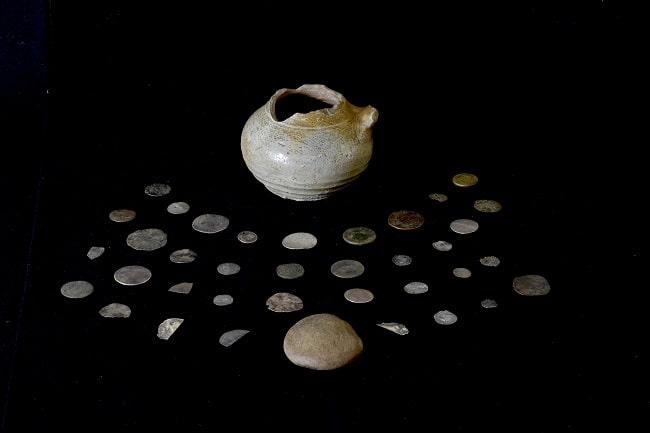
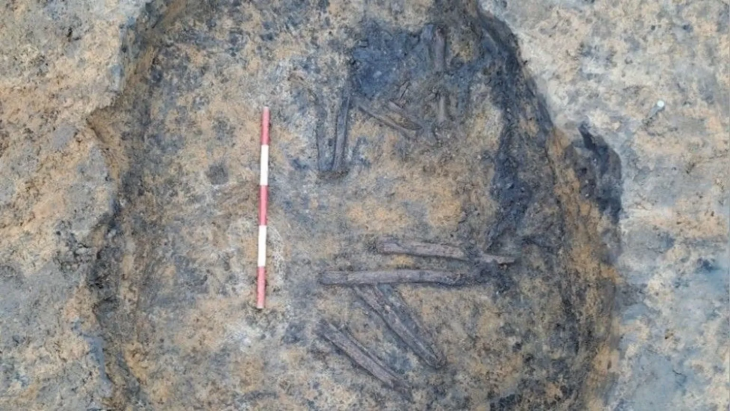
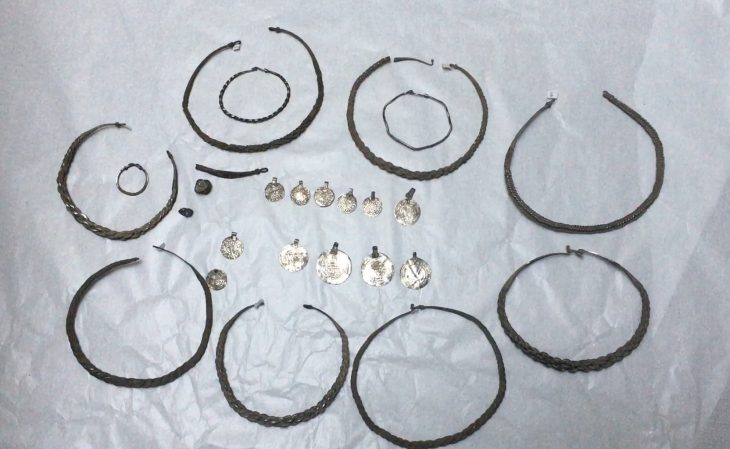
A dog named Kajtuś discovered the biggest treasure found in Poland in the last 100 years. The treasure was found buried in a clay pot near Wałbrzych by a dog named Kajtuś while he was on a walk with his owner.
Information about the unusual discovery was received by the Branch Office in Wałbrzych, WUOZ in Wrocław on Thursday, April 7th. The next day, Marek Kowalski the monument inspector, together with a team of archaeologists from the Wrocław University Archaeological Institute, examined the find and went to the discovery site.
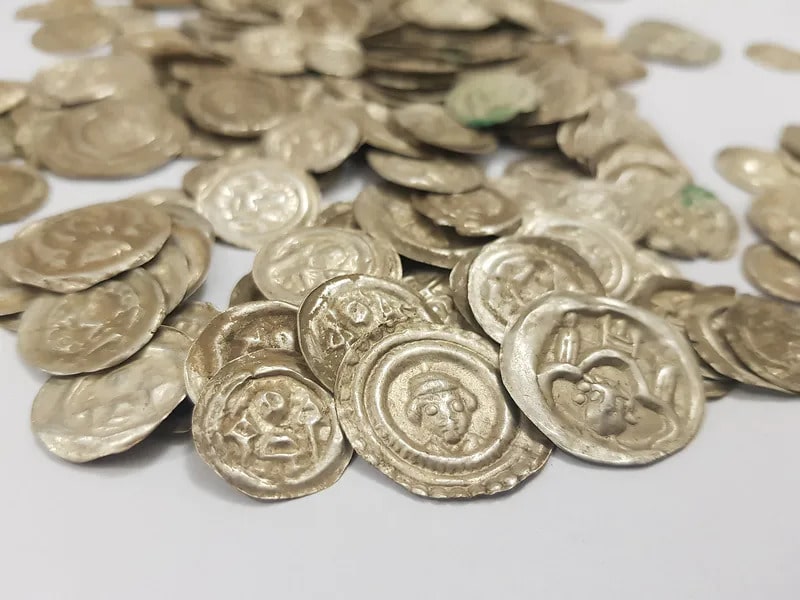
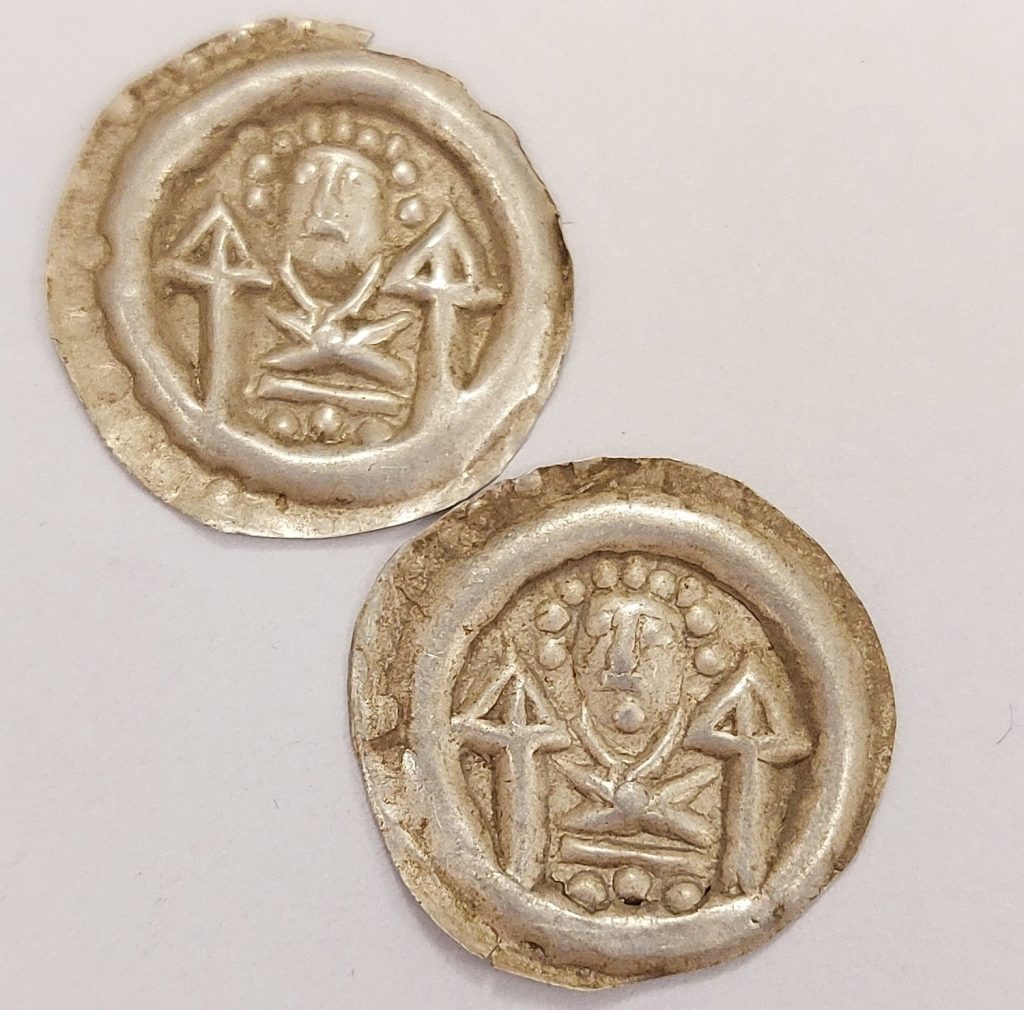
What was found turned out to be medieval bracteates from the first half of the 13th century, stored in a dilapidated clay pot. The medieval bracteates are thin coins with only one face embossed. The name of the coin is derived from the Latin word bractea, which means thin sheet metal.
Bracteats are made of thin plates. In the Middle Ages, they functioned as means of payment. The use of individual coin series is relatively short. It is known from historical data that the exchange of payment instruments took place 2-3 times a year in this period. The above-mentioned preserved coins of that period are few since they were remelted and minted in a new series. Finding a substantial amount of coins from this period is therefore unique.
The coins found in Wałbrzych are quite well preserved and the images on them are mostly clear and depict griffins, mermaids, and angels, as well as architectural elements such as towers and walls.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The location of the vessel and the coins suggests that someone had initially hidden them. Preliminary identification of the coins suggests that they originated in Brandenburg, Saxony, and Silesia.

The most recent similar discovery took place in Pomerania in 1972, when over a hundred Teutonic bracteates were found.
Kings, princes, and bishops could issue coinage during the period. This situation persisted until major silver reserves near Prague, Czech Republic, were discovered; after that, groschens began to be produced, gradually replacing bracteates.
However, the discovery brought some controversy. Some internet users argue that the story about the dog is exaggerated and that the 13th-century treasure was found by someone who scanned the area with a metal detector.
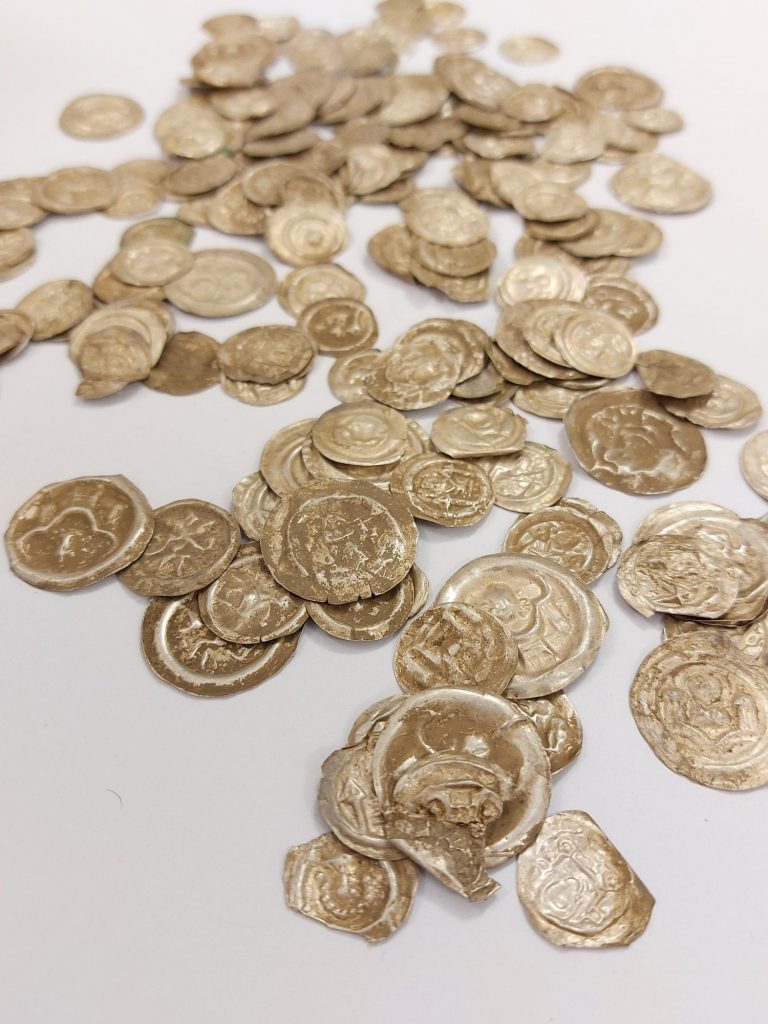

Wałbrzych heritage protection officer, Anna Nowakowska-Ciuchera, said: “The person who approached us was on a walk with their dog. At some point, Kajtuś started digging in the ground. And that’s how he came across the pot of coins. At least this is the version presented to us.”
The coins will first be extensively examined, and then, as property of the Treasury, they will go to the museum.
Cover Photo: Lower Silesia Heritage Protection Office/Facebook