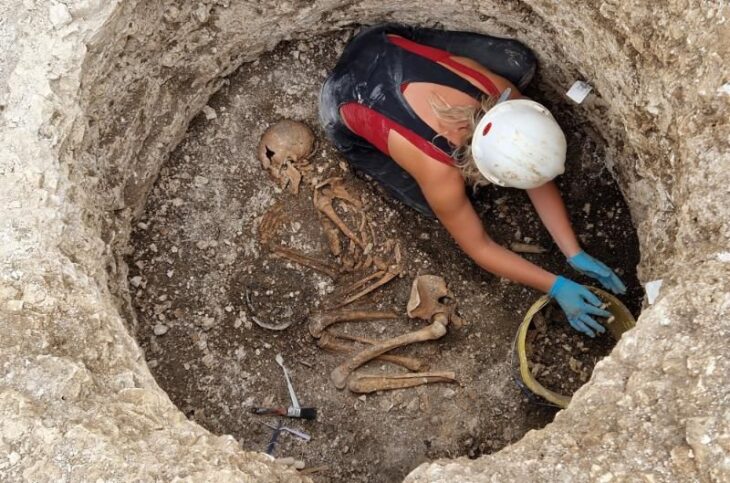
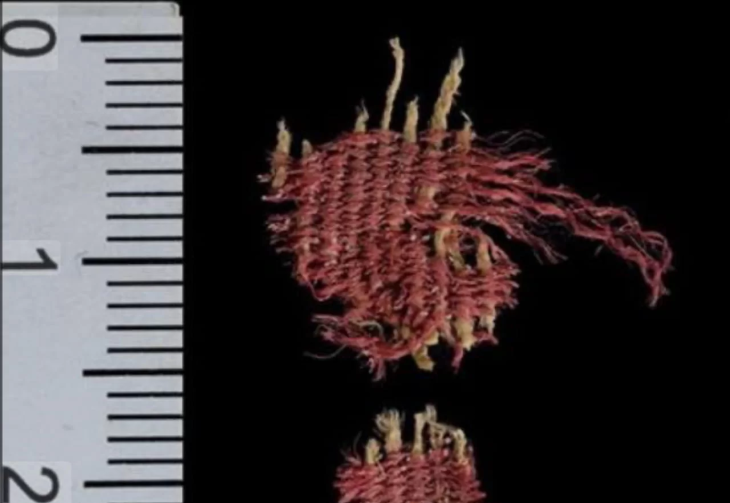
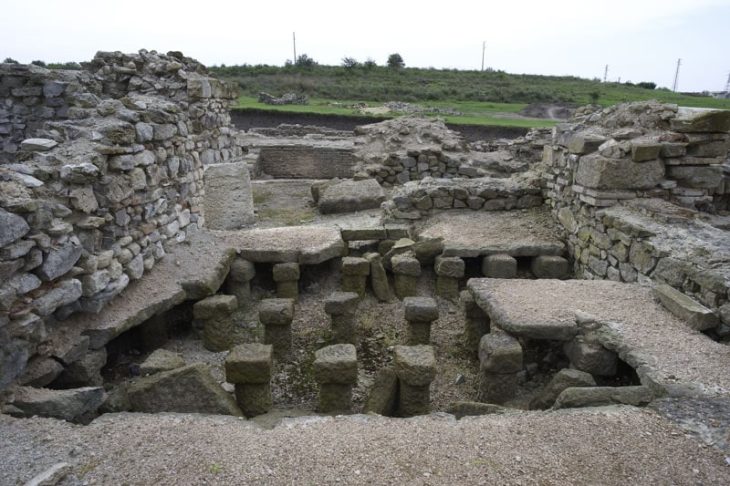
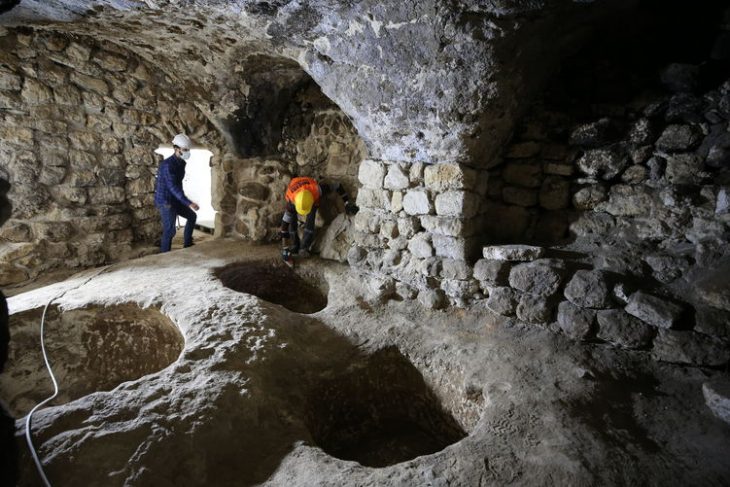
Excavation of vast Byzantine-era fortifications considered to be about 900 years old has begun at a dig site in western Turkey, archeologists working on the project said on Friday.
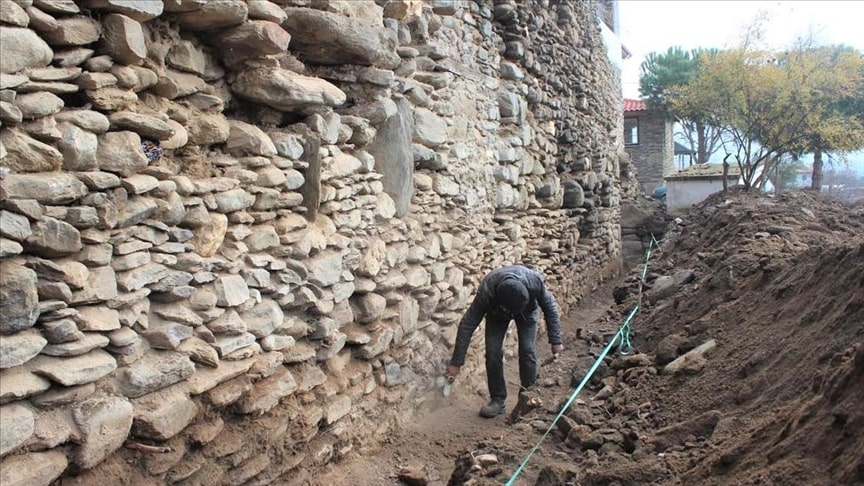
Located in what is now the small picturesque town of Birgi, the dig aims to uncover massive walls and fortresses that archeologist Veli Sevin said once stood 8 to 9 meters (about 26-30 feet) high.
“The walls of the Byzantine fortress will be uncovered in the excavations. There used to be a tremendous fortress here that covered an expanse of 6 hectares (14.8 acres),” Sevin told Anadolu Agency (AA). “The walls still stand, at least partially. We want to unearth these walls to present them to humanity.”
The name of the town Birgi was derived from its ancient name, Pyrgion, meaning fortress in Greek, added Sevin, who is serving as a scientific consultant to the excavations. The historical town of Birgi, located in the Odemis district of Izmir province, is on the UNESCO’s Tentative List.
Some of the findings uncovered in the rough stone walls during the excavations have been transferred to the local museum’s directorate in Odemis.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Birgi, which is thought to have been settled as early as 750 B.C., has been ruled by various civilizations throughout its history, including the Phrygians, Lydians, Persians, and Pergamon, as well as the Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman empires. It is still home to many historical remnants, including tombs, madrasas, mosques, fountains, baths, libraries, masjids, and homes.
The fortifications being excavated, however, were built in the late Byzantine period, at a time when “Turkish incursions gradually began to exert pressure on Byzantium,” said Sevin.
They constructed similar bastions as a final effort to defend themselves against the Turks in the present-day towns of Kiraz, Beydağ, Balabanlı, and Günlüce, he explained, adding that the fortress in Birgi was probably the largest of these.
He said the fortress did not have any ornamentations on it and was surrounded by a brick belt.
The excavations are also expected to contribute to the tourism in the region, said the archeologist and author.