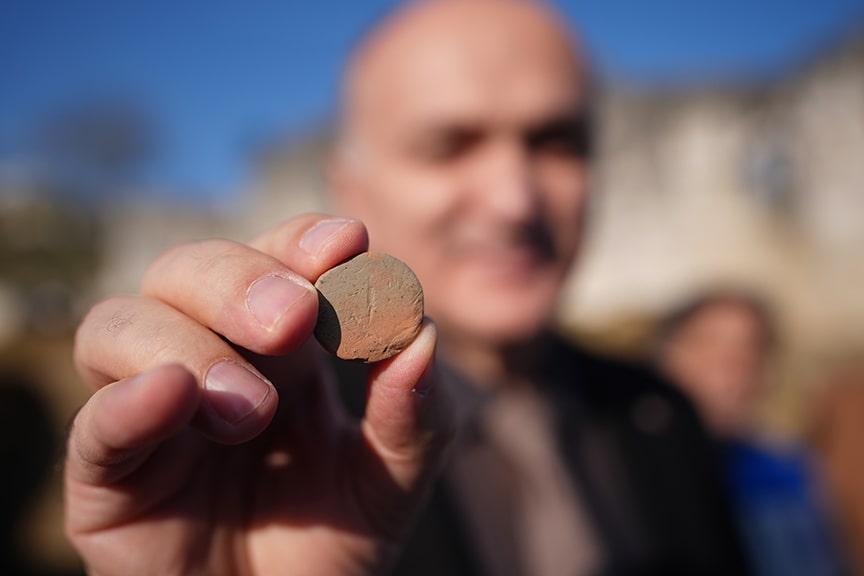
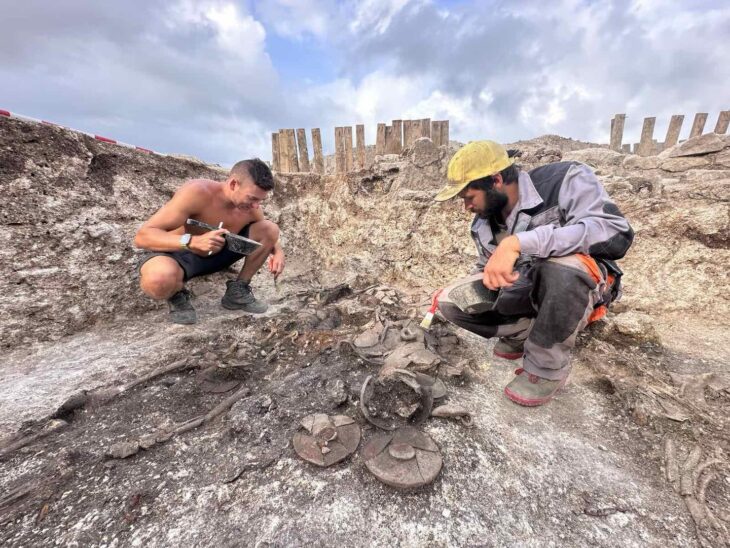
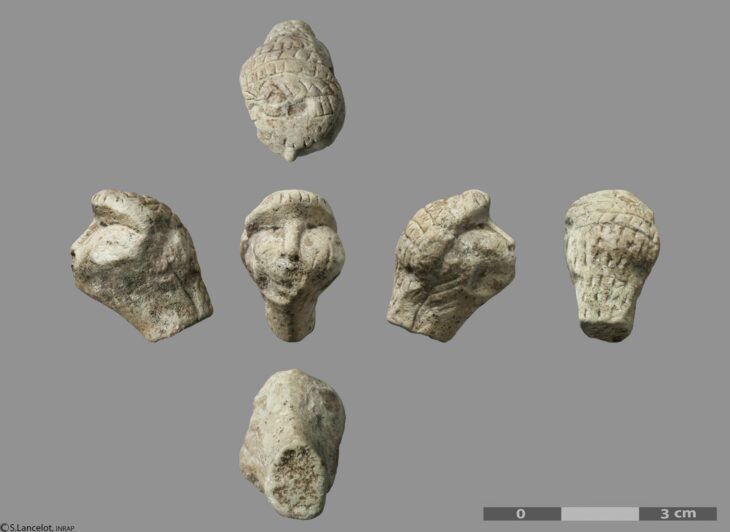
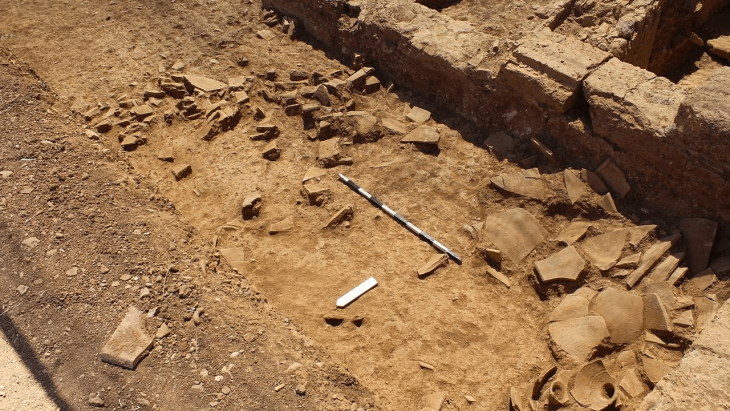
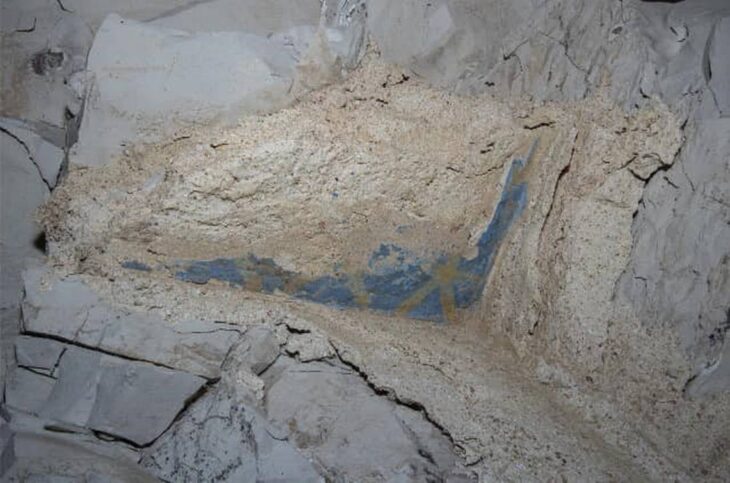
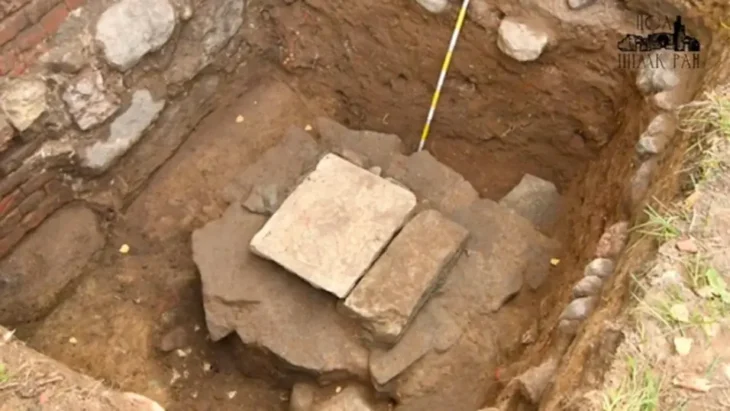
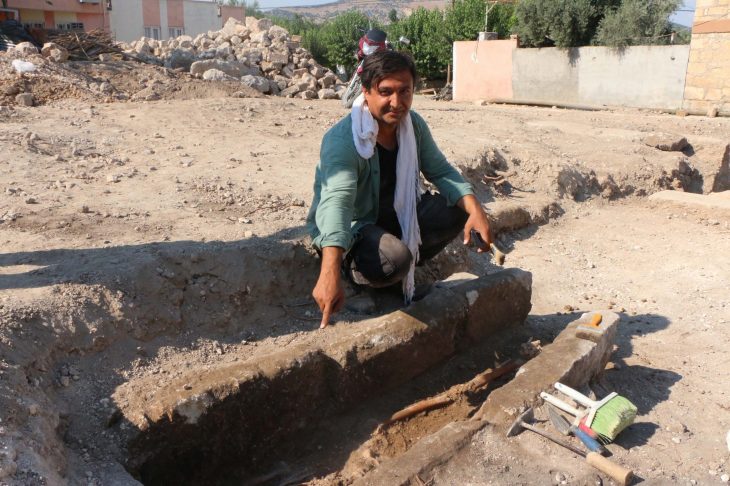
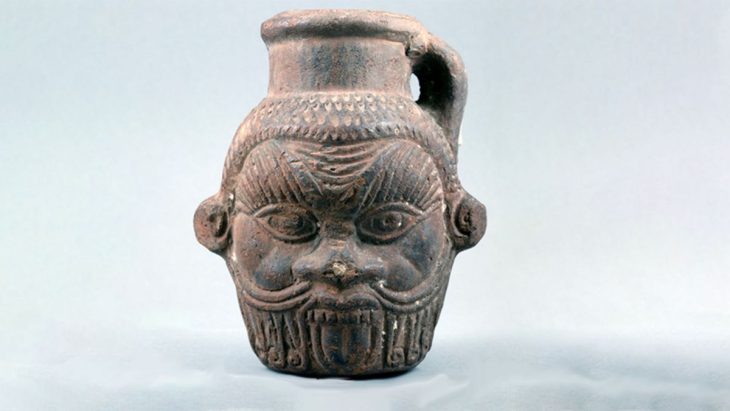
Excavations at the ancient city of Prusias Ad Hypium in the Konuralp region of Düzce in northwestern Türkiye have uncovered a Roman-era clay theater ticket, a figurine depicting Aphrodite, and a Thyrsus figure.
The ancient city of Prusias ad Hypium, which is called the Ephesus of the western Black Sea, was known as “Hypios” and “Kieros” in earlier periods. It was captured by Prusias I of Bithynia, and the people of Bithynia named the city in honor of their king. The people of Bithynia bequeathed the kingdom to the Romans. The city was already rich in terms of architecture but flourished more under the Romans.
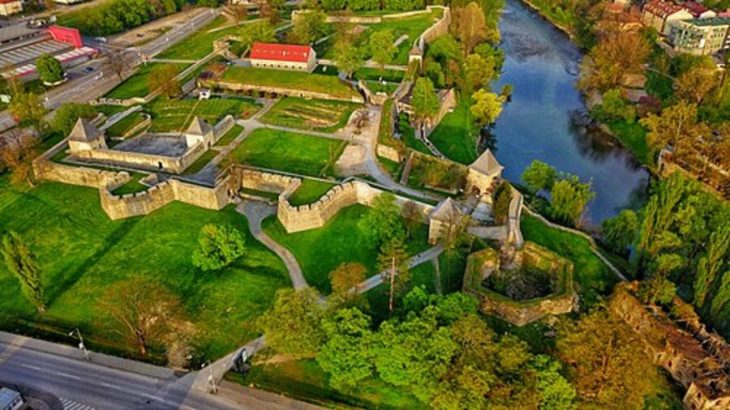
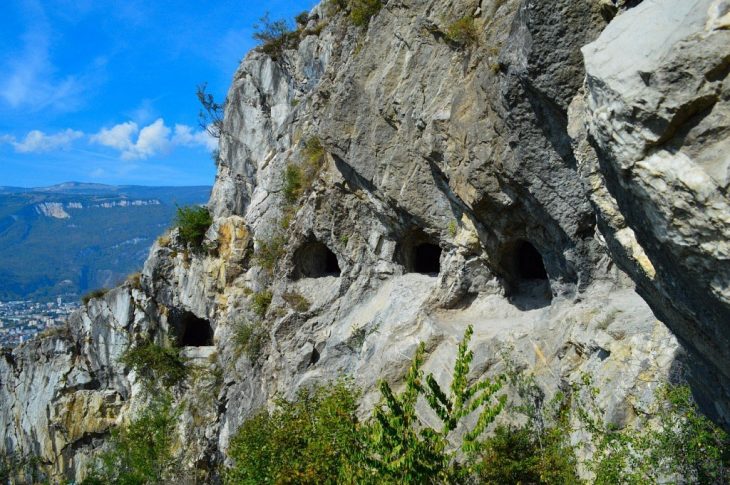
The ancient city of Prusias Ad Hypium, located in the northwestern province of düzce, is home to structures like an ancient theater, aqueducts, and a Roman bridge. Known as 40 Basamaklar by locals, the 100-meter-long and 74 -74-meter-wide ancient theater’s semicircle sitting field, steps decorated with lion claw figures, vaulted passages, and stage are still intact.
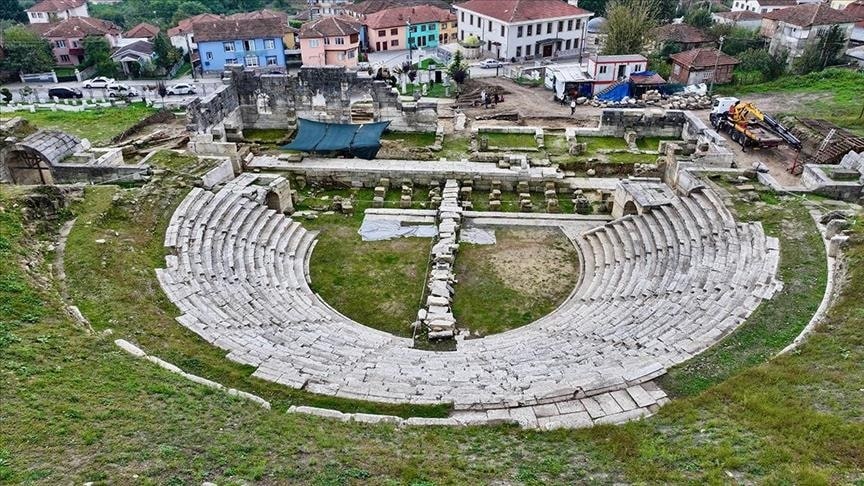

Dating back to the 3rd century BC, the city has survived numerous earthquakes over the centuries, and remarkably, the theater’s structural integrity has remained intact.
The General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums has approved the excavations, which started five years ago, and the Düzce Municipality is providing support. Led by the Konuralp Museum Directorate, the work has been ongoing uninterrupted for 12 months each year.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Düzce Mayor Faruk Özlü, speaking at the site, emphasized the importance of preserving the city’s 2,300-year history. “We have taken a major step in passing this city’s legacy to the future,” he said.

Özlü noted that around 80% of the theater area has now been exposed, revealing historical artifacts that are significant both locally and nationally. “We’ve found these priceless artifacts in pristine condition,” he added.
The mayor added that the ancient theater, once restored, will become a cultural and arts center with a capacity for 10,000 people. The ancient city of Prusias ad Hypium has reached to open the site’s theater for tourism next year.
Cover Image Credit: AA