A team of French, American and Turkish paleontologists and geologists led by CNRS researchers has discovered the existence of a forgotten continent they have dubbed Balkanatolia, which today covers the present-day Balkans and Anatolia.
Formerly inhabited by a highly specific fauna, they believe that it enabled mammals from Asia to colonize Europe 34 million years ago.
For millions of years during the Eocene Epoch (55 to 34 million years ago), Western Europe and Eastern Asia formed two distinct land masses with very different mammalian faunas: European forests were home to endemic fauna such as Palaeotheres (an extinct group distantly related to present-day horses, but more like today’s tapirs), whereas Asia was populated by a more diverse fauna including the mammal families found today on both continents.
![Map showing Balkanatolia 40 million years ago and at the present day [Credit: Alexis Licht & Grégoire Métais]](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Map-showing-Balkanatolia-min.jpeg)
We know that, around 34 million years ago, Western Europe was colonized by Asian species, leading to a major renewal of vertebrate fauna and the extinction of its endemic mammals, a sudden event called the “Grande Coupure.” Surprisingly, fossils found in the Balkans point to the presence of Asian mammals in southern Europe long before the Grande Coupure, suggesting earlier colonization.
Now, a team led by CNRS researchers has come up with an explanation for this paradox. To do this, they reviewed earlier palaeontological discoveries, some of which date back to the 19th century, sometimes reassessing their dating in the light of current geological data. The review revealed that, for much of the Eocene, the region corresponding to the present-day Balkans and Anatolia was home to a terrestrial fauna that was homogeneous, but distinct from those of Europe and eastern Asia. This exotic fauna included, for example, marsupials of South American affinity and Embrithopoda (large herbivorous mammals resembling hippopotamuses) formerly found in Africa. The region must therefore have made up a single land mass, separated from the neighboring continents.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
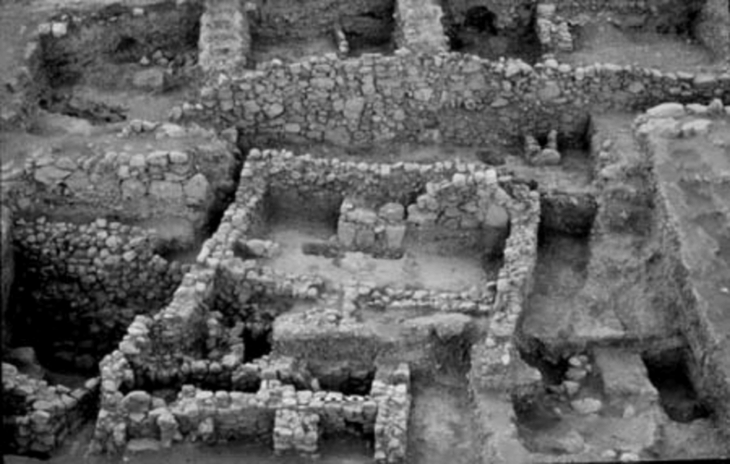
The team also discovered a new fossil deposit in Turkey (Büyükteflek) dating from 38 to 35 million years ago, which yielded mammals whose affinity was clearly Asian, and are the earliest discovered in Anatolia until now. They found jaw fragments belonging to Brontotheres, animals resembling large rhinoceroses that died out at the end of the Eocene.
![Site excavated in Turkey (Büyükteflek) [Credit: Alexis Licht & Grégoire Métais]](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Site-excavated-in-Turkey-Büyükteflek-min.jpeg)
All this information enabled the team to outline the history of this third Eurasian continent, wedged between Europe, Africa, and Asia, which they dubbed Balkanatolia. The continent, already in existence 50 million years ago and home to a unique fauna, was colonized 40 million years ago by Asian mammals as a result of geographical changes that have yet to be fully understood. It seems likely that a major glaciation 34 million years ago, leading to the formation of the Antarctic ice sheet and lowering sea levels, connected Balkanatolia to Western Europe, giving rise to the “Grande Coupure.”
Their findings are published in Earth Science Reviews.
Cover Photo: Upper molar of a Brontothere mammal of Asian origin [Photo: Alexis Licht & Grégoire Métais]

![Upper molar of a Brontothere mammal of Asian origin [Credit: Alexis Licht & Grégoire Métais]](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Upper-molar-of-a-Brontothere-mammal-of-Asian-origin-min.jpeg)