Archaeologists in Iran have discovered a plethora of artifacts and damaged structures near a former residence of Nader Shah, dubbed the “Napoleon of Iran.”
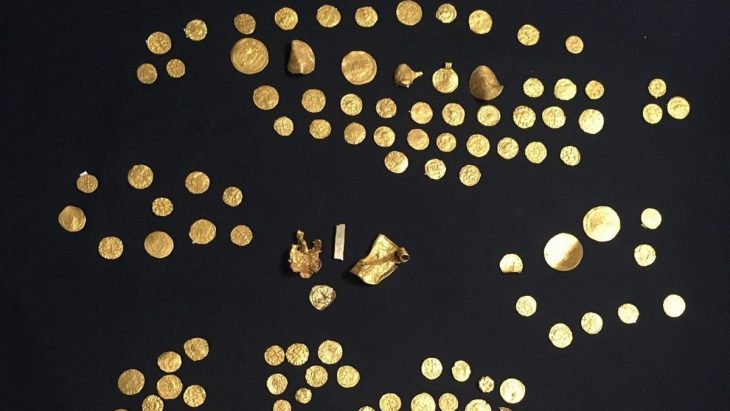
The objects, which are thought to date from the Bronze Age to the Qajar era (1789–1925), were discovered in the northern villages of Khalaj, Qolleh Zu, and Garu in Kalat County, Razavi Khorasan province.
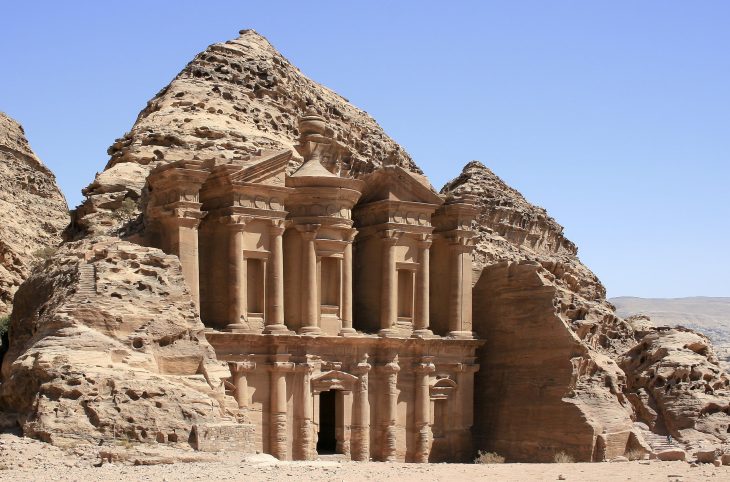
The three villages are located near Qasr-e Khorshid (meaning “the Sun Palace”), an 18th-century famous structure that served as a royal residence for Nader Shah of Persia (1688–1747), who established an empire that spanned from northern India to the Caucasus Mountains.
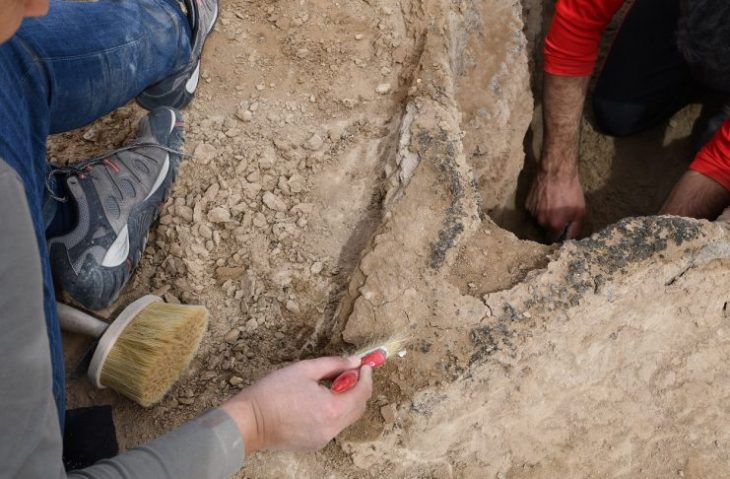
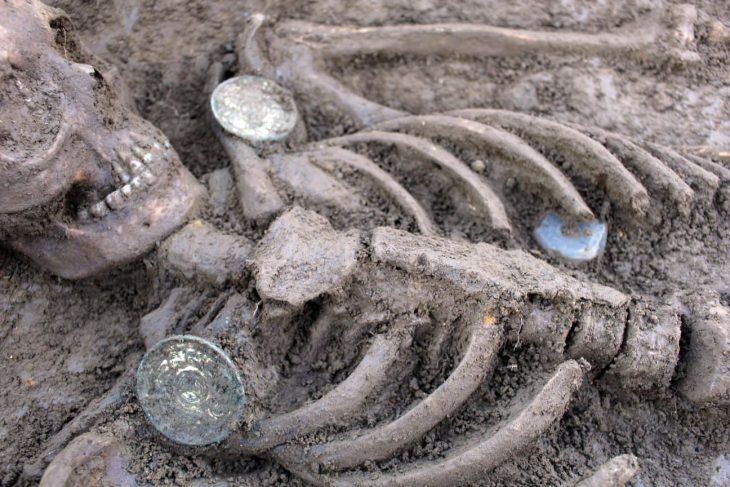
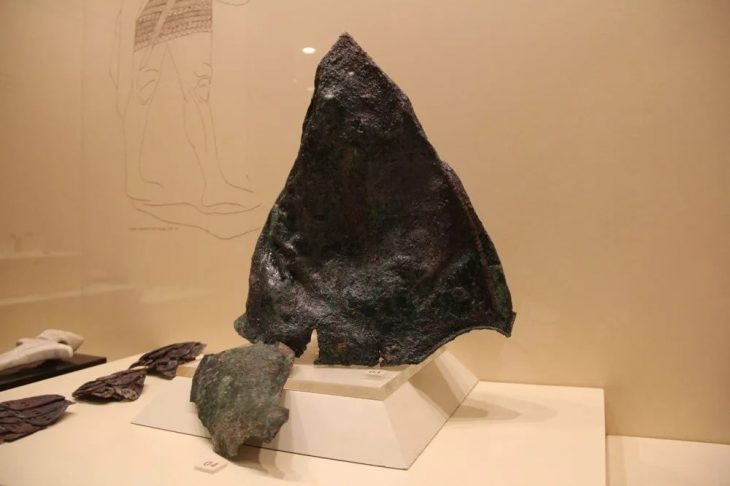
“So far, 127 historical relics and ruined monuments have been identified, covering the period from the Bronze Age to the Qajar era,” ISNA quoted Hamed Tahmasbizadeh, a senior local archaeologist, as saying on Sunday.
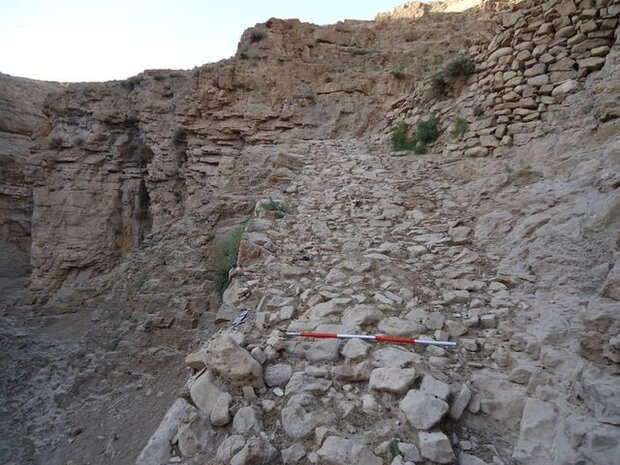

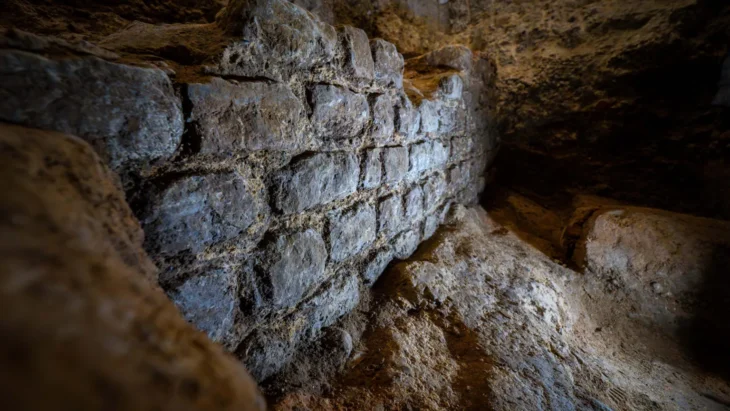
The ruined structures are related to watermills, Asbads (windmills), water irrigation systems, qanats (underground aqueducts), roads, stairways, and walls were part of the discoveries, Tahmasbizadeh said.
Moreover, the archaeologists have discovered a cemetery, which is estimated to date back to the Iron Age and Bronze Age, Tahmasbizadeh added.
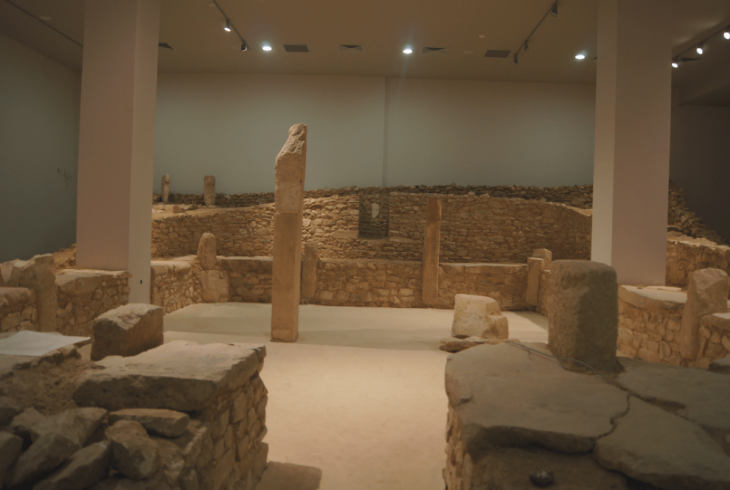
An ancient mine and the ruins of towers, fortresses, mosques, public bathhouses, bridges, and historical gardens were also found in the vast archaeological survey, the report said.
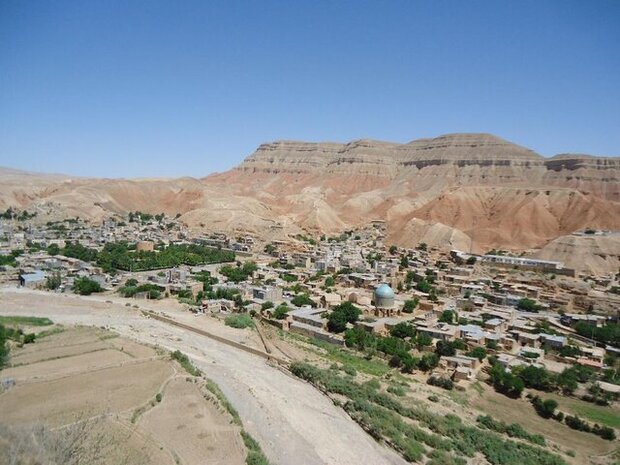

Qasr-e Khorshid (literally ‘the Sun Palace’), an 18th-century iconic is a monument that was once a royal resident for Nader Shah of Persia (1688–1747). According to narratives, the ‘palace’ is named after Khorshid, one of Nader’s wives. It was never completed, however, because of the uncertain state of things that arose following Nader Shah’s untimely death.
Some speculate that the monument was built by foreign artists since its outside panels include pineapple and pear patterns, which are thought to be uncommon in the Khorasan area at the time. The structure was most likely utilized as a residential headquarters during the early Qajar dynasty, according to evidence (I785 to 1925).
Nader Shah is regarded as one of the most powerful rulers in the country’s history. He came to power at a moment of instability in Iran. While repelling invaders, the strong ruler was able to unify the Persian realm. According to Encyclopedia Britannica, he was known as the Napoleon of Persia (Iran) or the Second Alexander.
Source: Tehran Times