Archaeologists, using drones and Google Earth imagery, have discovered a 4,000-year-old network of earthen canals in what is now Belize that were once used by the predecessors of the ancient Mayans to catch freshwater fish.
The findings, published in the journal Science Advances, highlight the creativity of the semi-nomadic people who built the system long before the rise of the iconic civilization of the Maya predecessors.
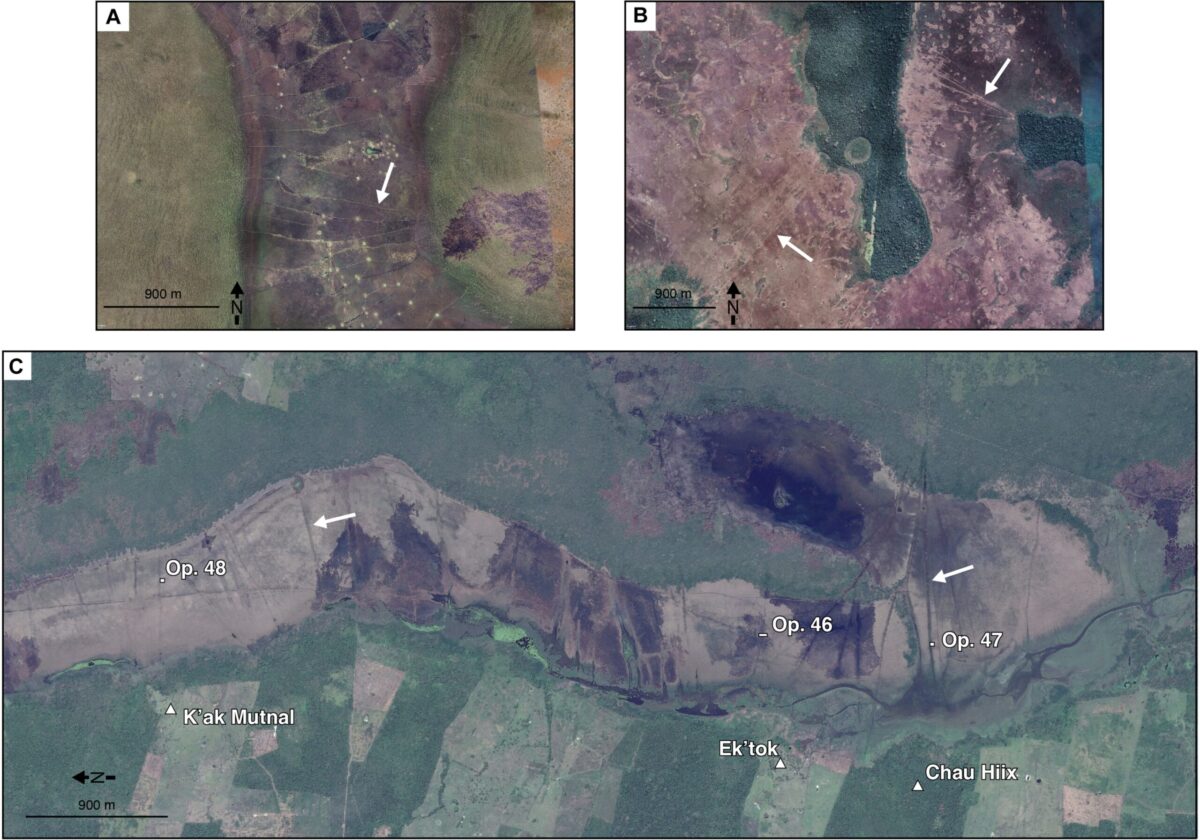
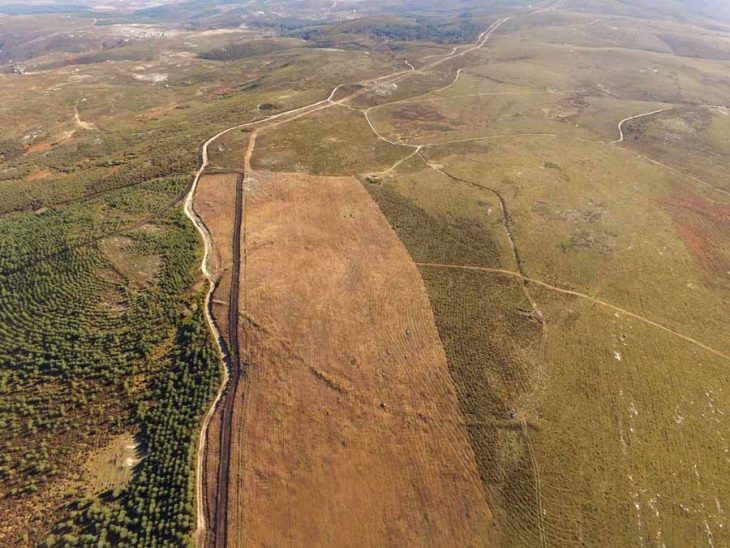
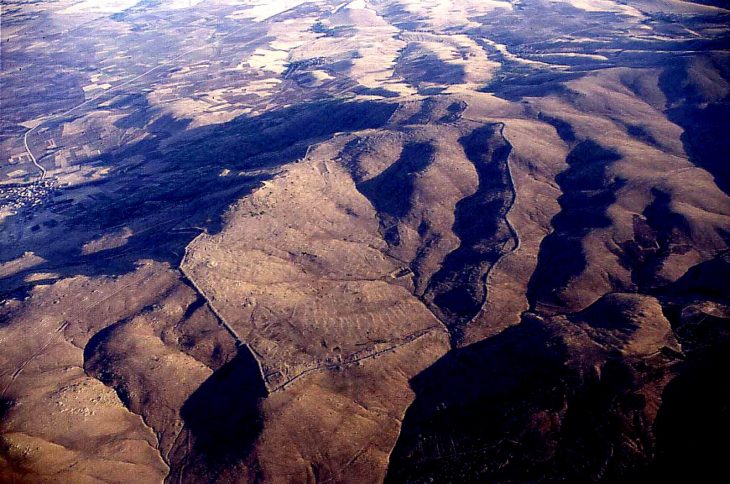
Using drones and Google Earth imagery, researchers identified miles-long zigzagging canals through wetlands in the Crooked Tree Wildlife Sanctuary.
“The aerial imagery was crucial to identify this really distinctive pattern of zigzag linear canals running for several miles through wetlands,” Eleanor Harrison-Buck, co-author of the study, stated, as reported by The Guardian.
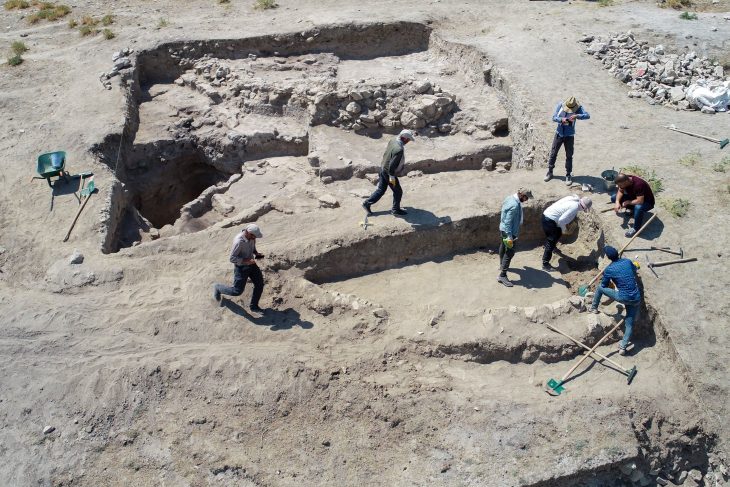
The team then conducted digs in Belize’s Crooked Tree Wildlife Sanctuary. The ancient fish canals, paired with holding ponds, were used to channel and catch freshwater species such as catfish.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The canal networks were built as early as 4,000 years ago in the Yucatán coastal plain, surprising researchers who initially assumed the ancient Maya made these constructions. The canals date back to a semi-nomadic period, predating the Maya by millennia, and were in use for about 1,000 years.
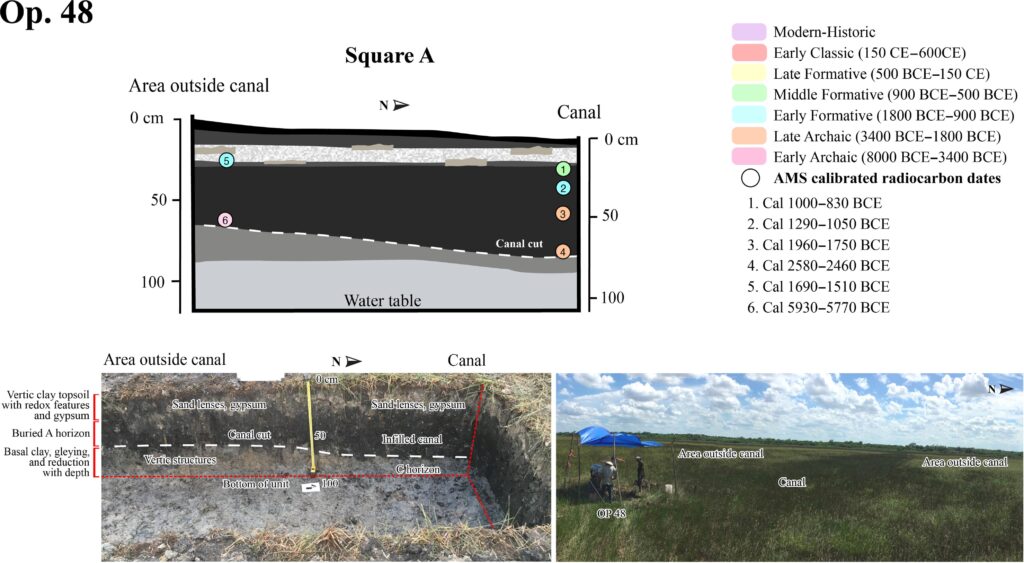
“The early dates of the channels surprised us at first because we all assumed these huge constructions had been made by the ancient Maya living in the nearby urban centers,” Eleanor Harrison-Buck explained.
“This is the earliest large-scale Archaic fish-trapping facility recorded in ancient Mesoamerica,” the study authors wrote in Science Advances, adding that “such landscape-scale intensification may have been a response to long-term climate disturbance recorded between 2200 and 1900 BCE.”
“Barbed spearpoints” found nearby may have been tied to sticks and used to spear fish, said study co-author Marieka Brouwer Burg of the University of Vermont.
This early large-scale landscape modification suggests a foundation for the complex society that later built temples, pyramids, and advanced systems of writing and astronomy.
“This shows continuity,” said Jeremy Sabloff, an archaeologist at the University of Pennsylvania, explaining how the resourceful strategies of these early communities likely supported the cultural and architectural achievements of the Maya.
E. Harrison-Buck, S. M. Krause, M. Brouwer Burg, M. Willis, A. Perrotti, and K. Bailey, 2024, “Late Archaic large-scale fisheries in the wetlands of the pre-Columbian Maya Lowlands,” Science Advances, Vol. 10, No. 47 DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq1444
















