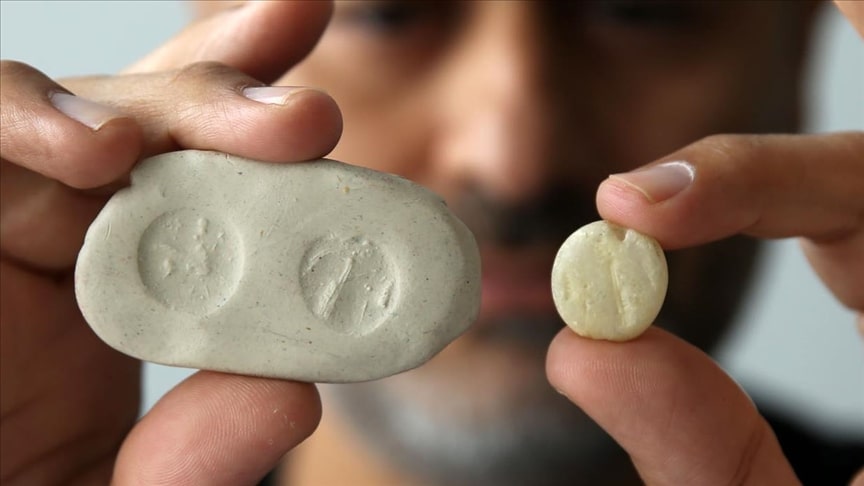
An alabaster seal, believed to be from the Assyrian Empire and belonging to a nobleman, was discovered in the ancient Kef Fortress built by the Urartians in the city of Bitlis in Türkiye’s southeastern.
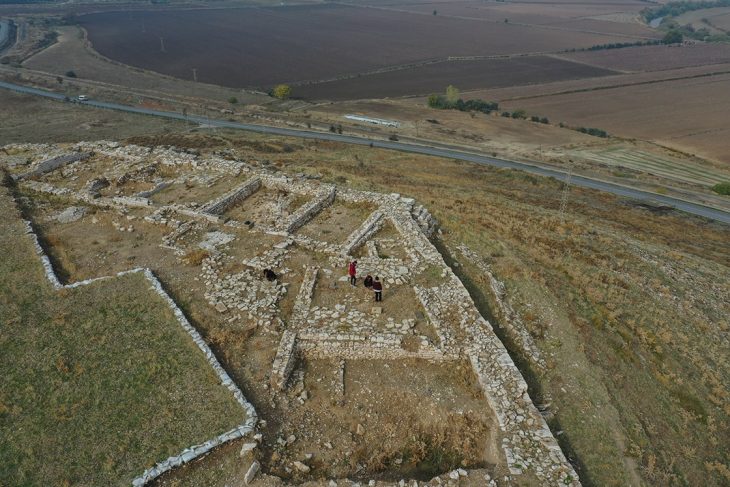
Archaeological excavations at the ancient Kef Fortress, built by Urartian King Rusa II at an elevation of 2,300 meters, have uncovered new artifacts that shed light on Urartian history.
Kef castle was built by Rusa II, who reigned between 685 and 645 BC. During his time four big iconic cities of the period were constructed. Kef Castle is one of the remaining parts of these cities. The city is strategically located as it can control trade routes and it can oversee the area.
The ongoing excavations, led by Associate Professor Ismail Coskun from the Archaeology Department of Van Yuzuncu Yil University (YYU), are conducted with permission from the Ministry of Culture and Tourism.
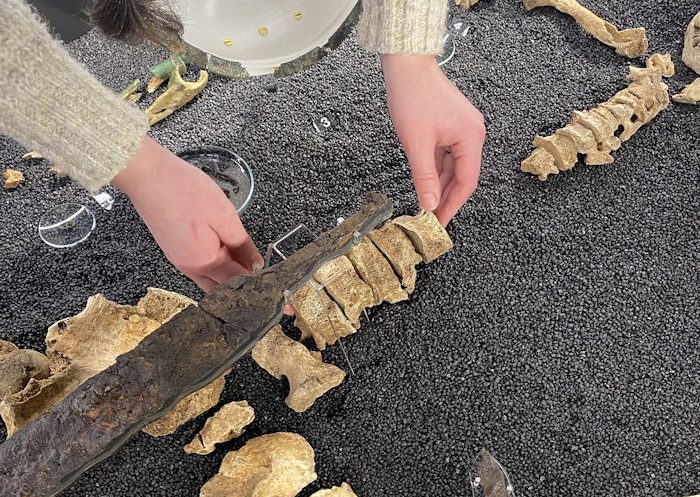
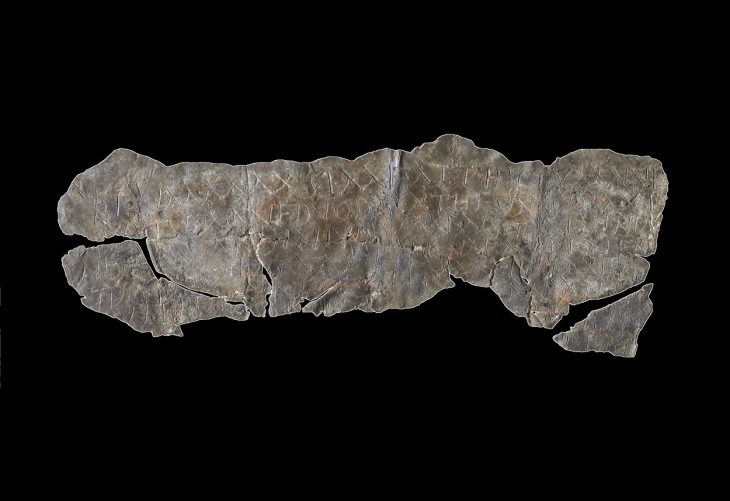
During the excavations in the architectural structures connected to the hall unearthed during the excavations carried out in previous years, arrowheads, seven elephant foot columns, spindle whorls used in textiles, and a button-shaped seal made of alabaster with figures on both sides, which is thought to have come from the Assyrian Empire, were unearthed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
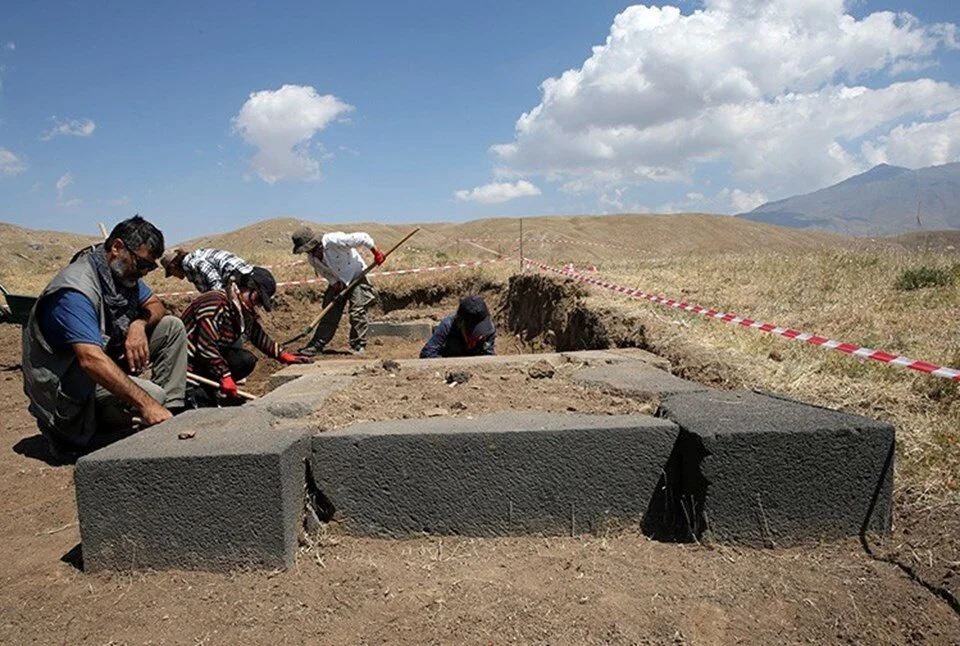

Coşkun stated that they worked in 6 trenches on the side of the upper hall this year and that in these trenches they identified 7 new elephant feet in addition to last year’s 3 elephant feet.
The use of basalt stones in the construction of Kef Fortress sets it apart as a unique Urartian structure. The basalt stones were likely sourced from Mount Suphan, which looms over the site.
Coşkun, who informed that they also opened the rooms on the side that are related to the hall, said the following:
‘In these rooms, we found arrowheads, spindle whorls used in textiles, and a seal made of alabaster. There are figures on both sides of this button-shaped seal. When we look at the content of the figures, we think that the seal is not local but imported. We think that the seal came from the Assyrian Empire, a neighbor of Urartu. When we look at its characteristics, we think that this seal belonged to a nobleman since alabaster is rare in the region and it is an important material.’
These discoveries are important for deepening our understanding of Urartian history and contributing to the cultural heritage of the region.
Cover Image Credit: Harun Nacar/AA