A Viking Age grave rich in artifacts has been discovered for the first time in Norway’s capital city, Oslo.
The Viking grave was found during preliminary work for the construction of a house in Norway.
The grave was discovered beneath a thin layer of topsoil on a small hill overlooking the Holmendammen lake in a residential area just north of Oslo’s center, where the Holmenbekken stream once ran.
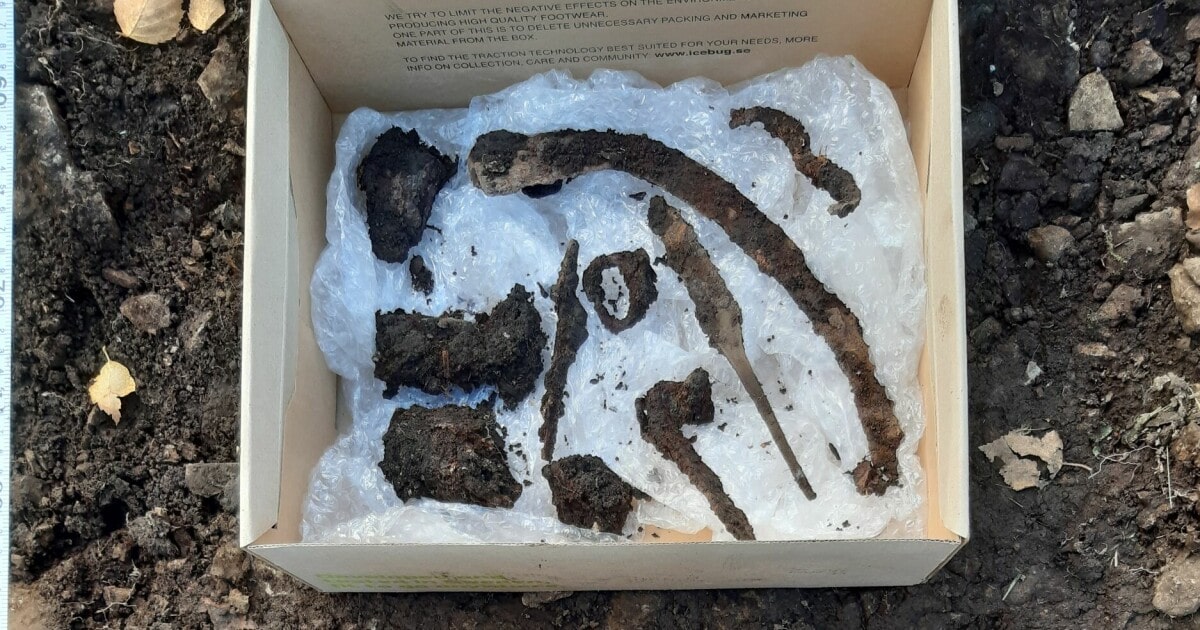
The grave is a cremation burial, accompanied by several grave goods such as fragments of a soapstone vessel, a buckle, a Celtic brooch (more properly called a penannular brooch), a pair of knives, a sickle, and horse tack.
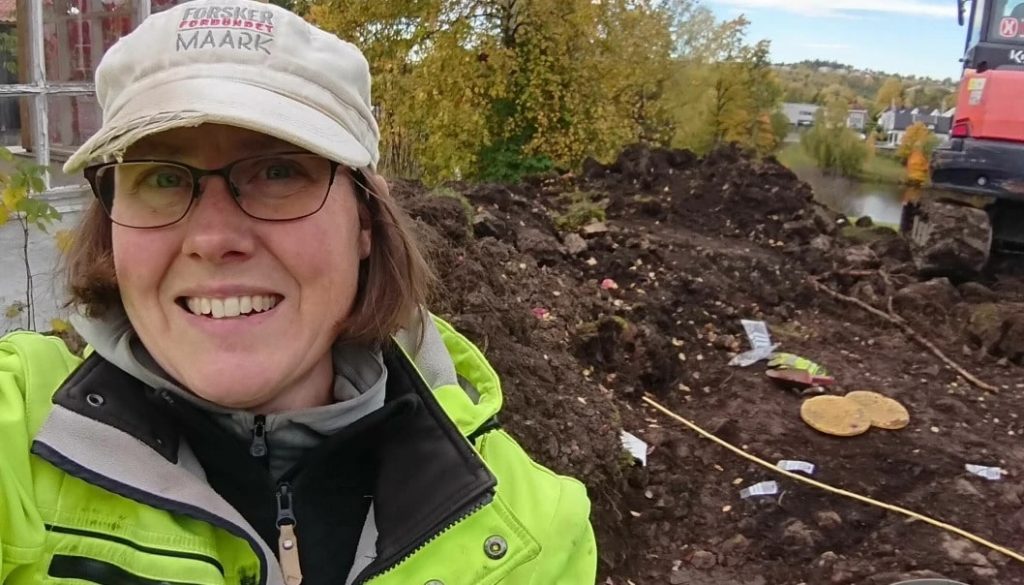

Archaeologist Marianne Bugge Kræmer, from the Oslo Municipality Cultural Heritage Management Office, told Science Norway: “For now, the grave has been dated based on the artifacts it contains. This type of brooch with spheres begins to appear in approximately AD 850 and became common after the 10th century AD.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery of a cape brooch along with the discovery of a shield boss indicates that the deceased was a man, according to Zanette Tsigaridas Glrstad, an archaeologist and associate professor at the University of Oslo’s Museum of Cultural History. This type of cape brooch was typically worn by men.
According to Zanette Tsigaridas Glørstad, this is the first artifact-rich Viking grave in Oslo that has been opened by archaeologists. But many objects that can be linked to Viking graves have been found by, among other things, construction workers in Oslo over the years.
Glørstad says that they know about the discovery of remains from around 60 graves from the Viking Age in Oslo. The majority were discovered in 1900, when the town was expanded to include St. Hanshaugen, Grünerlkka, Bjlsen, Tsen, and Sinsen.
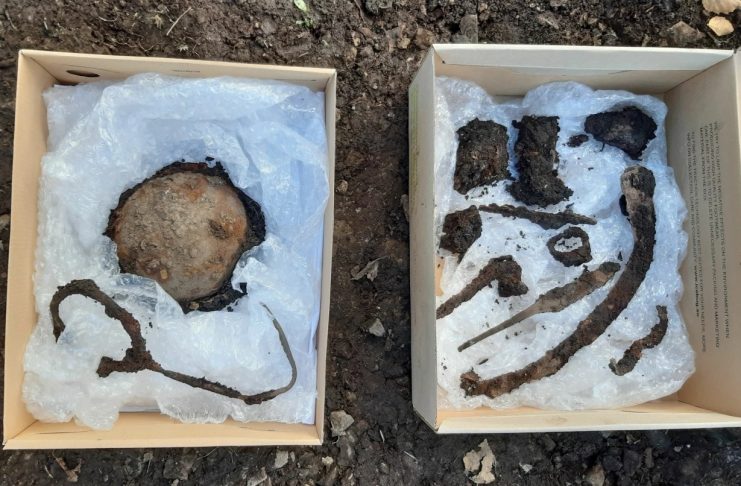

According to the Norse sagas, Harald Hardrada founded Oslo around AD 1049. Recent archaeological research has uncovered Christian burials dating back before AD 1000; however, the most recent Viking burial may predate these, indicating that occupation in some capacity occurred much earlier.
Zanette Tsigaridas Glørstad told that the discoveries are now in their conservation lab and they are still waiting to be ready before they can reveal more information about the objects.
Cover photo: Byantikvaren in Oslo