Waterworks in Giugliano, a suburb of Campania (Naples), have uncovered an untouched chamber tomb full of frescoes ceilings, and walls in pristine condition.
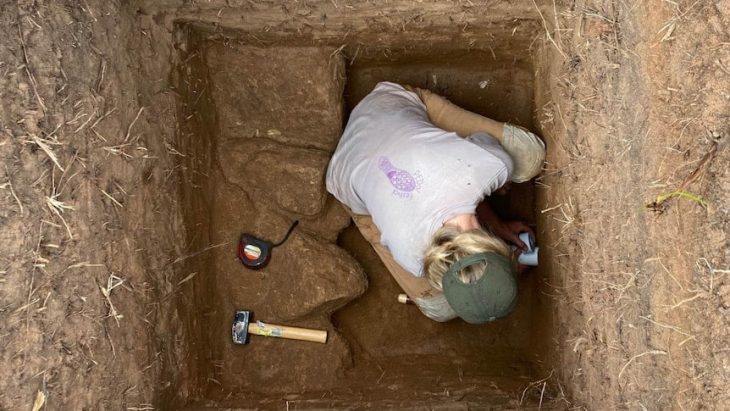
The tomb was found on farmland during an archaeological survey in advance of updates to the city water supply system.
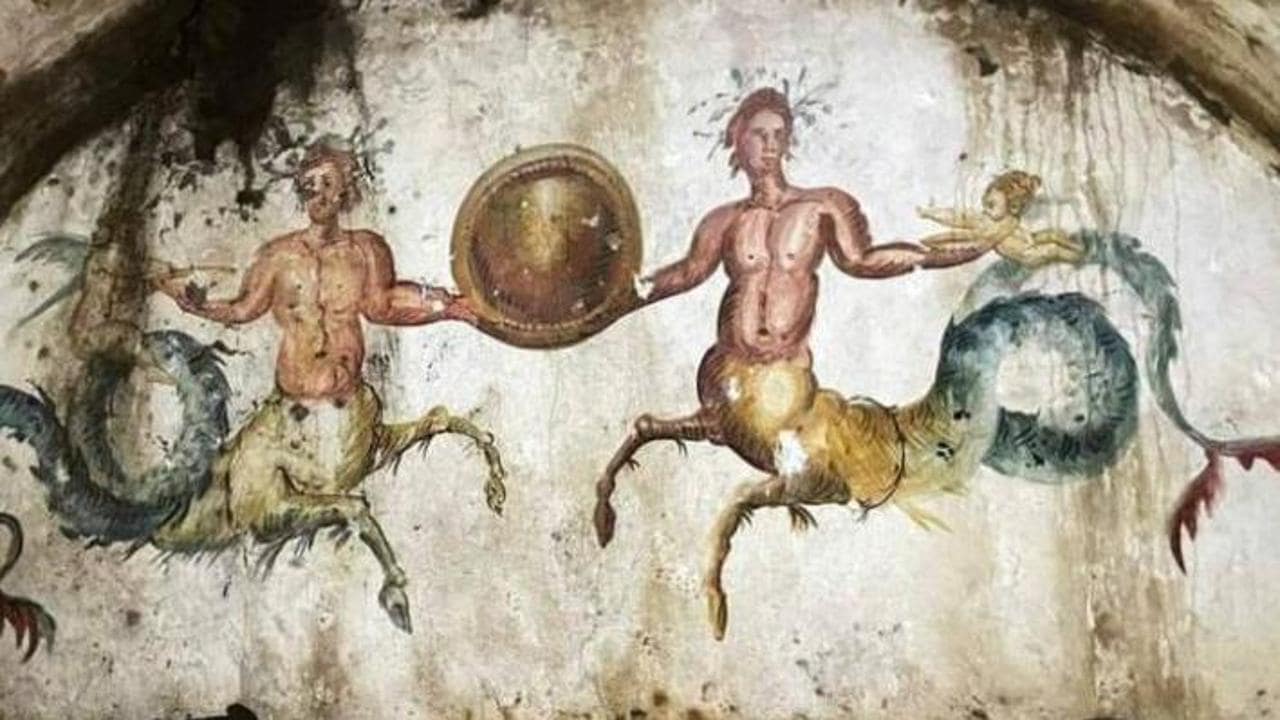
The room has the ceiling and walls frescoed with mythological scenes, Ichthyocentaurs (a pair of sea gods with the upper bodies of men) holding a clypeus on the front wall, festoons that go all around the funerary chamber, and figurative representations among which a three-headed dog stands out, hence the name of the mausoleum as the Tomb of Cerberus.
The striking painting that has given the tomb its monicker depicts the 12th and most dangerous of the Labors of Hercules: when he descended to Hades guided by Mercury to capture the three-headed monster dog Cerberus.
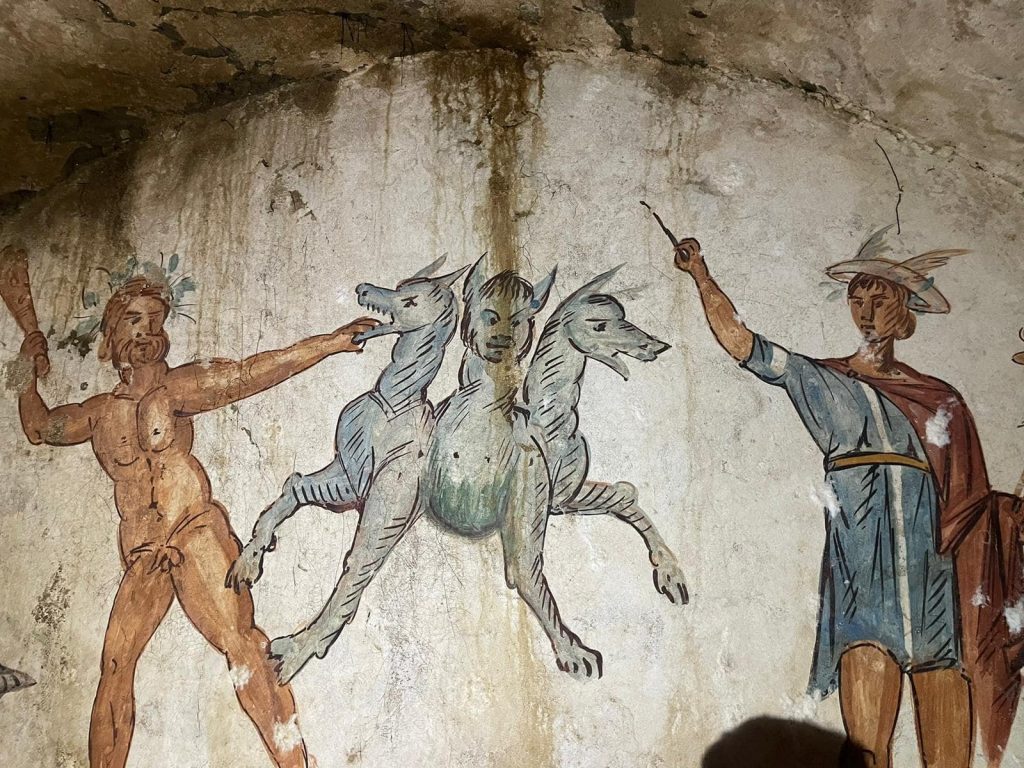

The frescoes are perfectly intact and still maintain their brilliant color. Preliminary estimates date the tomb to around 2,000 years ago.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
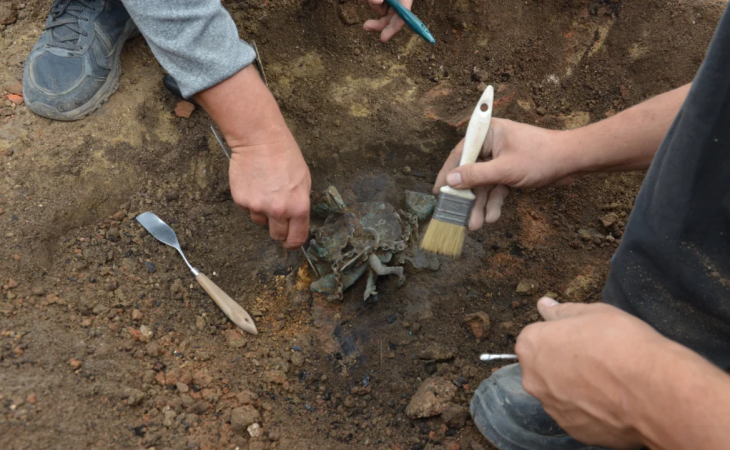
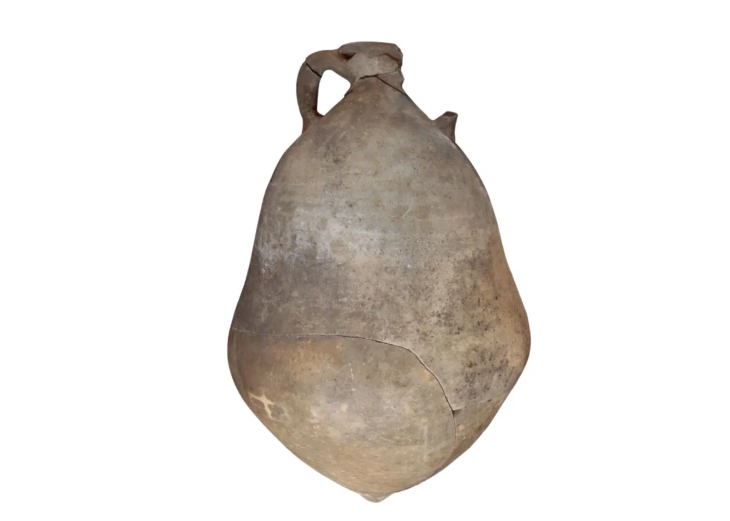
A test excavation uncovered numerous ancient burials, inhumations, and cremations dating back at least 400 years, from the Republican to the Imperial eras.
At the edge of the necropolis, archaeologists found an opus incertum (masonry style using different shapes and sizes of uncut stone) wall. It proved to be the front wall of a chamber tomb and like the interior, it too was in outstanding condition, still sealed with a heavy tufa slab over the square entrance.
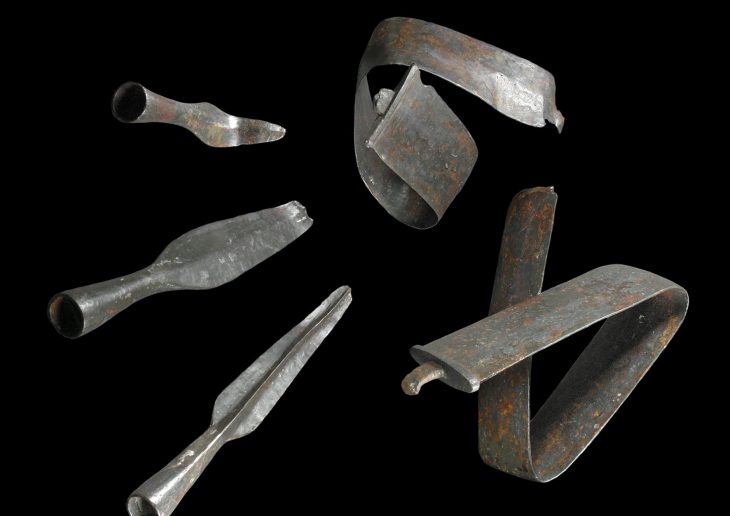
Three painted klìnai, an altar with vessels for libations, the inhumed still placed on the funeral beds with rich objects, complete the picture of a discovery which, in this area, is unprecedented.
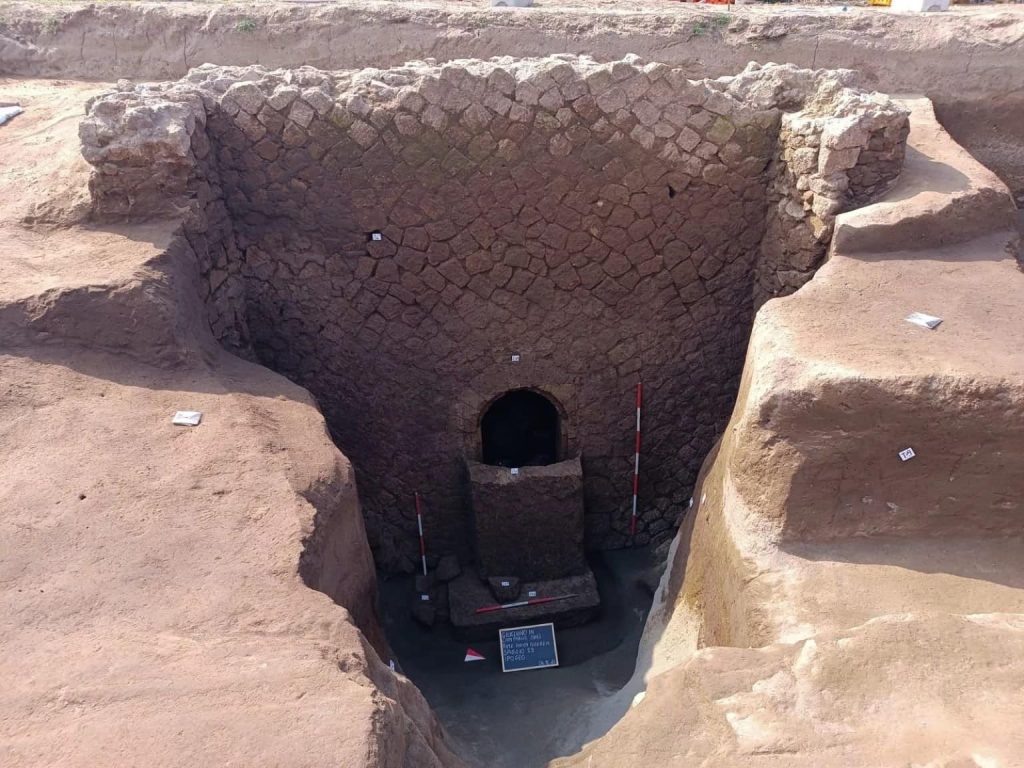

Surface reconnaissance during the preliminary archaeological investigations prescribed by the Superintendence for the Metropolitan Area of Naples resulted in the recognition of a dispersion of material from the historical era, and an intuition of Dr. Simona Formola, official responsible for the territory, an excavation test was positioned precisely in correspondence with the area which proved to be full of burials, with different rites (both inhumation and cremation).
The excavation of the chamber tomb is still ongoing, and archaeologists intend to look into the larger necropolis as well.