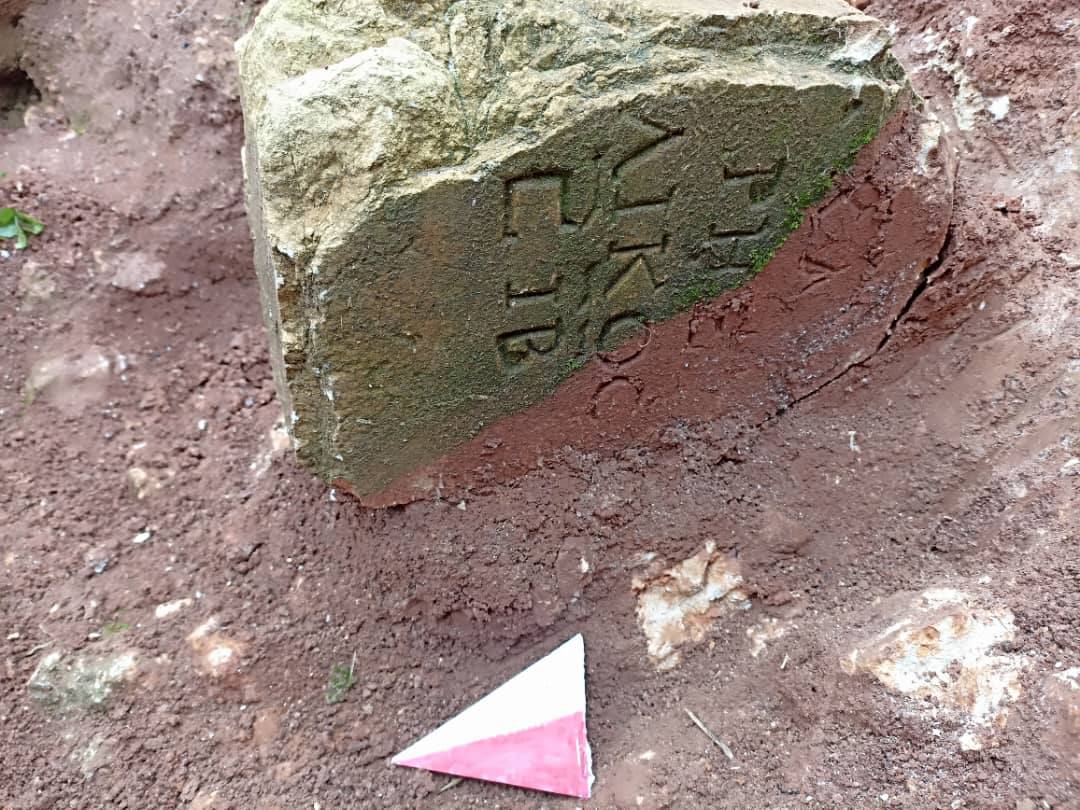
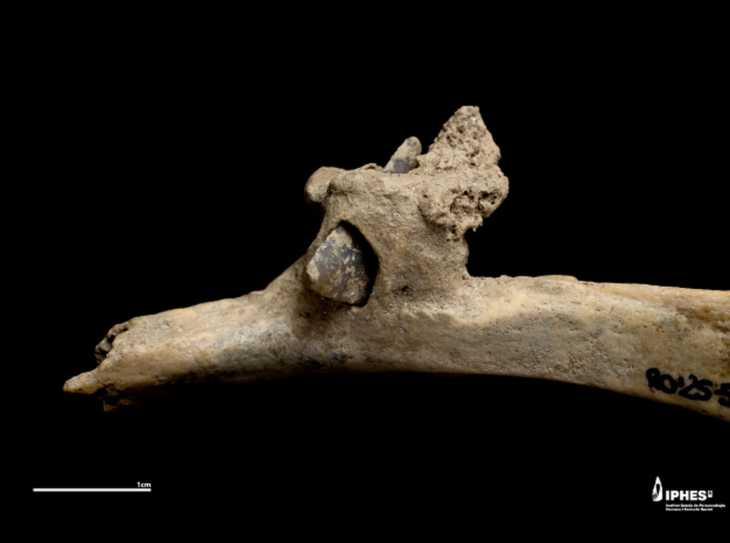
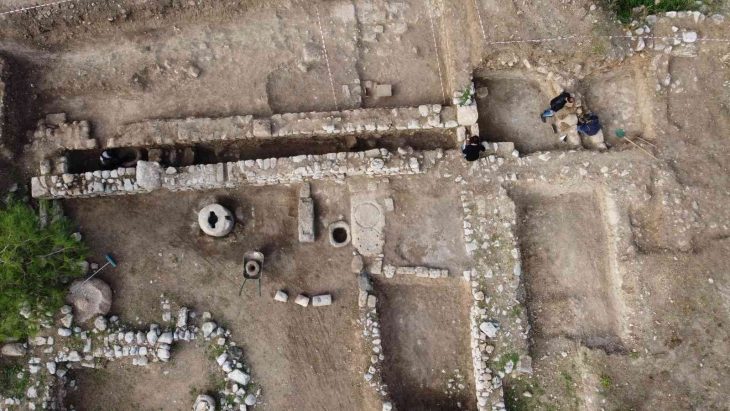
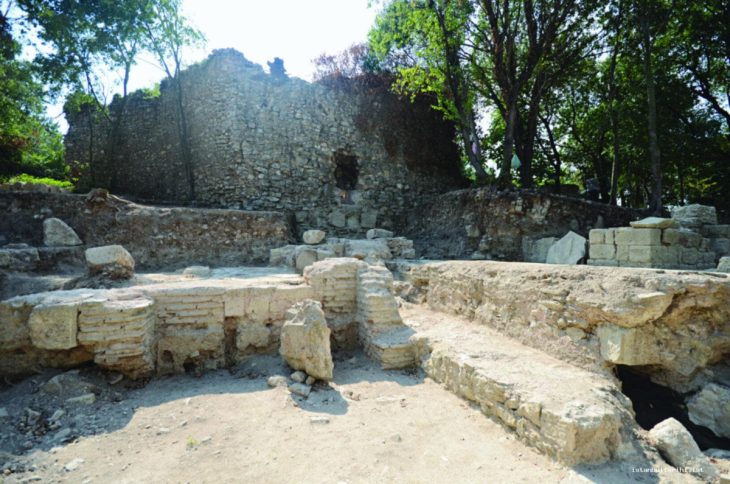
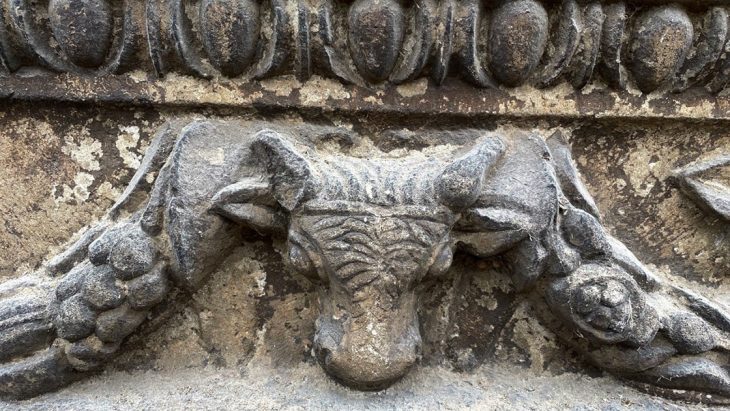
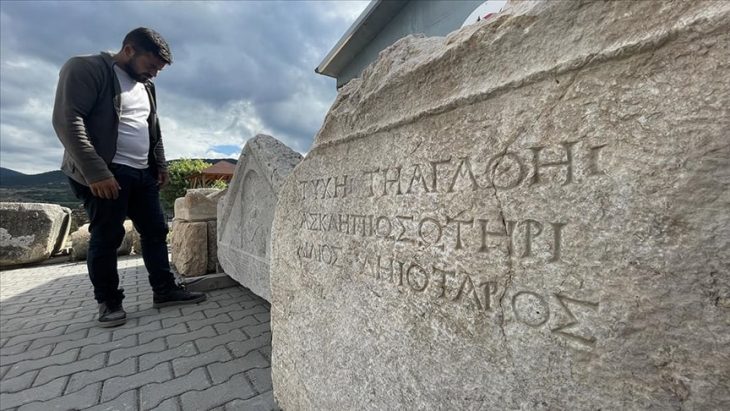
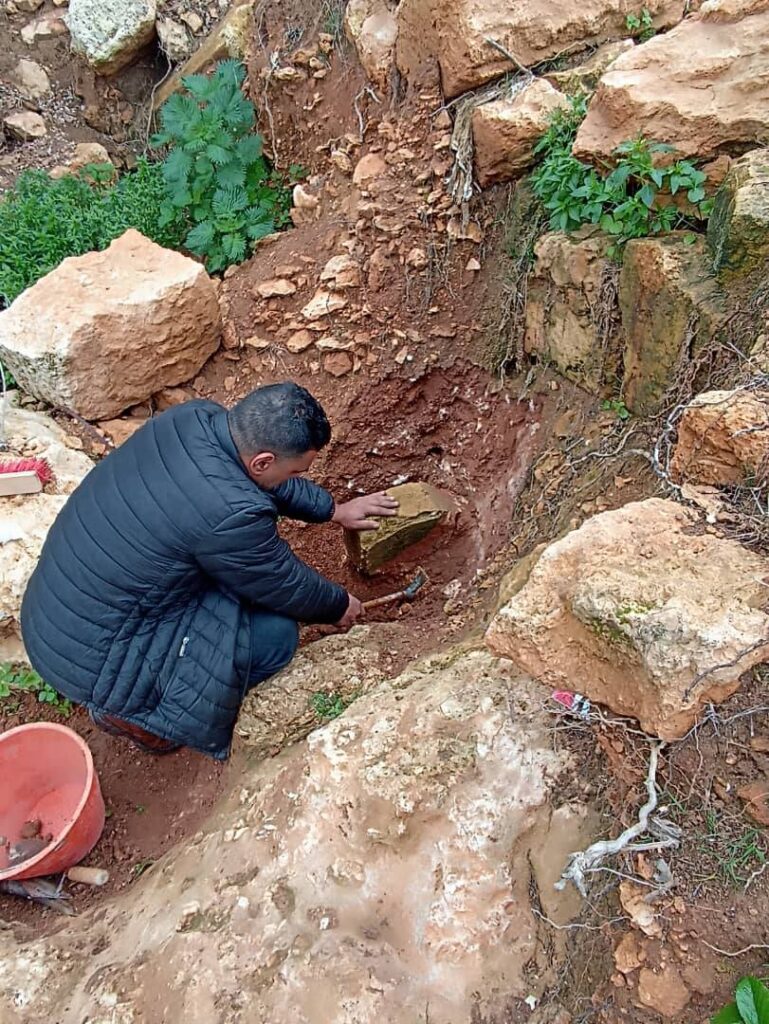
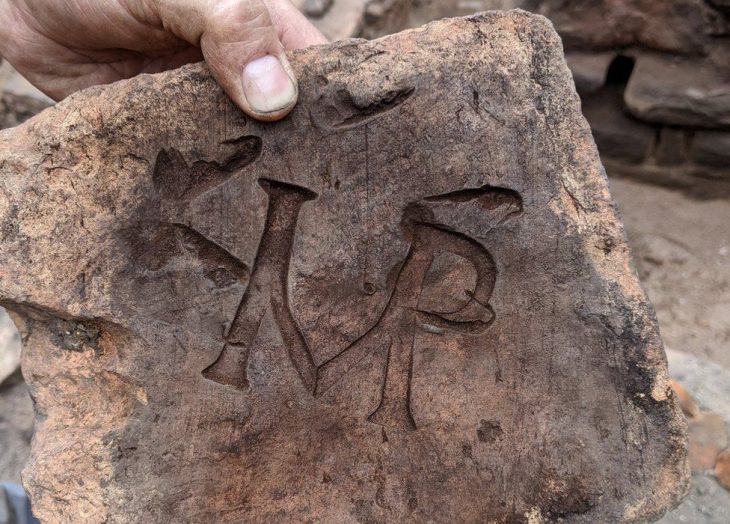The Libyan Antiquities Authority has officially confirmed that an ancient artifact uncovered in the torrents caused by Storm “Daniel” in the city of Shahat is a Greek tombstone made of limestone, located in the northern cemetery area.
In the wake of Storm “Daniel,” which struck Libya in September 2023, significant archaeological discoveries have come to light. Reports indicate that the flooding caused by the storm has revealed several ancient artifacts, particularly in the cities of Shahat and Derna.
One notable discovery was a Greek tombstone found in Shahat, as confirmed by the Libyan Antiquities Authority. According to their official statement, the tombstone, made of limestone, was uncovered in the northern cemetery area as a result of the torrents created by the storm. The Authority emphasized the importance of this find, stating that it sheds light on the region’s rich historical past.
The Authority explained via its Facebook page that after news spread on social media about the appearance of this piece, a work team was formed. An excavation and rescue operation began, and the inscription was transferred directly, which is a Greek tombstone on limestone, indicating that it decided to continue working at the same site to complete the work and publish the results immediately after completion.

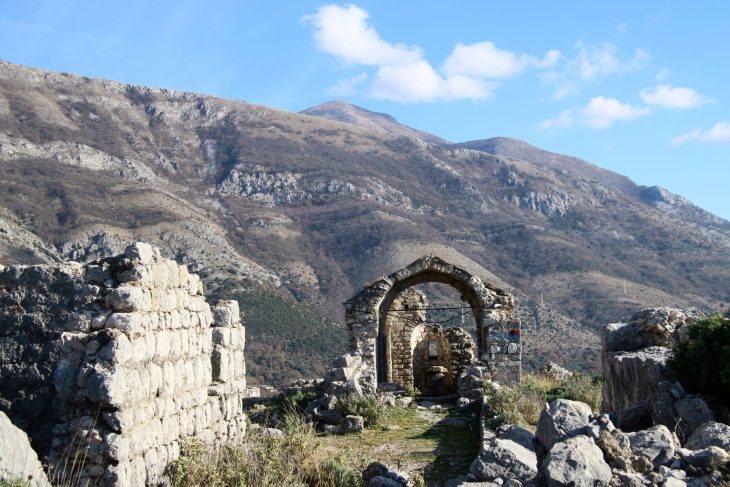
Shahat, historically known as “Cyrene,” is an ancient city located on the eastern coast of Libya. Founded in the 7th century BC as a Greek colony, Cyrene eventually became an important cultural and commercial center. The city is renowned for producing significant figures in philosophy, science, and the arts.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Cyrene is considered one of the most important Greek cities of antiquity and is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It is famous for its impressive ruins, which include temples, theaters, stadiums, and cemeteries. Notably, the Temple of Apollo is recognized as one of the largest temples of the ancient world.
The city also thrived during the Roman period, experiencing considerable wealth and structural development. The ancient remains reflect the region’s rich history and cultural heritage.
In light of this discovery, the Authority has urged citizens to refrain from sharing information on social media without first consulting the relevant authorities and obtaining the necessary permissions. This precaution is essential for protecting the integrity of archaeological findings and serves the public interest.
Cover Image Credit: Libyan Antiquities Authority