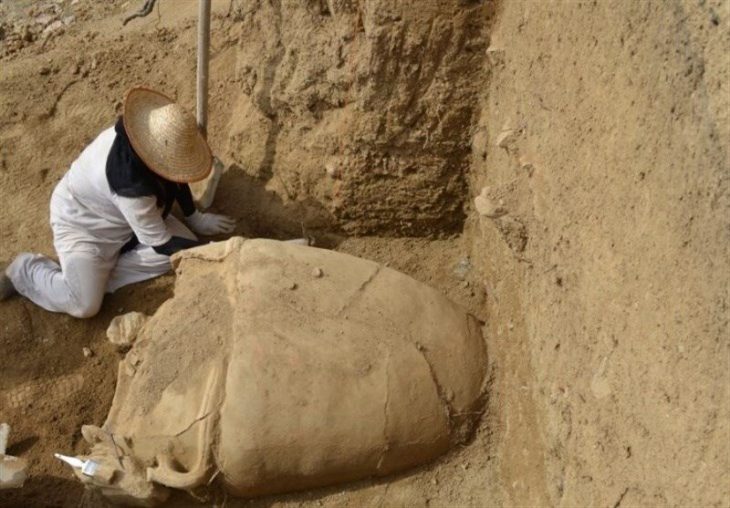
Archaeologists have discovered an interesting ancient Iron Age “shrine” in the Yorkshire Wolds, which was marked out by meticulously placed animal skulls and bones.
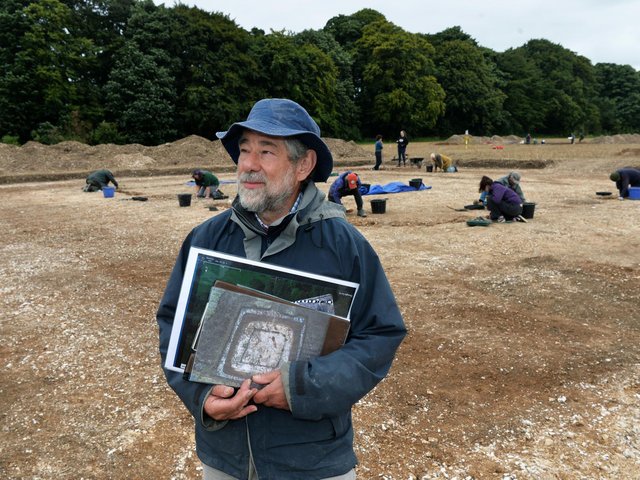
A team led by Dr. Peter Halkon and James Lyall excavated a fortified settlement with a substantially circular structure in the middle a few hundred yards from the “shrine” over the last four years.
Both the shrine and the older Bronze Age “ring fort” initially appeared in aerial images plotted by Cathy Stoertz over 20 years ago as crop marks on the top of a hill in the Wolds.
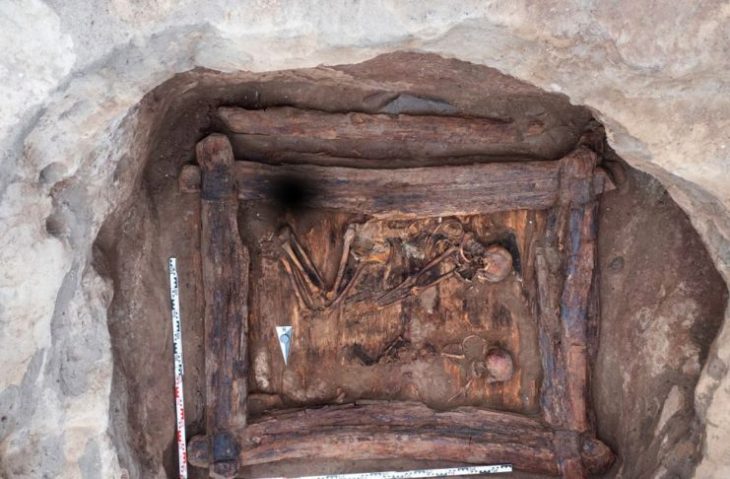
The shrine consisted of a square enclosure surrounded by a deep ditch, with a central area hidden from view by a palisade. In the center were the remains of a child, however, the bones are in such poor condition, and have been damaged by plowing. It is not known in what period the child was buried there.
The animal remains left on the ground after the palisade was taken out were quite remarkable.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
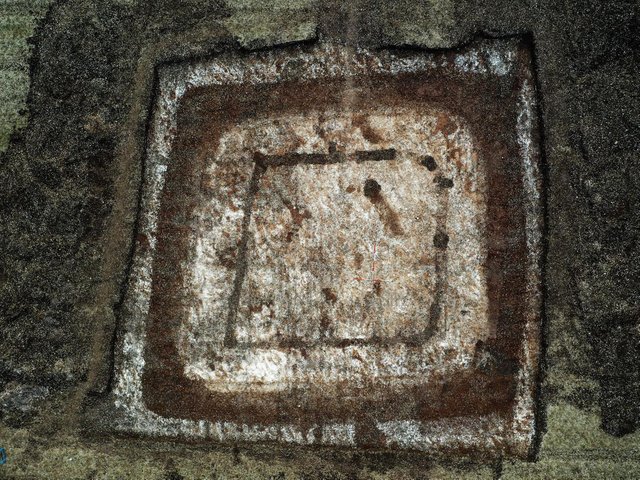

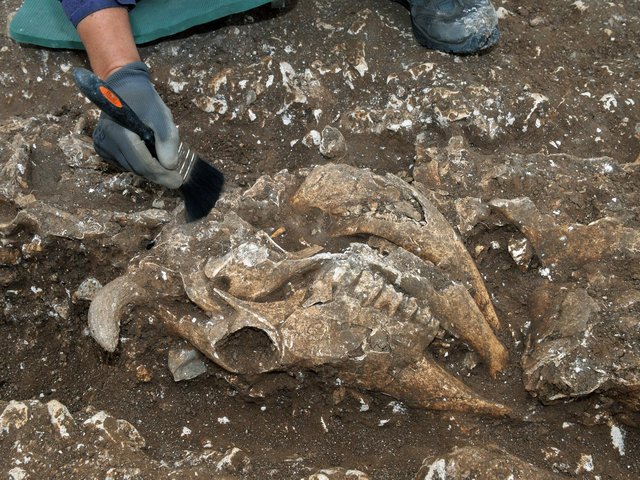
Up to 40 cow skulls, some arranged in pairs, along with cow bones and deer antlers, were placed around the square enclosure, sometime after it was taken down.
Dr. Halkon said the butchered remains of cattle, as well as sheep and pork, were found at the nearby fort which could once have been home for a powerful man and his extensive family.

However, only cow skulls and bones, as well as deer antlers, a wild, hunted animal, were placed in the shrine on purpose. Archaeologists discovered forelegs, three cow skulls, another skull, and a deer antler in one corner. Skulls were arranged in pairs in other locations.
Dr. Halkon said the bones were too carefully deposited to be “just rubbish disposal”.
He said: “At some point, they demolished the monument, pulled out the palisade and reopened the slot where the palisade had been and inserted all the animal bones.
Dr. Halkon said human heads were venerated and it is possible cattle heads had some kind of symbolism. He said: “Cattle were very important to them, and they probably measured wealth in the numbers of cattle.”
The excavation was sponsored by the Yorkshire Archaeological and Historical Society.