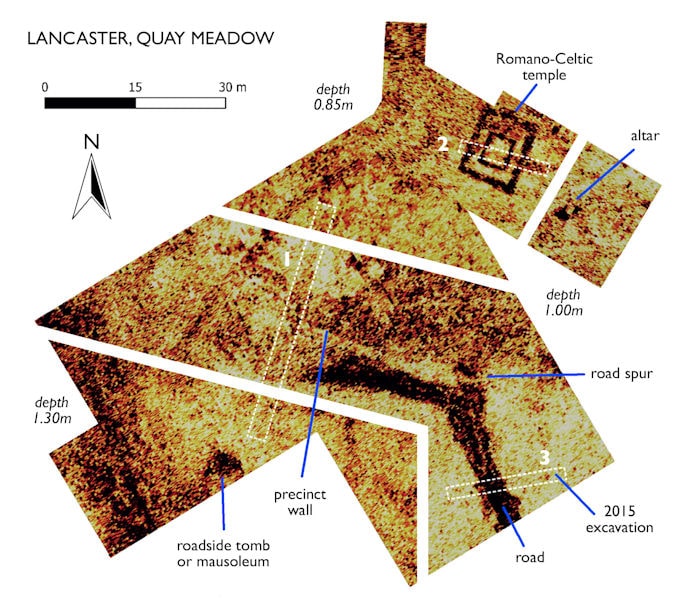
A study exercise for students from Lancaster University has uncovered a Romano-Celtic temple, only the second of its type in northern Britain.
The discovery was made during a hydrogeophysics training session near Lancaster’s Roman military fort and castle, revealing an extensive religious enclosure identified as a Romano-Celtic temple.
Lancaster had a large military fort and garrison in Roman times. It was an important command center between Chester and Hadrian’s Wall and a base for naval operations and supply.
Around AD 80, the Lancaster Roman Fort, also known as Wery Wall, Galacum, or Calunium (the fort’s modern name), was first built atop Castle Hill in Lancaster to guard a bridge over the River Lune. Archaeological evidence suggests that the fort remained active until the end of Roman occupation of Britain in the early 5th century.
Professor Andy Binley, an expert in hydrogeophysics at Lancaster Environment Centre, offered to use his research expertise and equipment to continue the work of the Beyond The Castle archaeological project, when heritage lottery funding ran out in 2017.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“I had a few PhD students doing geophysical research and thought this was an interesting group hobby project, training them on techniques and getting them to work as a team,” said Professor Binley, who uses geophysical methods to solve hydrological problems, such as assessing underground water in agriculture and tracking groundwater contamination.
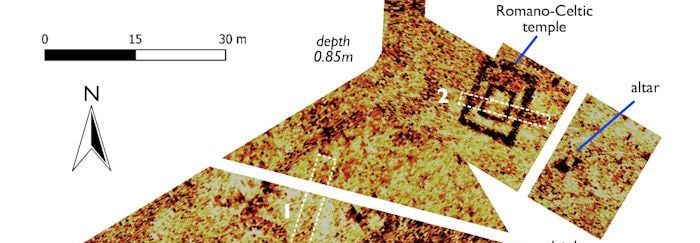
The Beyond the Castle project had been using standard geophysical techniques followed by trial excavation to explore the green open space between Lancaster Castle and the River Lune. These had revealed evidence of a building, thought to be a Roman warehouse, under an area called Quay Meadow, owned by Lancaster City Council. But Professor Binley and his students would make much more extensive, and exciting discoveries.
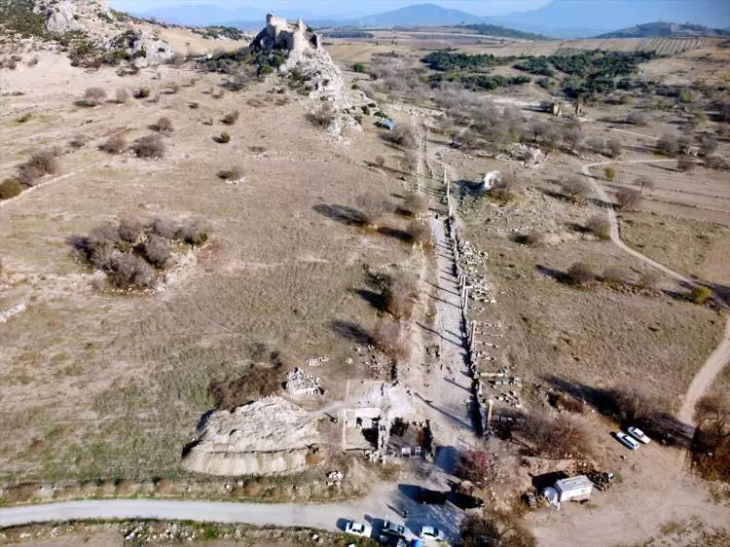
Using ground penetrating radar, resistivity mapping, and modeling to produce high-resolution 3D images, the study found evidence of a Romano-Celtic temple showing a walled enclosure with a gateway leading to a processional way. The mapping data also shows a possible roadside mausoleum outside the enclosure, and what might be the base of an altar close to the temple.
The major discovery was what Beyond the Castle project’s leading archaeologist, Jason Wood believes is a Romano-Celtic temple – only the second such temple found in Northern Britain – the other one is close to Hadrian’s Wall.
These temples have a very specific design – two sets of walls forming a square within a square, with a very small interior.

“It would have been dedicated to a god, probably associated with the sea or river. The inner sanctum was reserved for the priests, and the outer ambulatory space was for elite members of society,” said Mr Wood.
“Most of the religious activities would have happened outside the temple, including sacrifices. There would have been a sanctuary or enclosure, possibly with another temple and buildings associated with hospitality and curing the sick. The enclosure would have been separate from the fort, but connected to it by a road or processional way.”
“So few of these sites have been excavated in the UK, so it is significant to have found a Romano-Celtic temple in its temenos (enclosure) by a river,” said Mr Wood.
The findings are outlined in the paper ‘Lancaster Romano-Celtic temple is significant find’ published by British Archaeology.
Find out more about the research findings and Lancaster’s Roman past here.
Cover Photo: Jason Wood, Andrew Binley from Lancaster Environment Centre and British Archaeology magazine Nov/Dec 2022