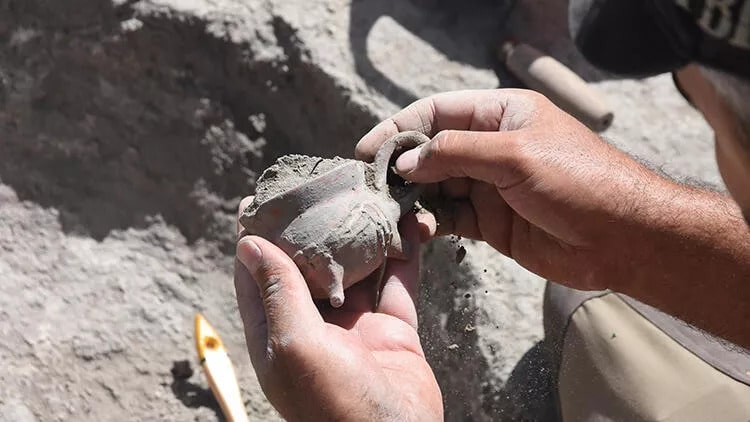
Türkteki stated that they found some finds related to interregional trade in these studies, “Another phenomenon that spread with this trade was the pits we call ritual pits, ceremonial pits or votive pits. We find various items in these pits. Among the finds, there is also a ‘depas form’, which we can call a double-handled beverage container. Some of the analyzes we have done on this form show us that these containers are used to store various painkillers,” he said.
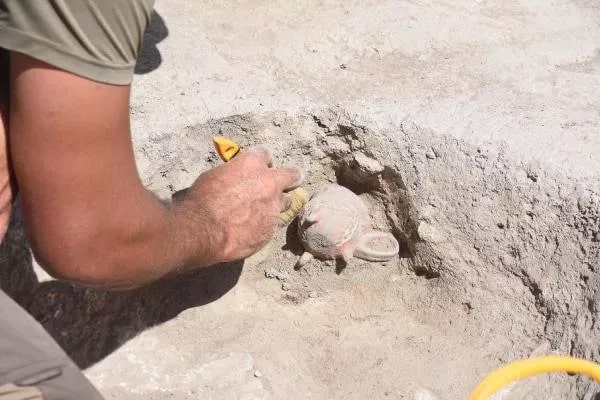

“The depas form, which we found in our analyzes to contain painkiller residues, is a form that has been seen intensely since 2,500 BC, especially in Central West Anatolia and mostly in the Eskişehir region. On the one hand, it reaches Syria through the southern connection of Central Anatolia, and on the other hand, it is a form that reaches Northwest Anatolia, Troy, and the Aegean world. It is a form that became very popular in the Aegean region afterward. However, we can say that the origin region is Eskişehir or Inner West Anatolia. The specimens we have identified so far are on display at the Eskişehir Archeology Museum.”
İsmail Tarhan, Associate Professor at the Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science at Konya Selçuk University in the excavation team, said that the remains of painkillers in the found container were found for the first time.
Stating that this result emerged with detailed analysis, Tarhan said:
“The most common artifacts found in archaeological excavations are ceramic artifacts. Since these ceramic artifacts have a porous structure, they can somehow imprison the products that are transported or preserved in their pores. In this way, these molecular residues can remain undisturbed even if they remain under the ground for thousands of years.”

“With the biochemical techniques we have, we can analyze the molecules trapped in these ceramic artifacts and interpret what is happening.”
“We also carried out our analyzes on these 4,500-year-old depas containers found in Küllüoba, and we found very interesting results because we identified molecules that we can call more for medical purposes than for daily use. In these molecules, especially biomolecules coming from green leafy plants, poppy and olive oil were predominant. We even detected salicylic acid, which is the active ingredient of a very known pain reliever, in these containers,” he said.
Küllüoba mound is 35 km southeast of Eskişehir, 15 km northeast of Seyitgazi, and 1.3 km south of the village of Yenikent.