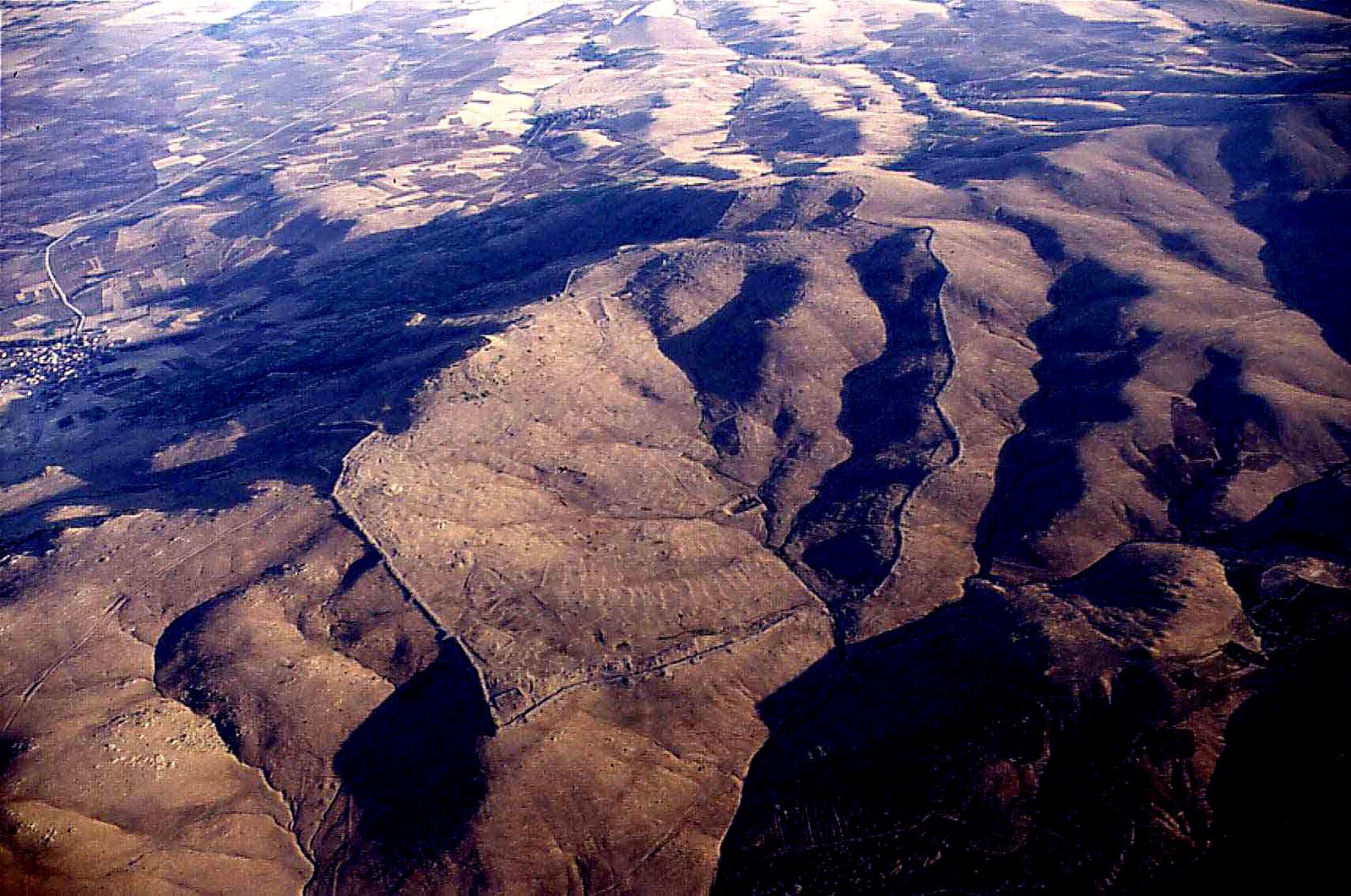
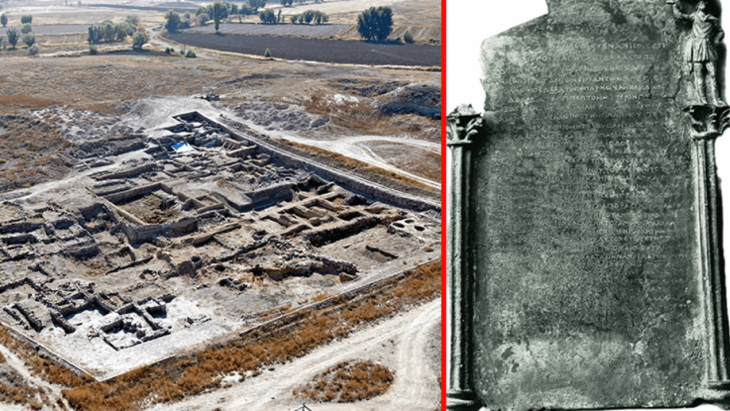
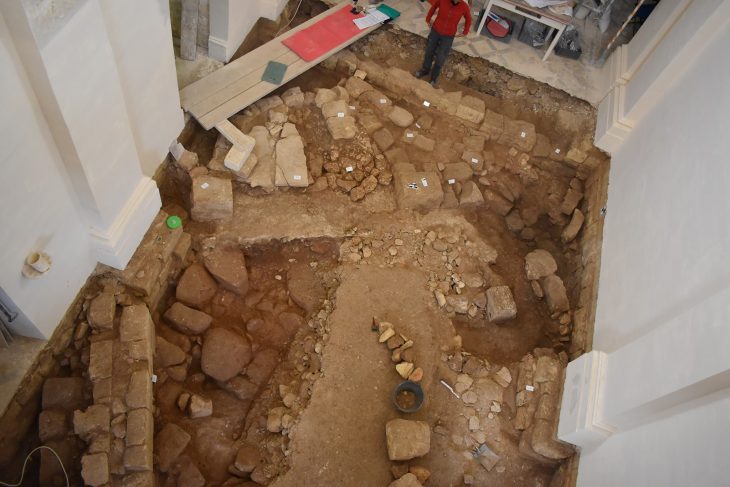
Although the settlement on the Kerkenes mountain, located within the borders of Sorgun district of Yozgat, has been known and researched for a long time, it still has many secrets.
For example, we still do not know the name of this settlement. In the 2003 excavation season, the discovery of Phrygian inscriptions in the settlement believed to have been a Med city for a period pointing that the city may have been a Phrygian settlement.
Although it is thought that this is the city recorded as Pteria in ancient sources, studies that have been going on since 1993, unfortunately, could not provide sufficient evidence as to whether the settlement was the ancient city of Pteria.
So what happened in this long time? Let’s take a look at what has come to light and what is still hidden.
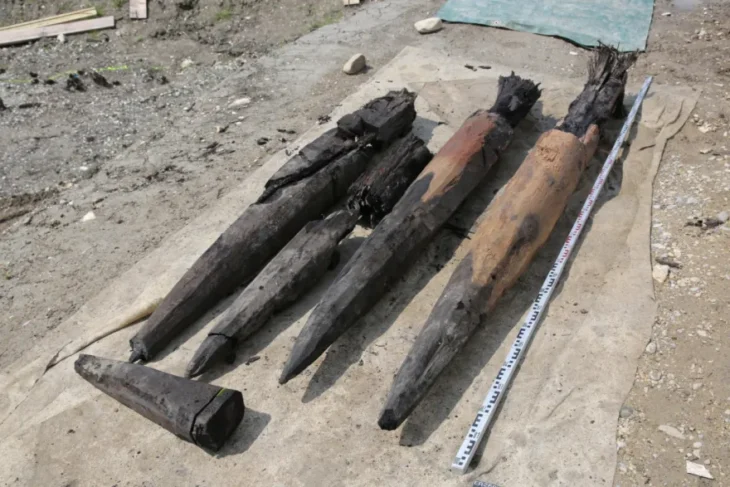
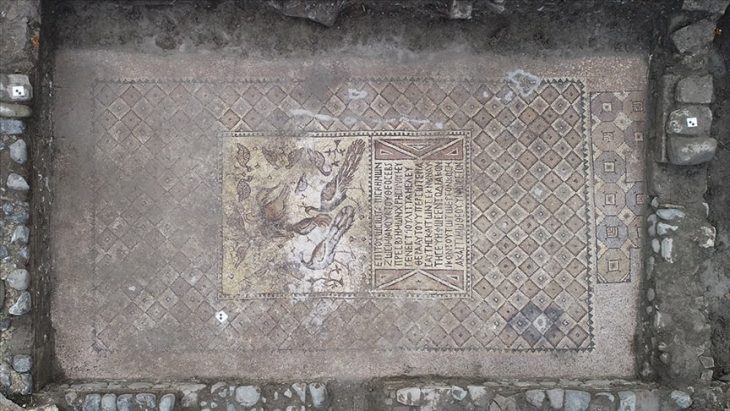
First of all, we are now almost certain that the city is not a Med city. Every excavation that took place in the settlement showed us that this was a Phrygian (Phrygian) city. With the Phrygian inscriptions on the monuments and ceramic remains, we know that the people of Phrygian origin lived here. It is possible to follow not only the inscriptions but also the traces of religious beliefs belonging to the Phrygians step by step here.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The results of the Gordion excavations show that the settlement ended with a fire that started as a result of a military attack around 700 BC. Eusebius gives the date of 696-695 BC and Sextus Julius Africanus 675-674 BC for the Cimmerian invasion that plundered and destroyed the capital Gordion and caused the death of Midas.
According to studies, the Kerkenes city was built and inhabited for a generation in the late 7th and first half of the 6th centuries BC. Enough time must have passed to establish a new second capital Gordion.

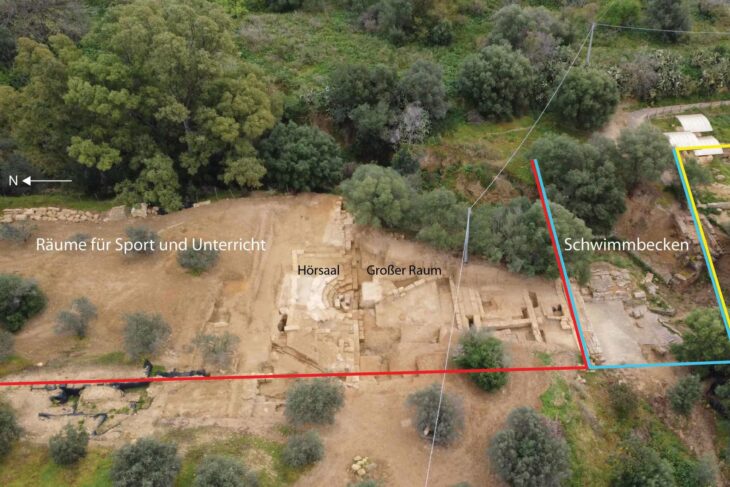
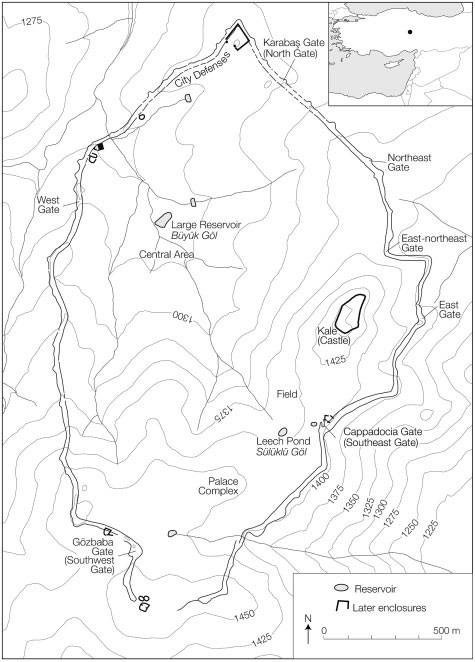
757 building blocks were unearthed in the settlement. In addition, artificial ponds have been created to meet the water need, which can manage all summer. The bottoms of these artificial ponds are covered with stone flooring. There are 7 main gates in the settlement and the monumental appearance of the gates is quite remarkable. It should be noted that the 7 main gates open to the main roads, which is not surprising considering that the city was probably built during a period of intense Cimmerian attacks, which was always in danger. It is also worth noting that Anatolia was going through a mixed period, far from being a political union, during this period.
The Battle of the River Halys or the Battle of Eclipse was a conflict between the Medes and Lydians in the early 6th century BC. When a solar eclipse takes place on one day of the 5-year war between the Lydian king Alyattes and the Med king Kyaksares, the war is ended by saying “Gods do not want this war” and a peace agreement is made. This event, which will be called the “Battle of the Eclipse”, took place on May 28, 585 BC. It does not seem possible for Lydia to endure 5 years unaided against the armies of the Medes in a region so far from Sardis. Probably, Alyattes continued the war by getting support from the settlement of Kerkenes, which was under Phrygian rule and even became the new capital of the Phrygians during the war. As a result, the war resulted in a peace agreement and the foundations of an agreement that would last 40 years in the region were laid.
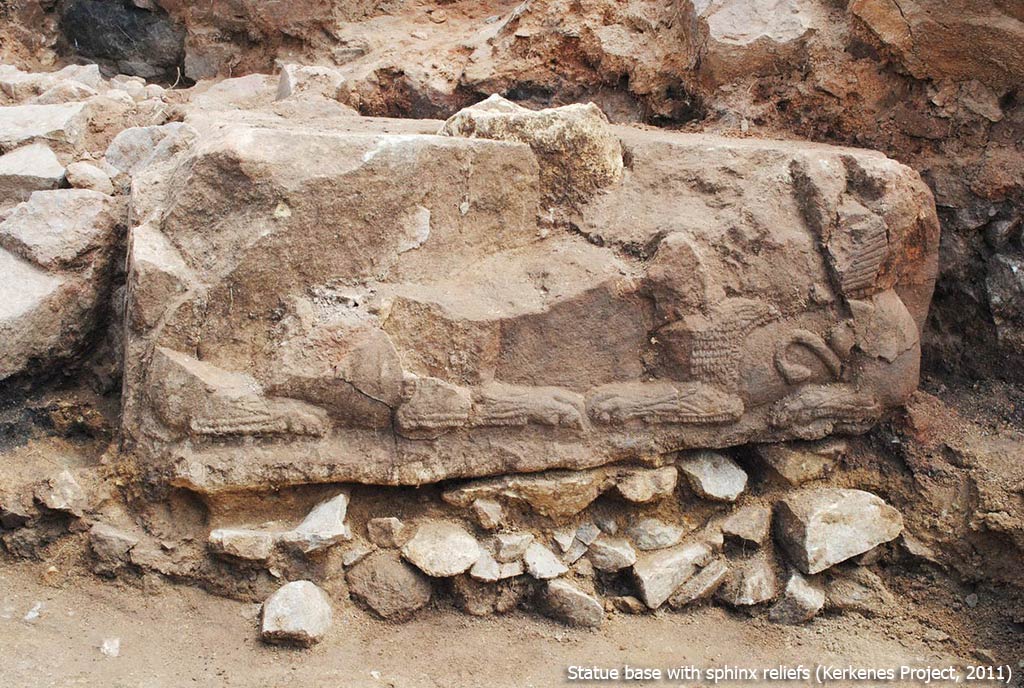

During this period, the Kerkenes people began to gain strength and grow together with the newly joined peoples such as Muski, Tabal, and Kashka. Just like the people of Gordion, who made a leap in the last period of Gordion and started to build ostentatious and monumental buildings, they felt more secure as a result of this peace and started working to create a new Gordion.
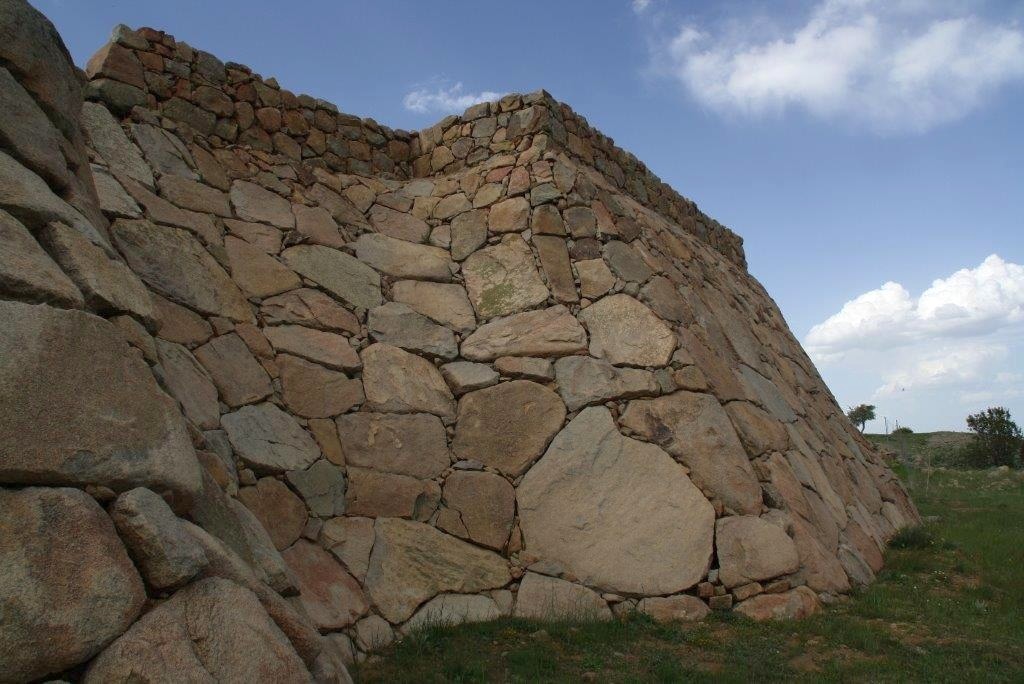
The city’s fortification walls, which are about 7 kilometers long, form a settlement area of 2.5 square kilometers. It is certain that such a large settlement needs great economic power, population density, and knowledge. The most important result that should not be forgotten here is that these people already have the capacity and knowledge to build a monumental city. The presence of the palace complex and administrative structure found indicates the existence of an authority. It is quite natural that people who are already familiar with Gordian architecture try to build stronger fortification systems to protect themselves further.
It is observed that there are examples of these walls in the settlement established after the Hittites in Boğazköy. As a result of the peaceful relations with Lydia, the construction of a stronger and sloping fortification like Sardis means that learning has improved. Perhaps it would be more accurate to look for the lost city of Pteria in Boğazköy.
It is thought that the Kerkenes settlement faced fiery destruction just like the capital Gordion in 540 BC and was abandoned.

With the collapse of the Lydian Kingdom in 540, Phrygian lands were connected to the Great Phrygian satrapy together with Cappadocia, Paphlagonia, and Hellespontos as a part of the Persian Empire.
The excavation uncovered over 8,000 square meters of this enormous city. The earliest excavations were undertaken for a few weeks in 1928, long enough to place the city within the Iron Age. These brief excavations were followed by long-term excavations across the city since 1996. Major areas of excavation have included a portion of the city’s palatial complex as well as one of the seven city gates.
Despite the difficult climatic conditions of the settlement, the excavations continue in the best way possible. Excavations are under the direction of Professor Scott Branting.
Important note: I would like to thank my esteemed teacher, Professor Şevket Dönmez, who gave us different perspectives in his lectures.
Cover Photo: Kültür Portalı